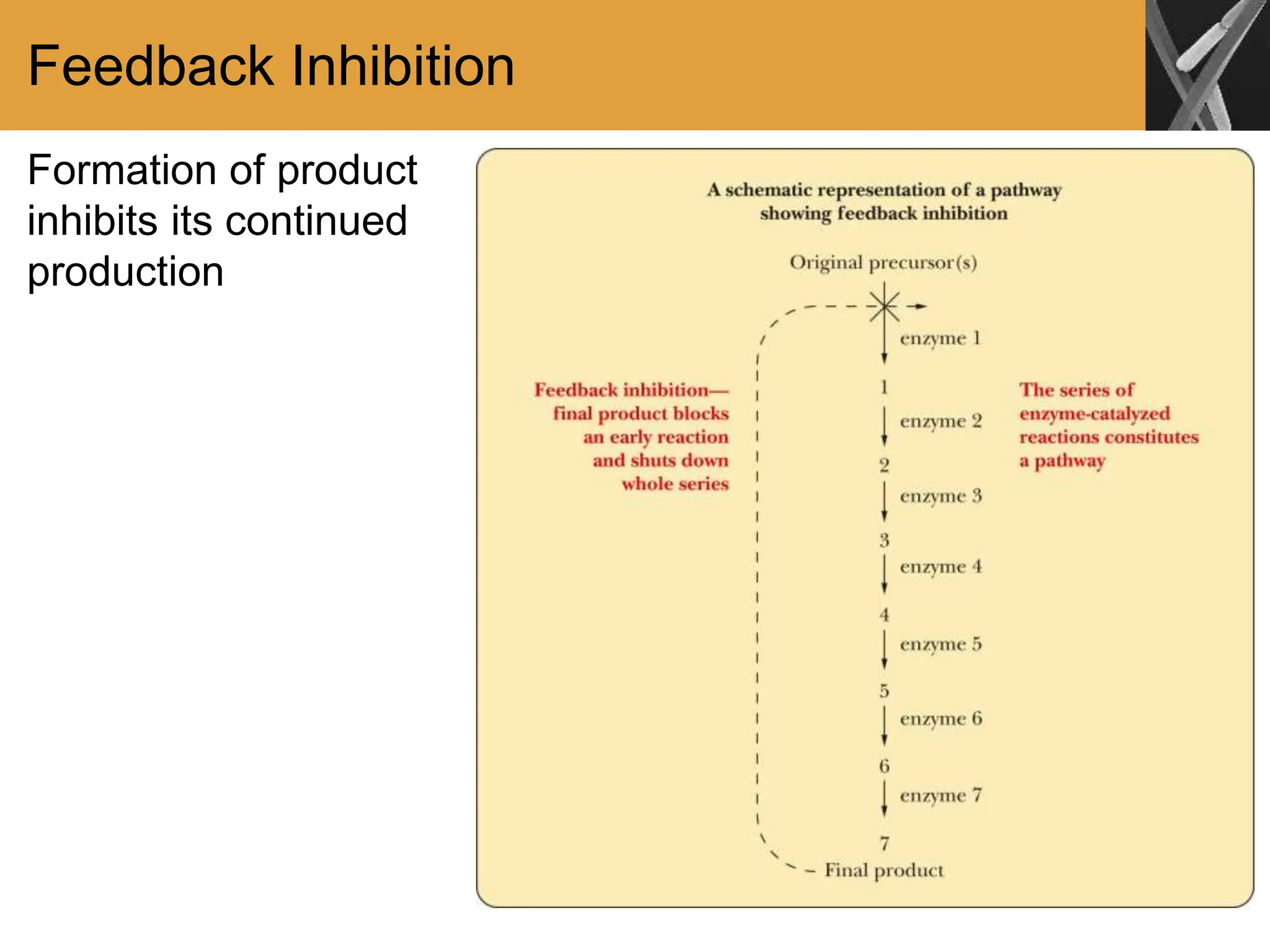
