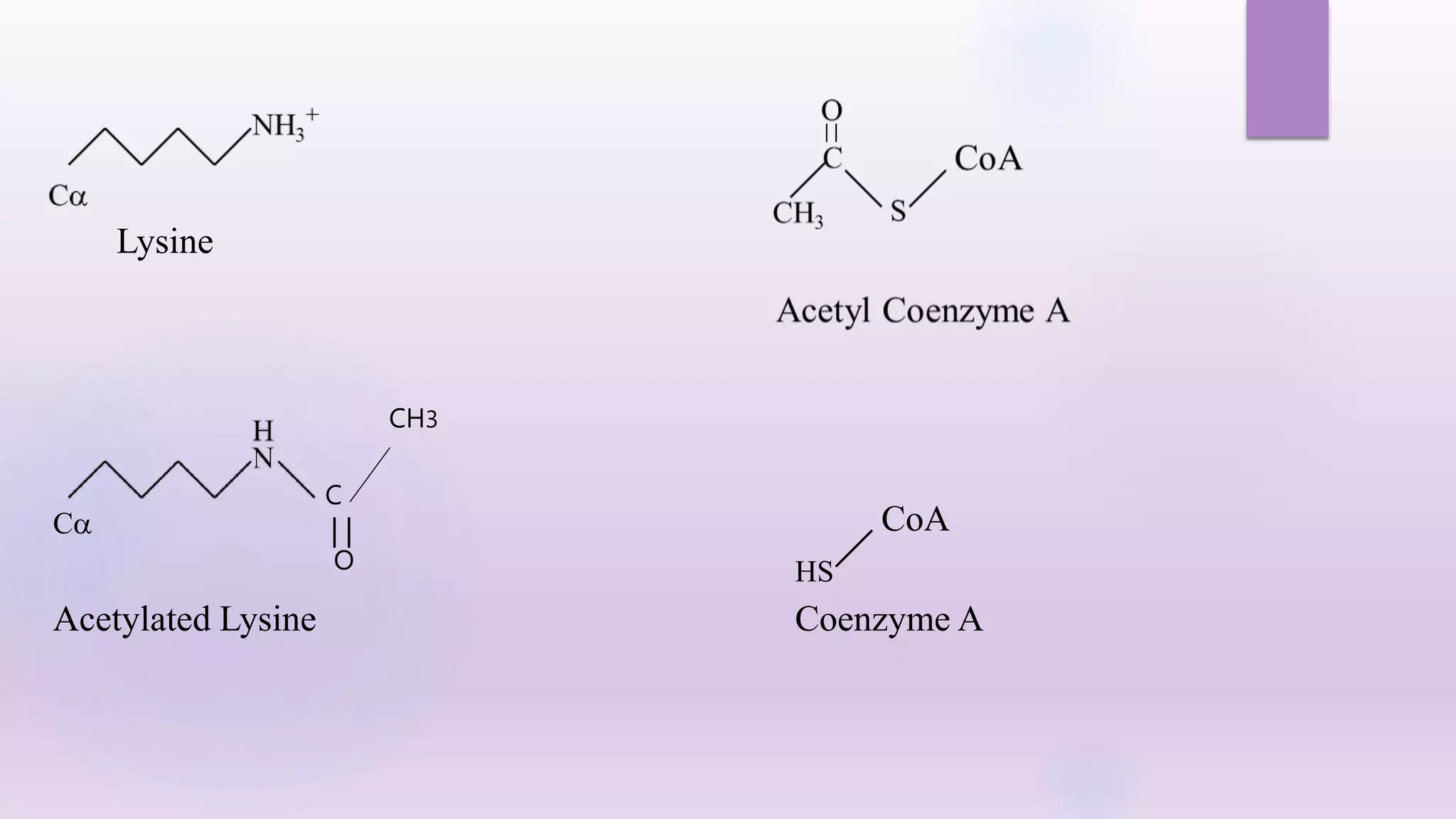
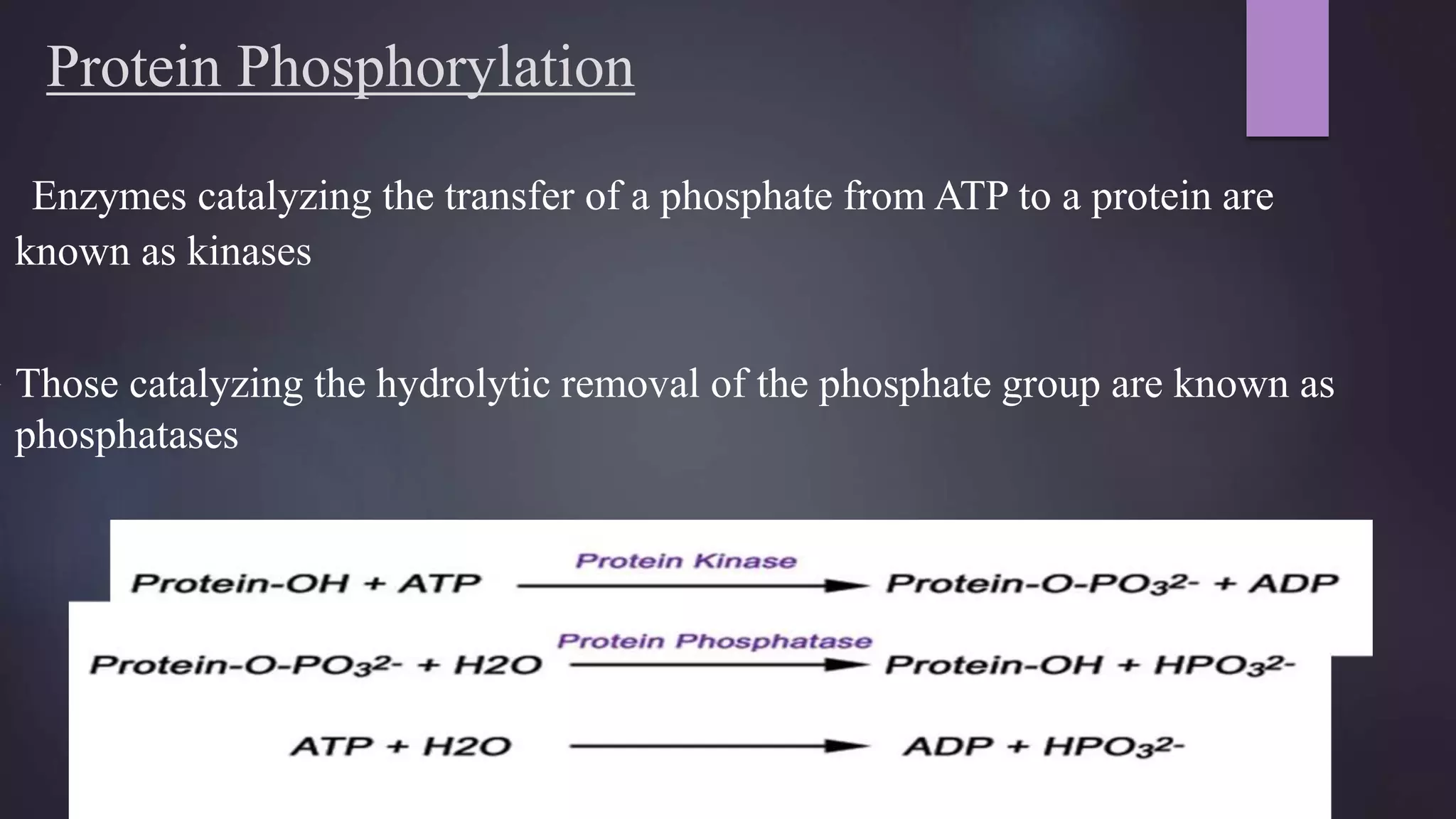
1) Covalent modifications, both reversible and irreversible, play important roles in regulating enzyme function. Reversible modifications like phosphorylation fine-tune enzyme activity, while irreversible proteolysis activates zymogens into active enzymes.
