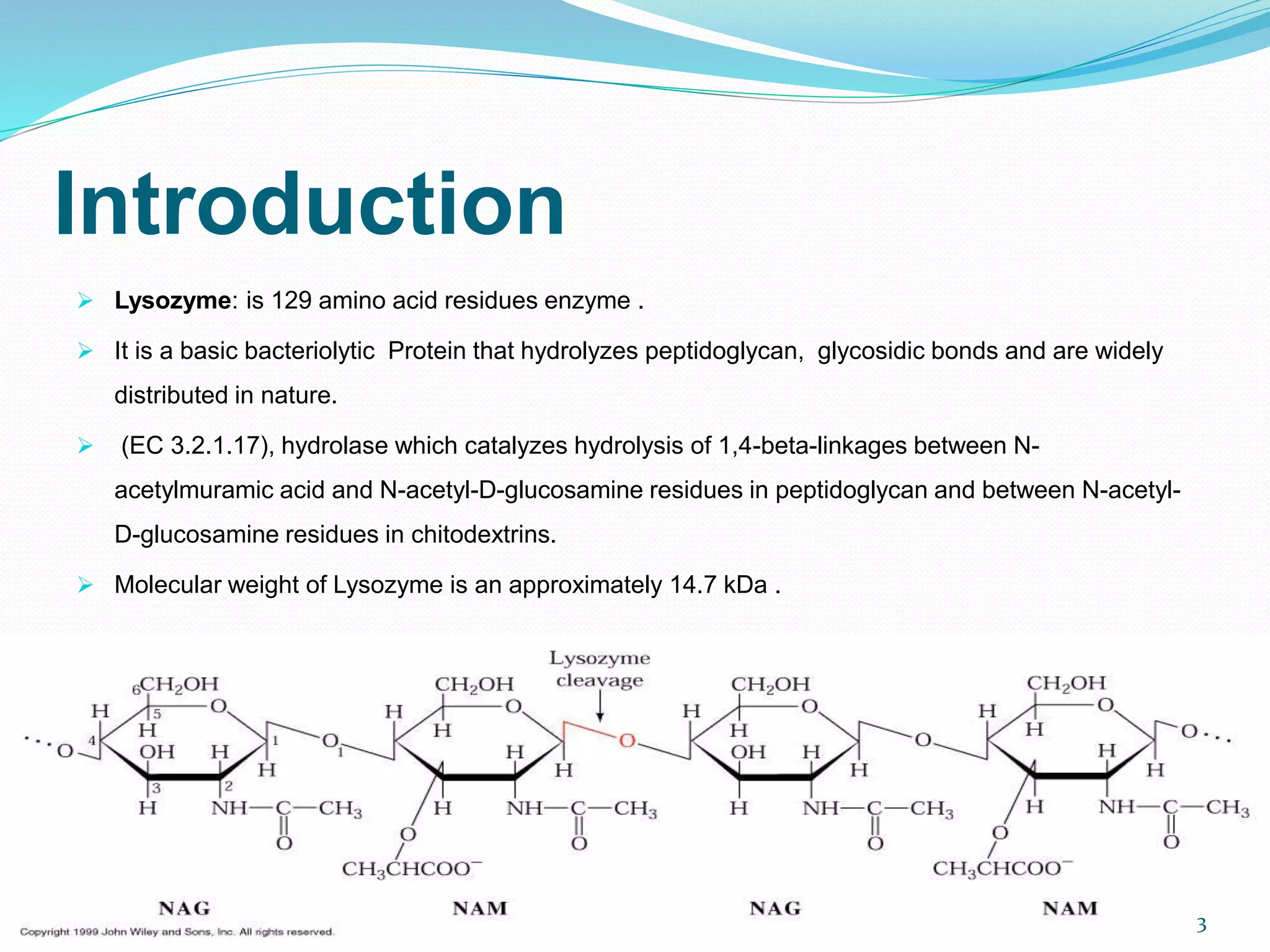
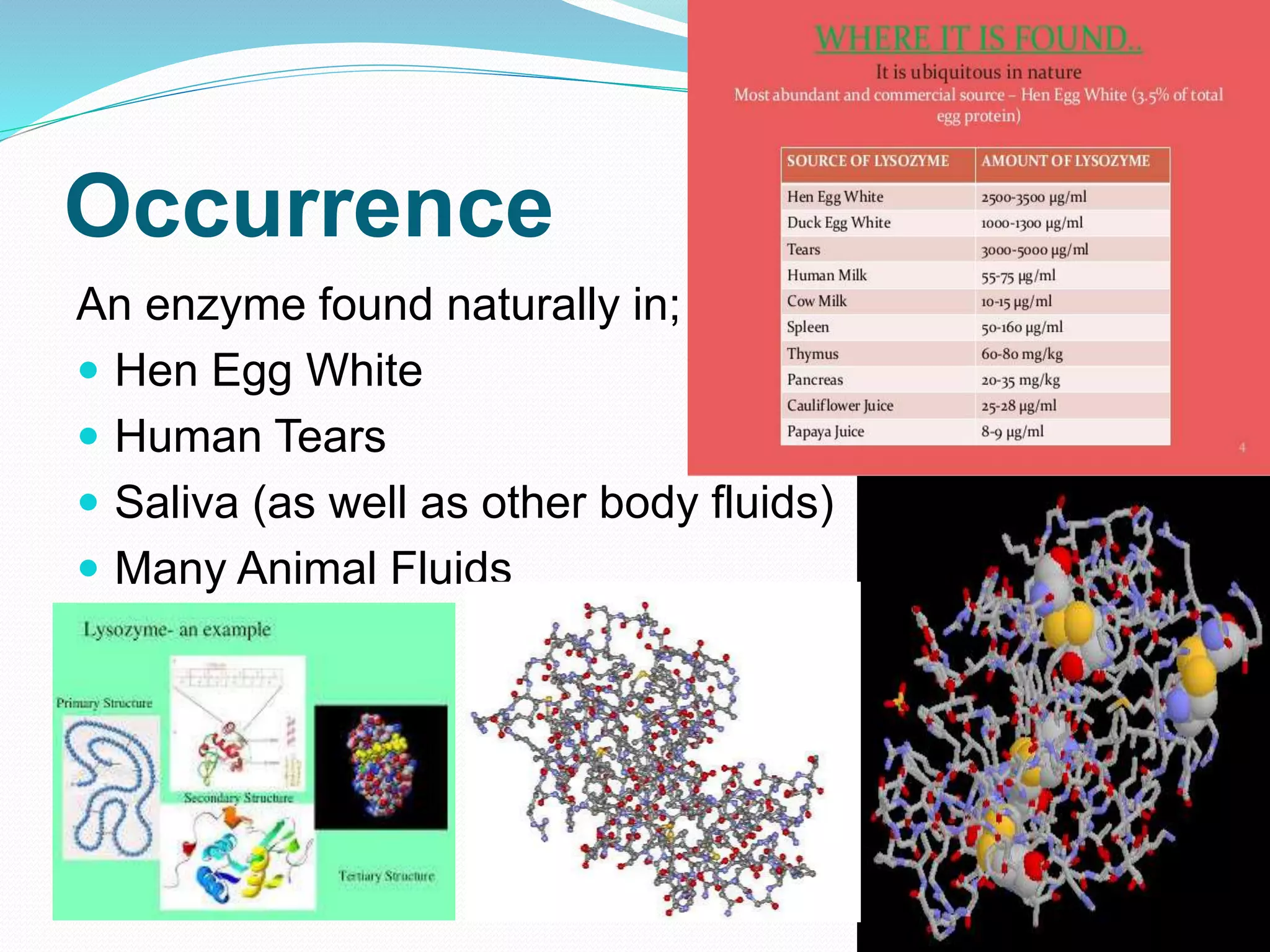
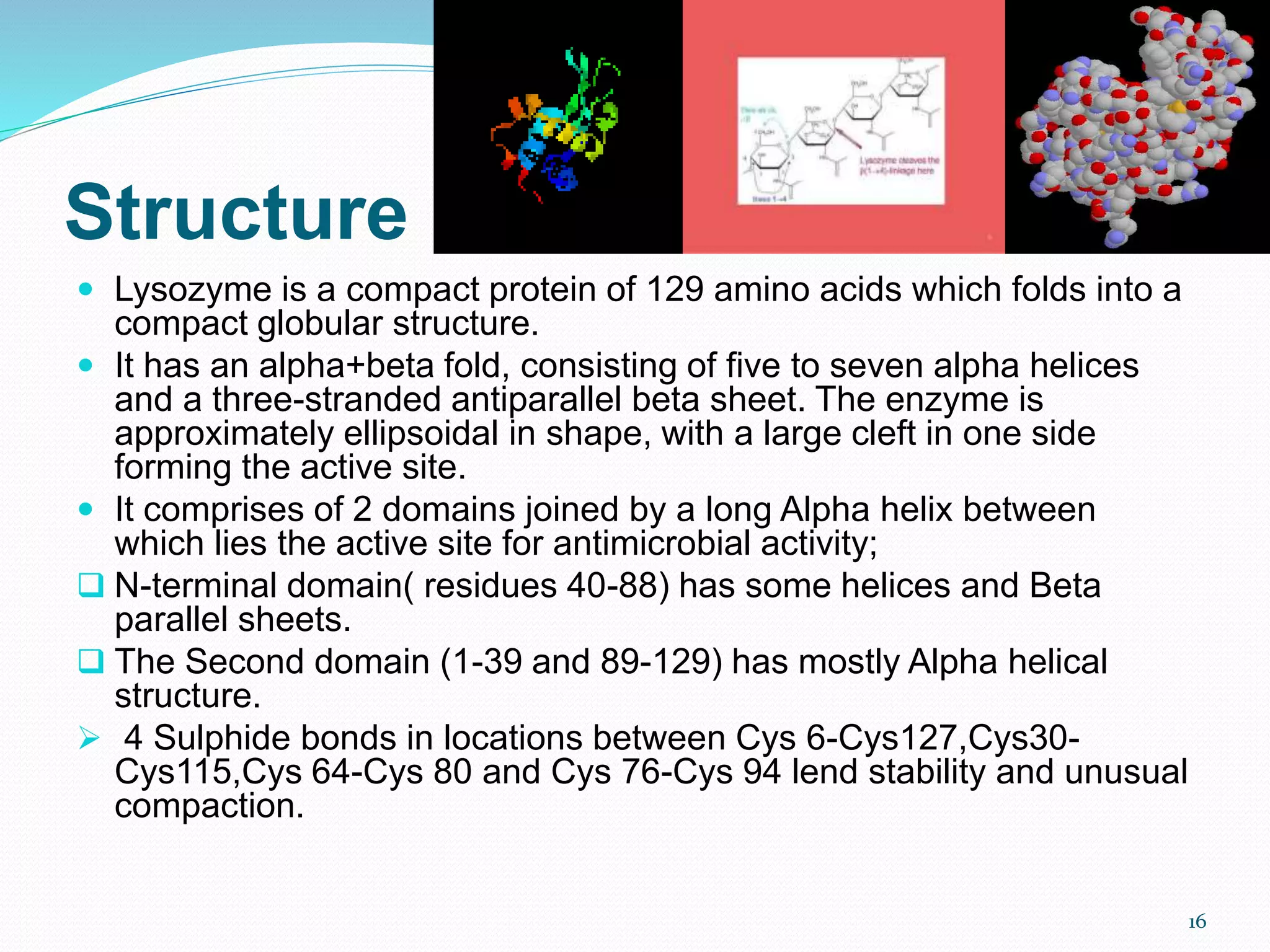
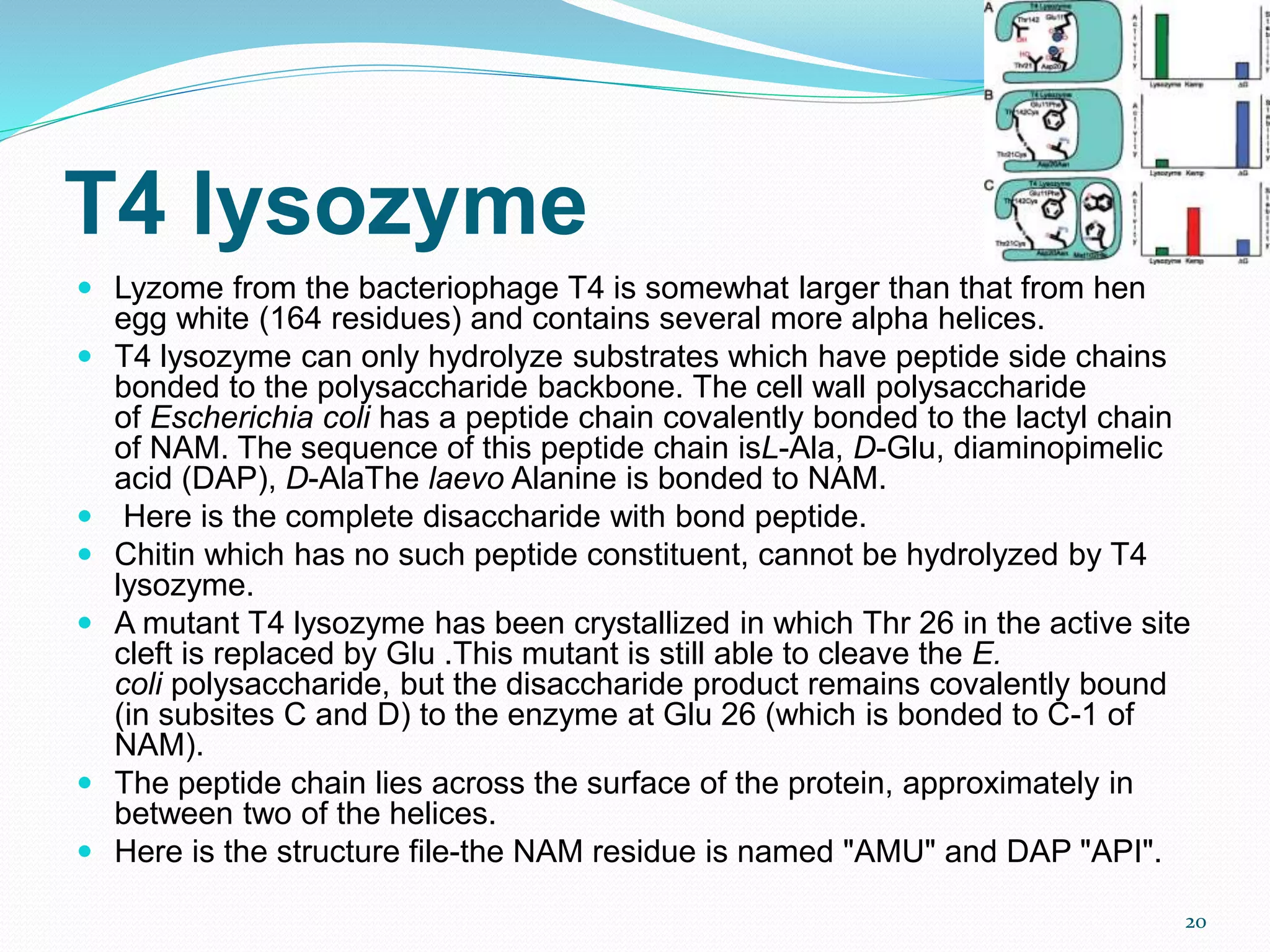