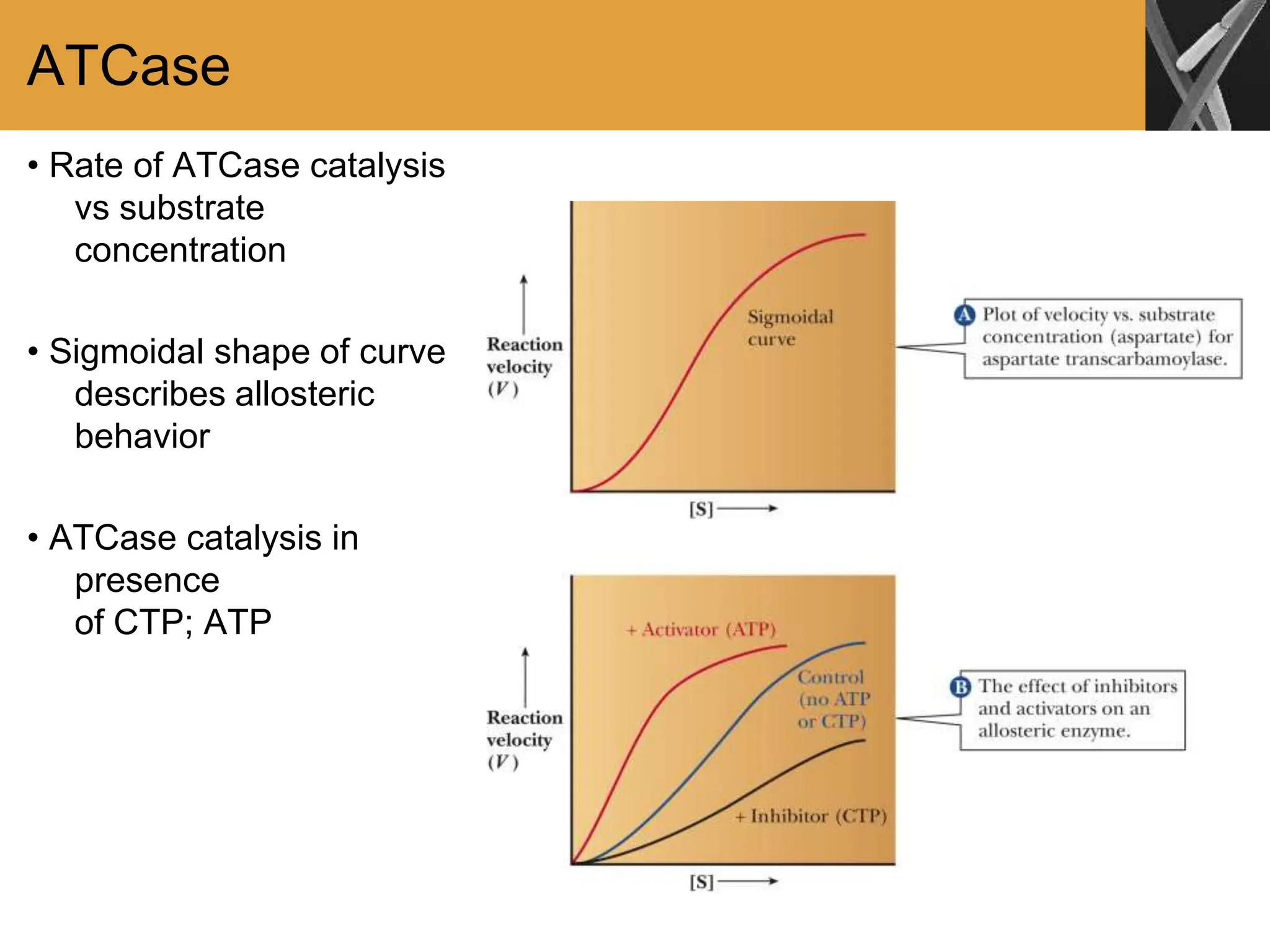