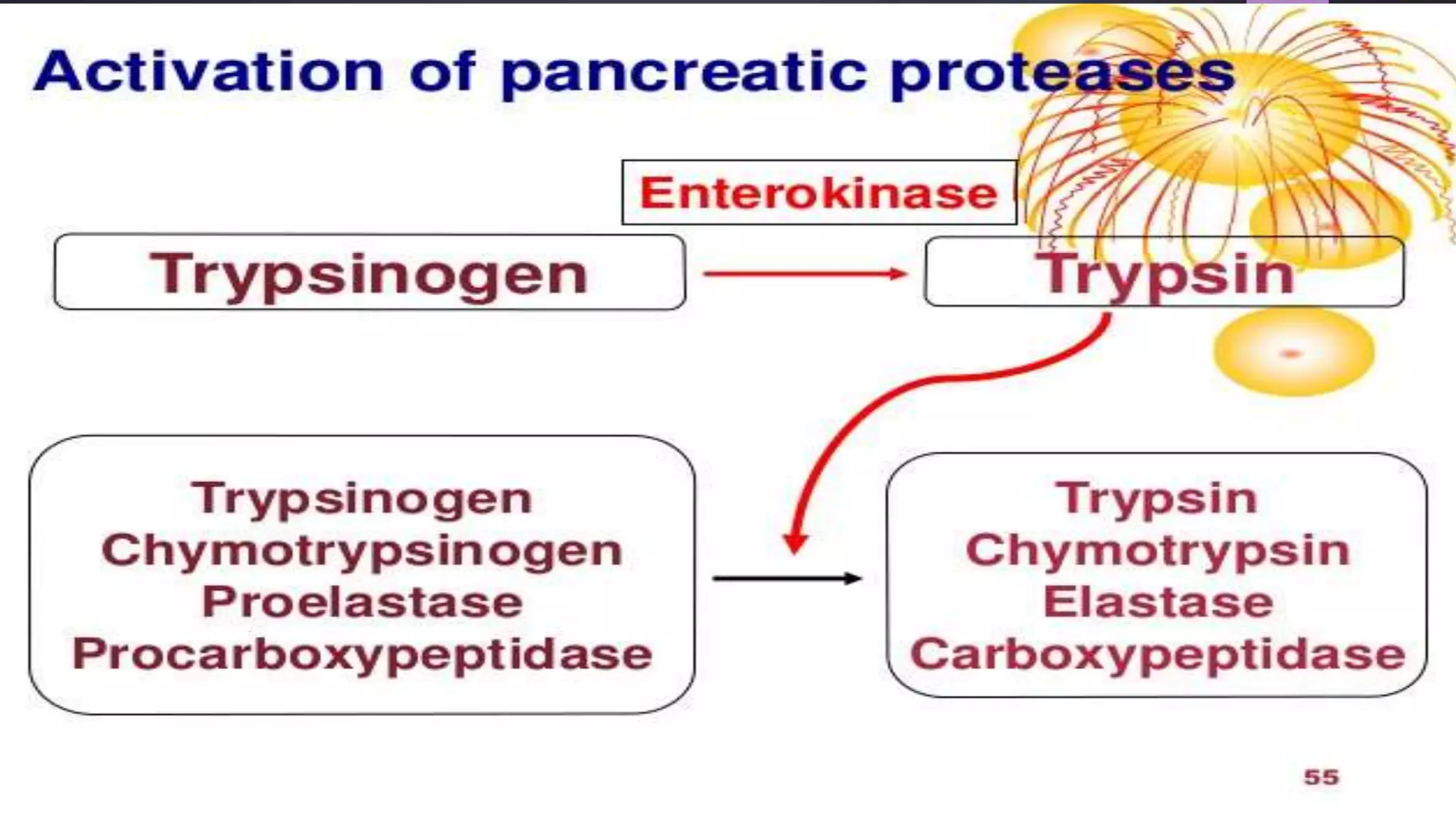
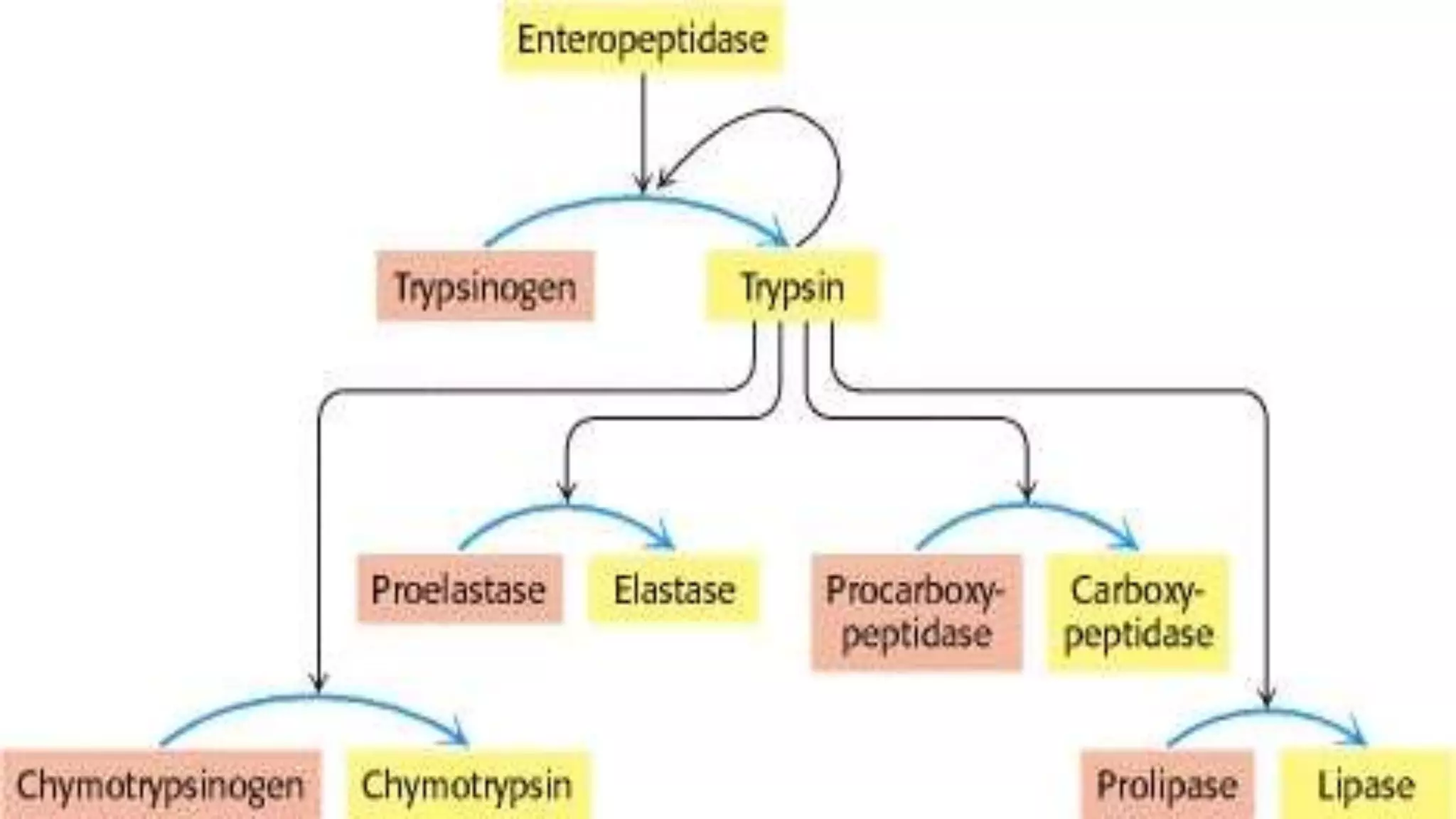
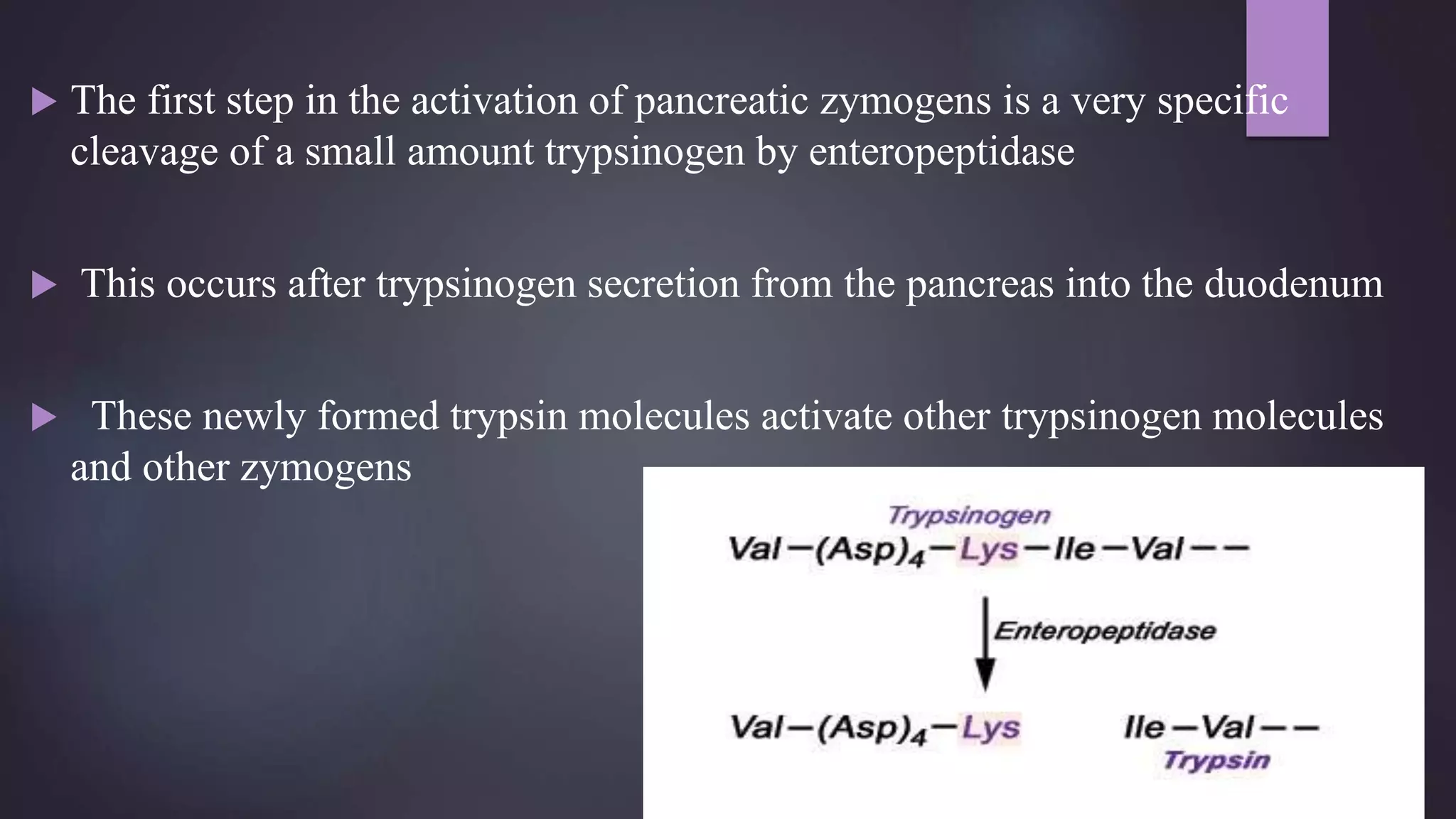