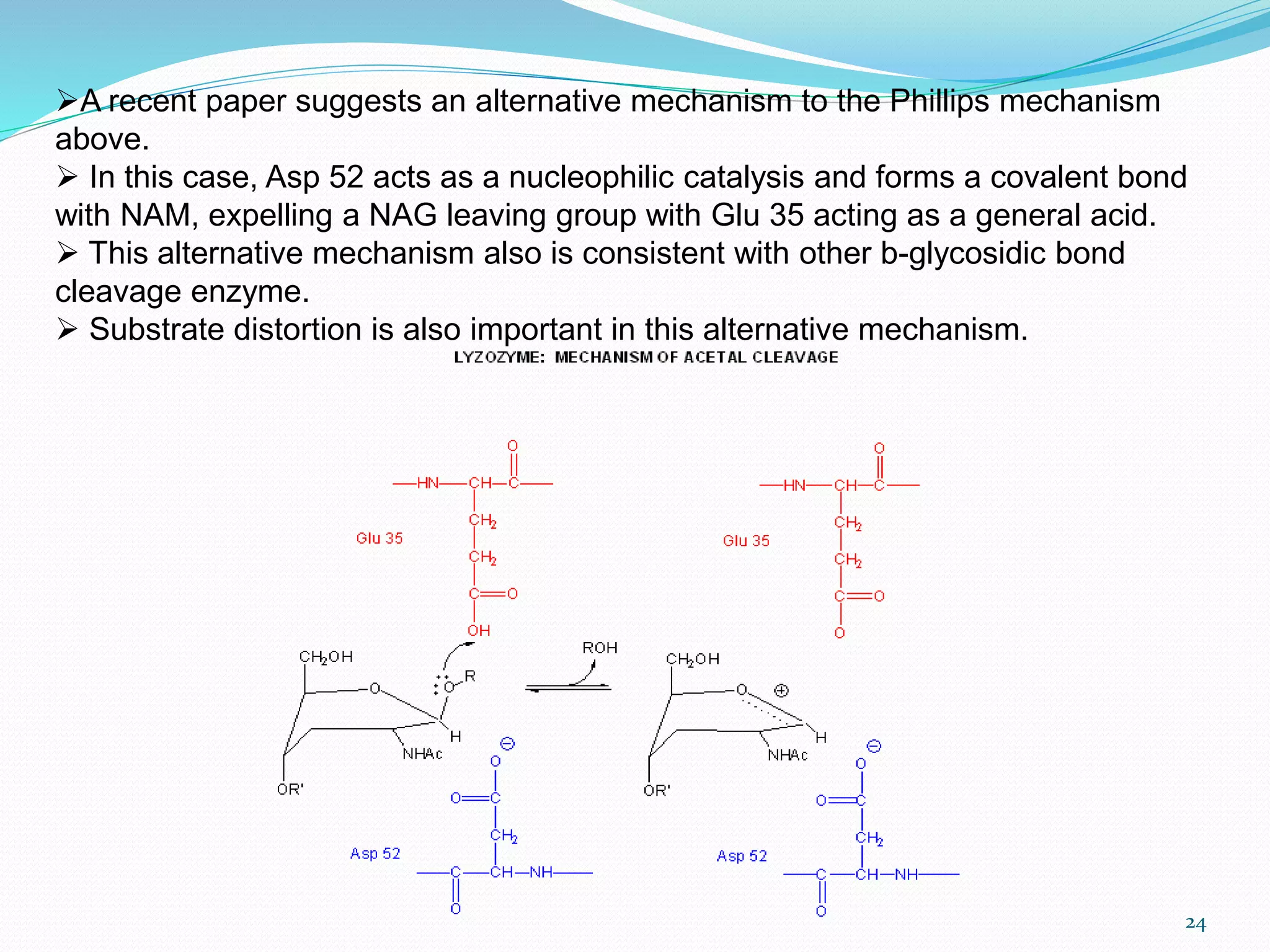
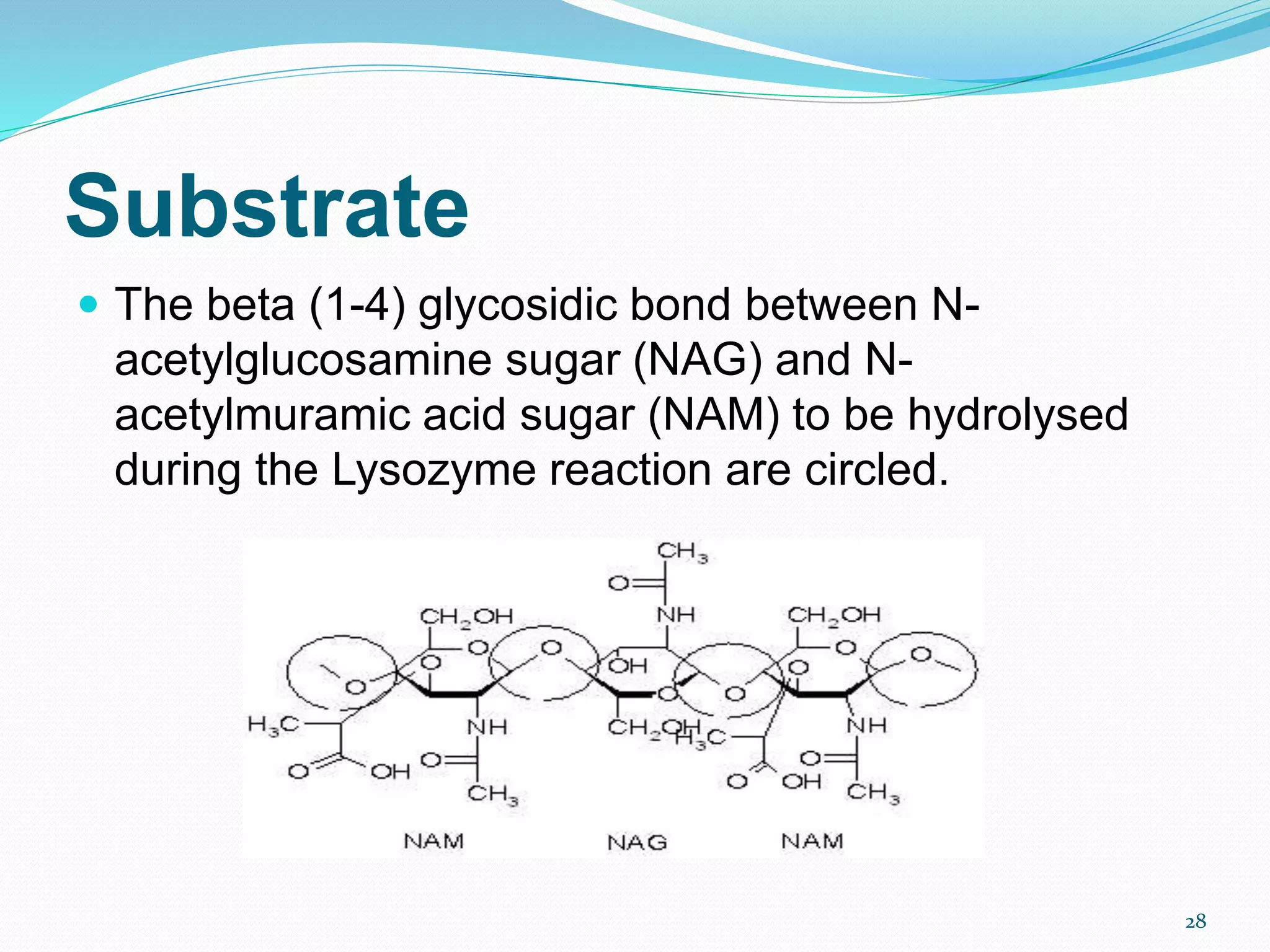
Lysozyme is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of bacterial cell walls. It was first discovered in 1922 by Alexander Fleming. The enzyme hydrolyzes beta linkages between N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid in peptidoglycan. Lysozyme has antibacterial properties and is found naturally in human tears, saliva, and egg whites. It has important applications in protein purification and nucleic acid preparation. The enzyme has a compact globular structure and contains four disulfide bonds that provide stability. Its active site contains the residues glutamic acid 35 and aspartic acid 52, which work together to catalyze the hydrolysis reaction.