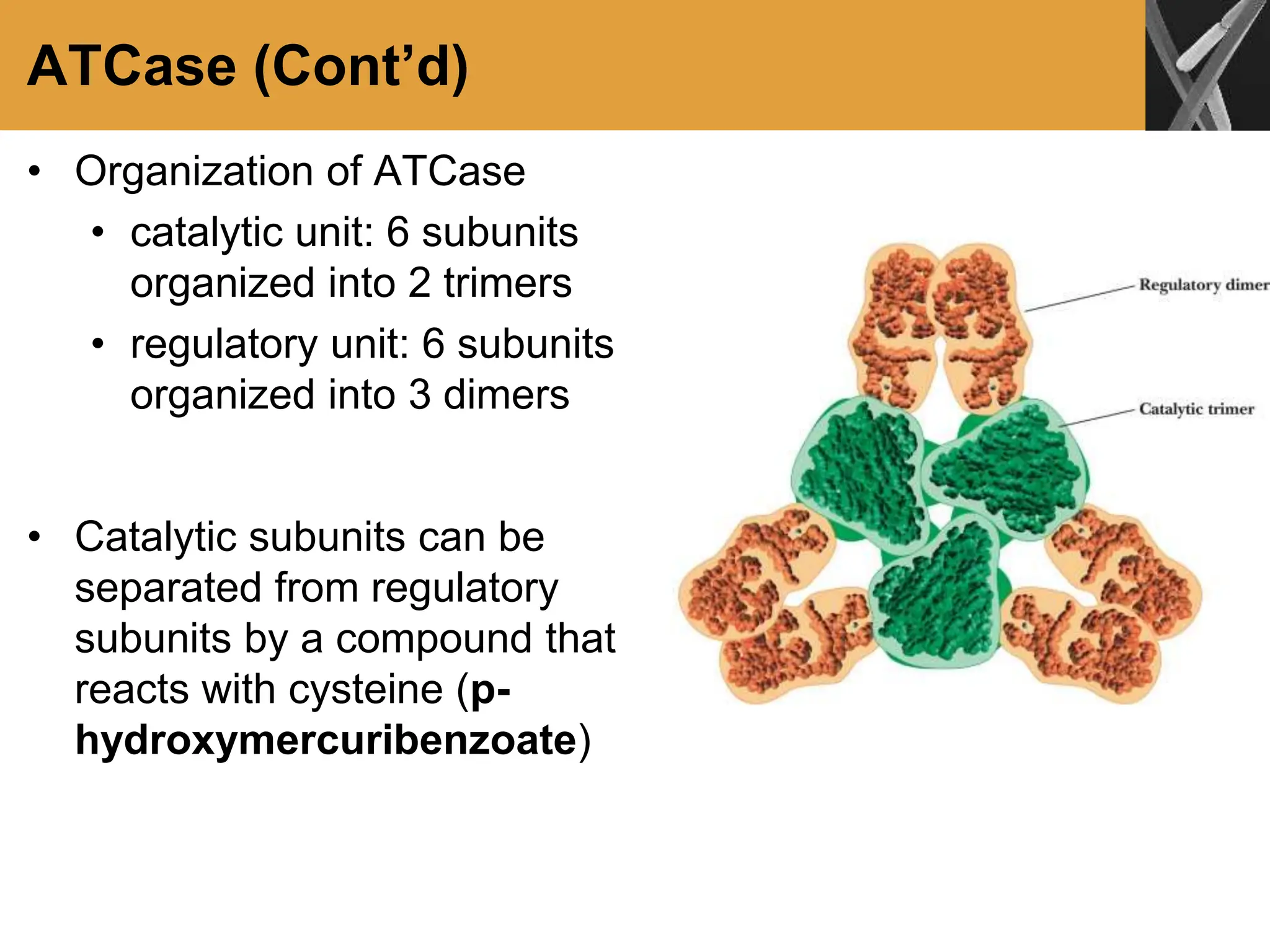