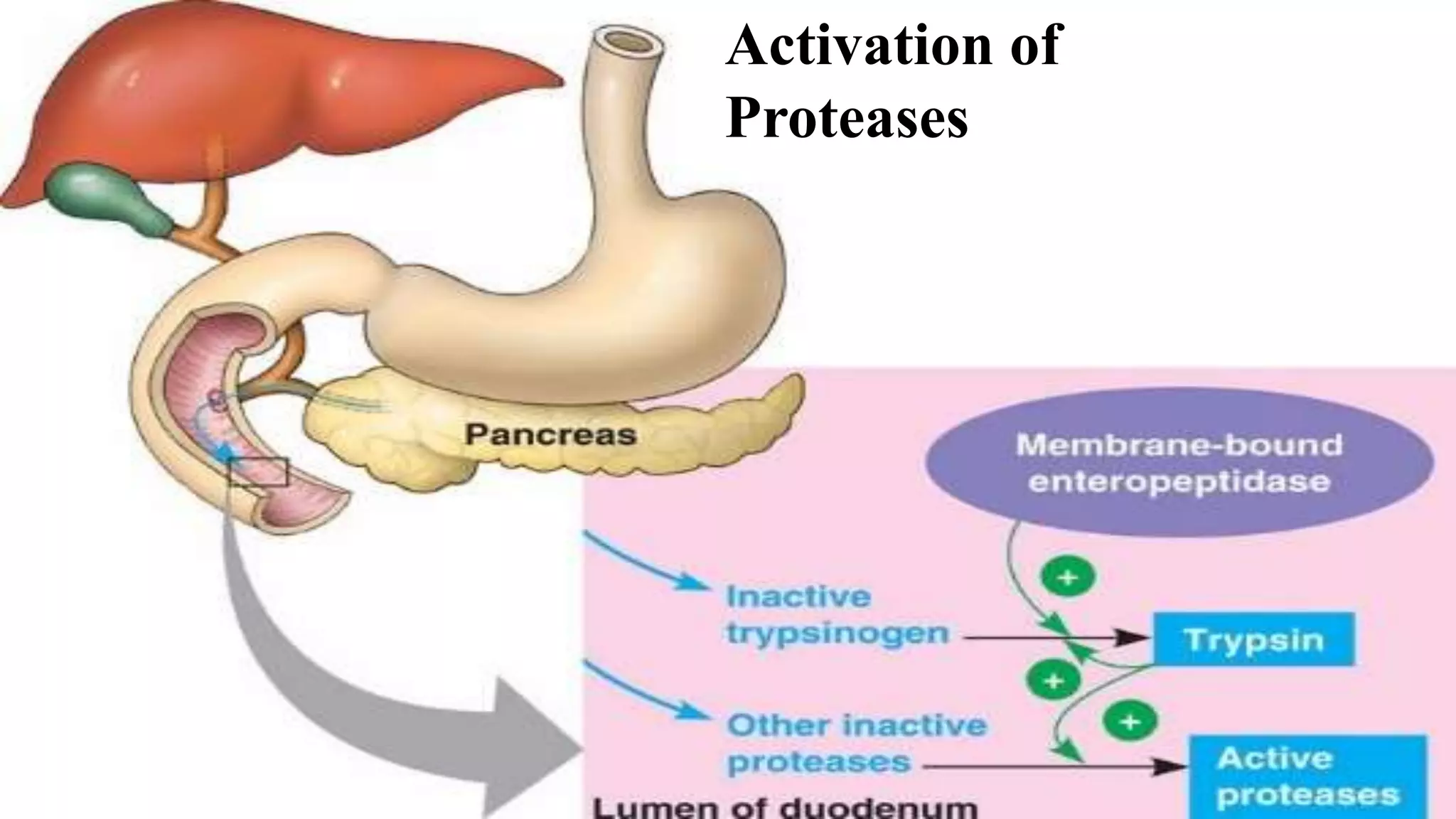
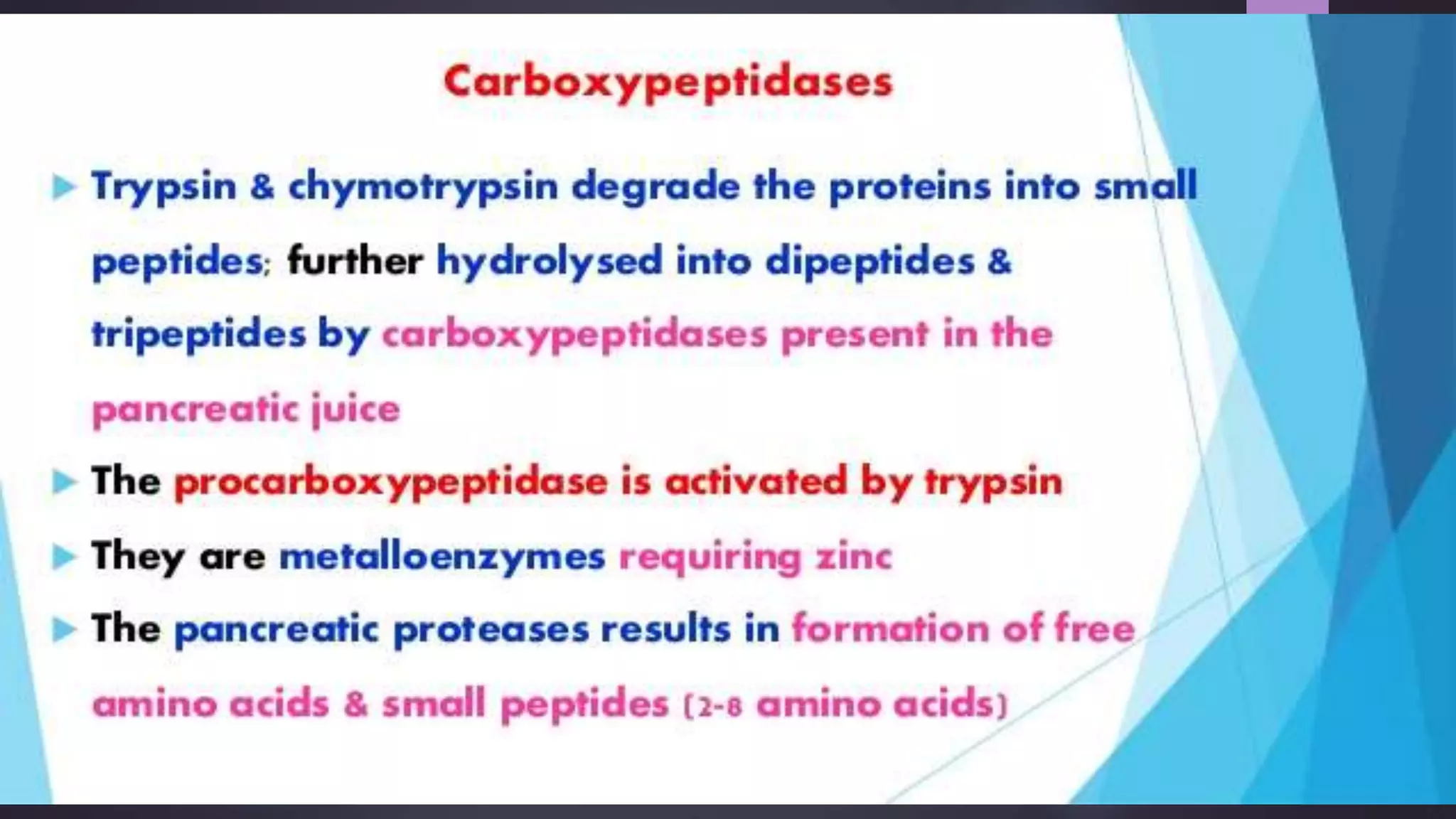
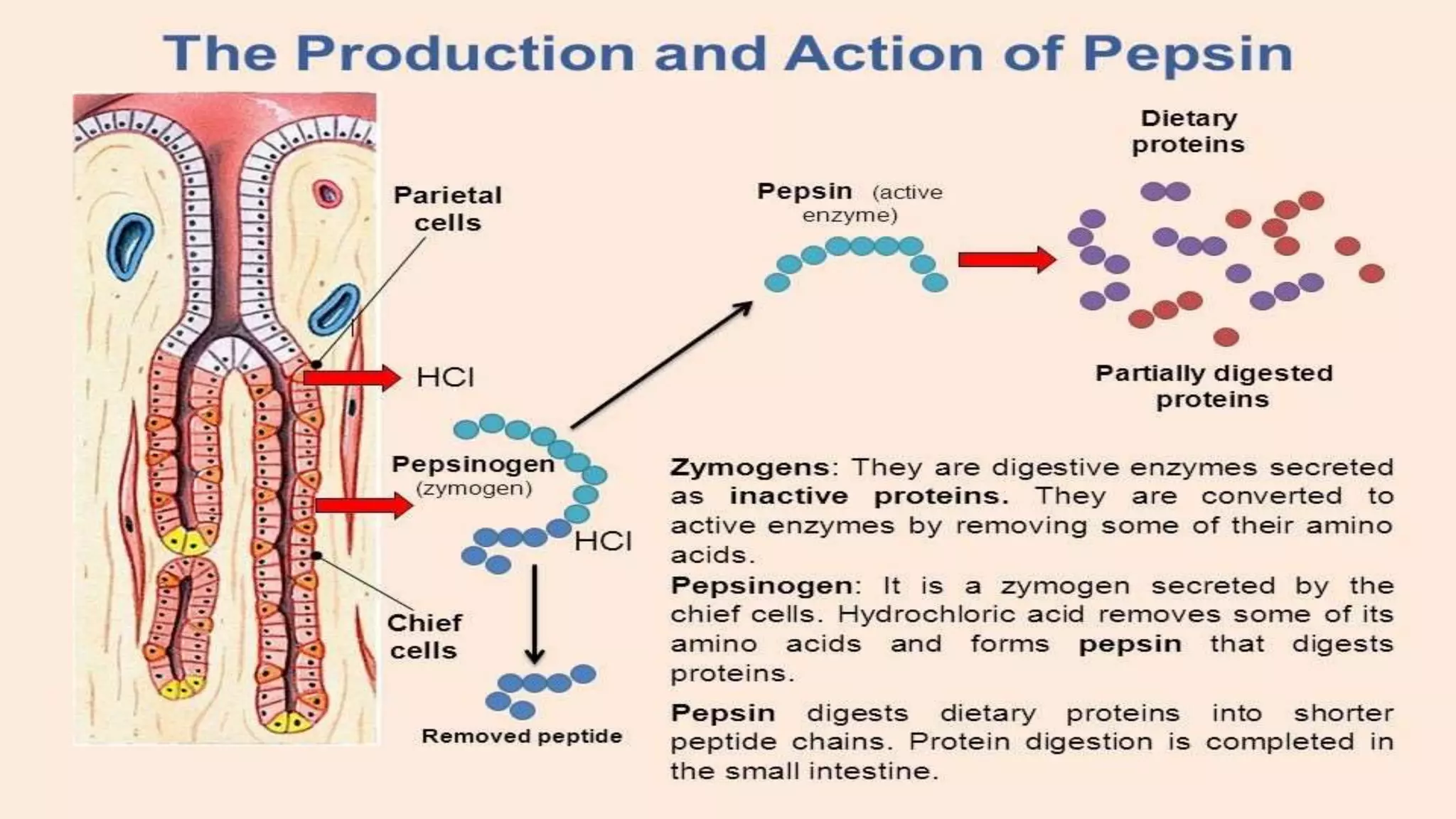
2) Digestive enzymes like trypsinogen are synthesized as inactive zymogens to avoid unwanted catalysis, then activated through limited and specific proteolysis. This proteolysis removes inhibitory peptide sequences and allows catalytic activity.
3) Activation of zymogens through proteolytic cascades amplifies hormonal signals, allowing a small stimulus to elicit a large response. This cascade activation greatly increases the potency and efficiency of regulation compared to direct hormone binding.