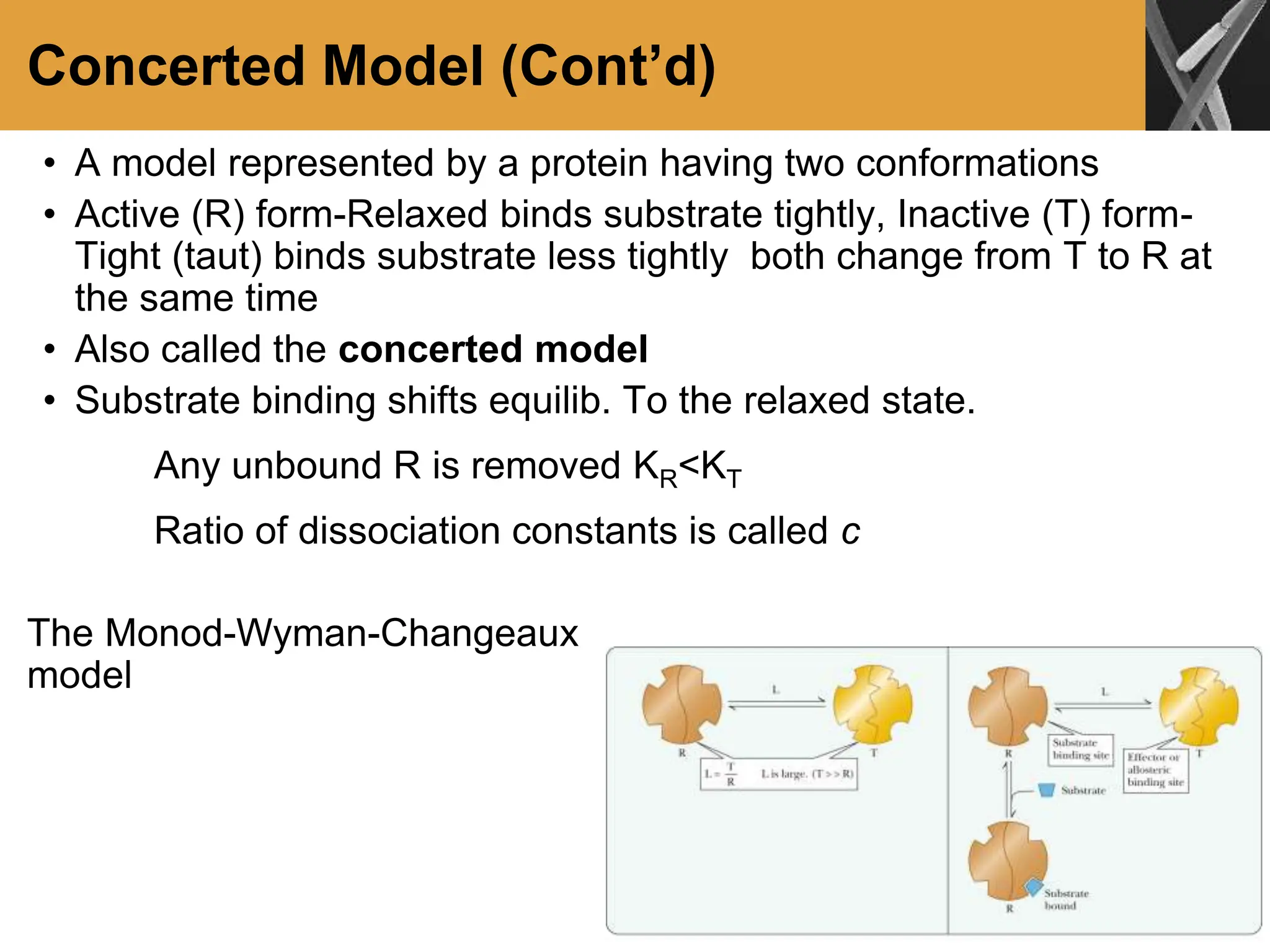
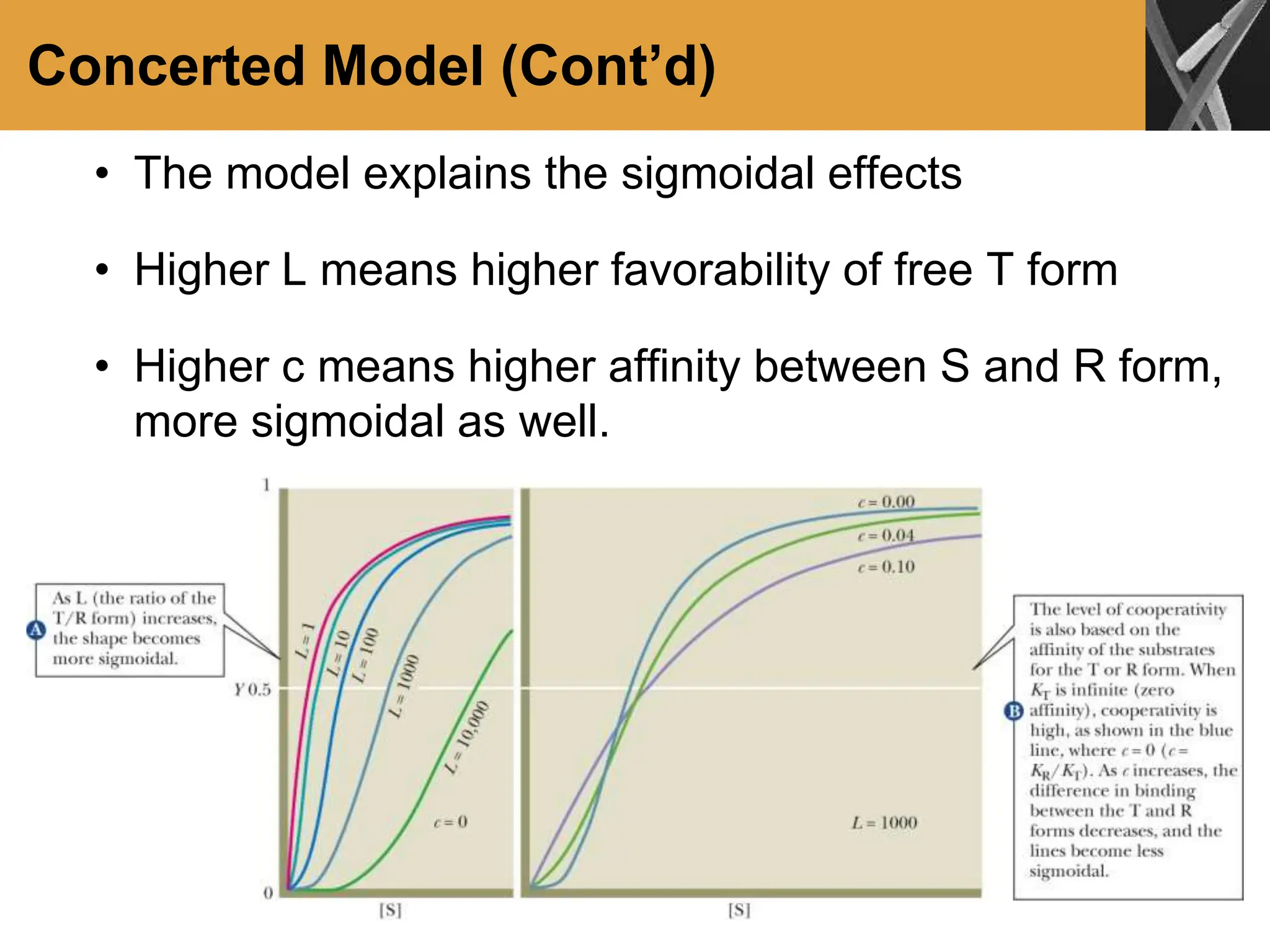
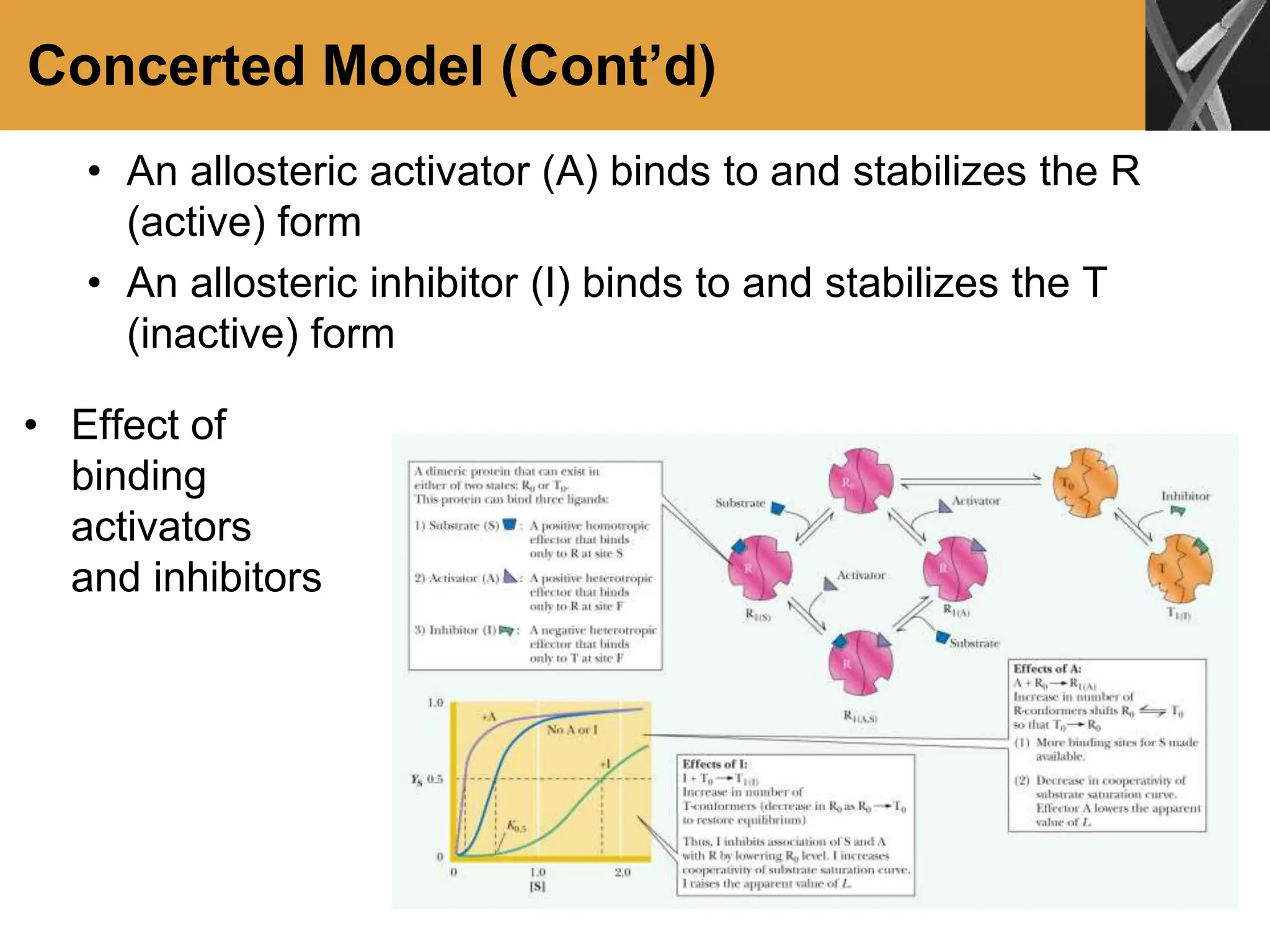
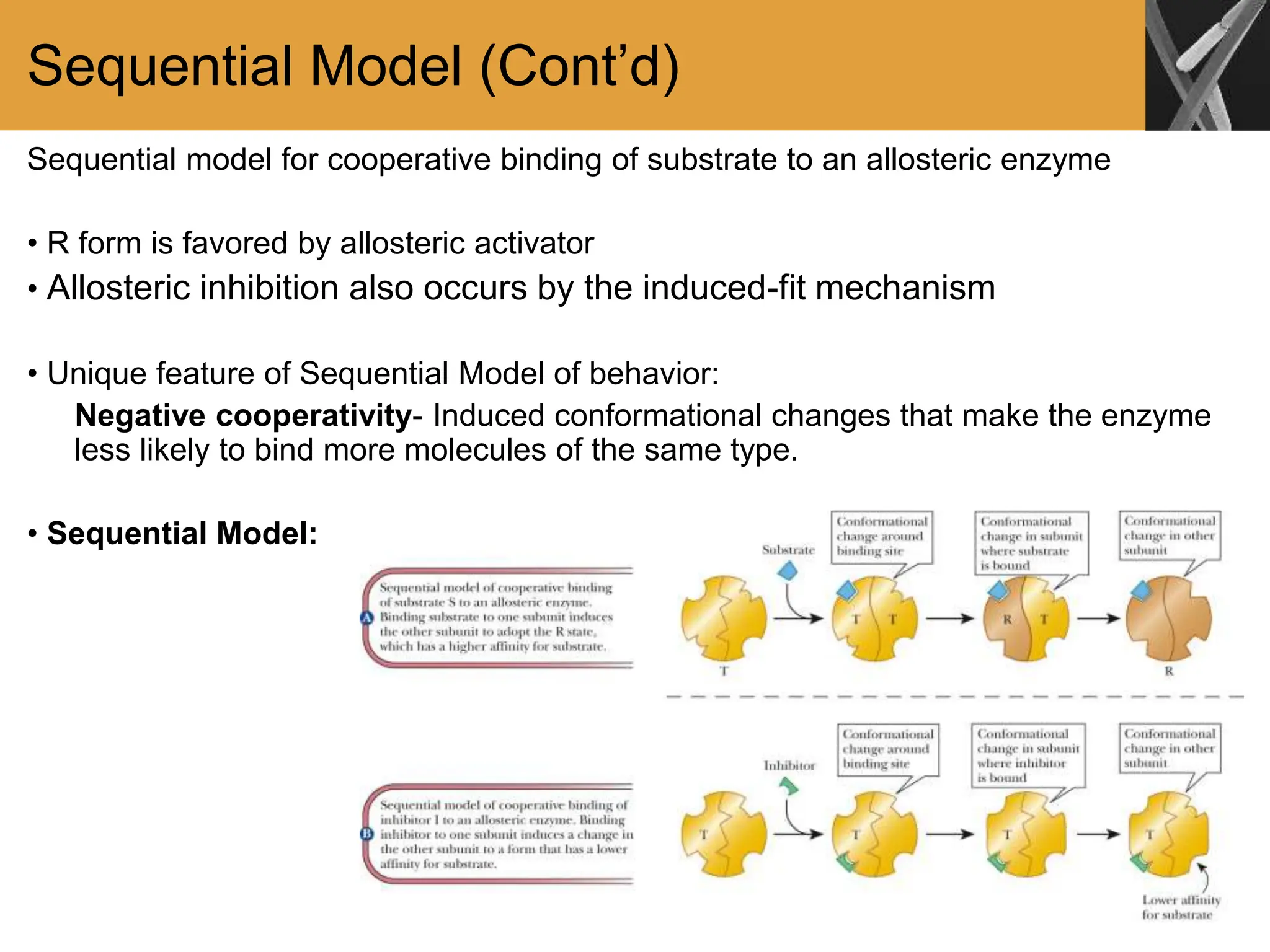
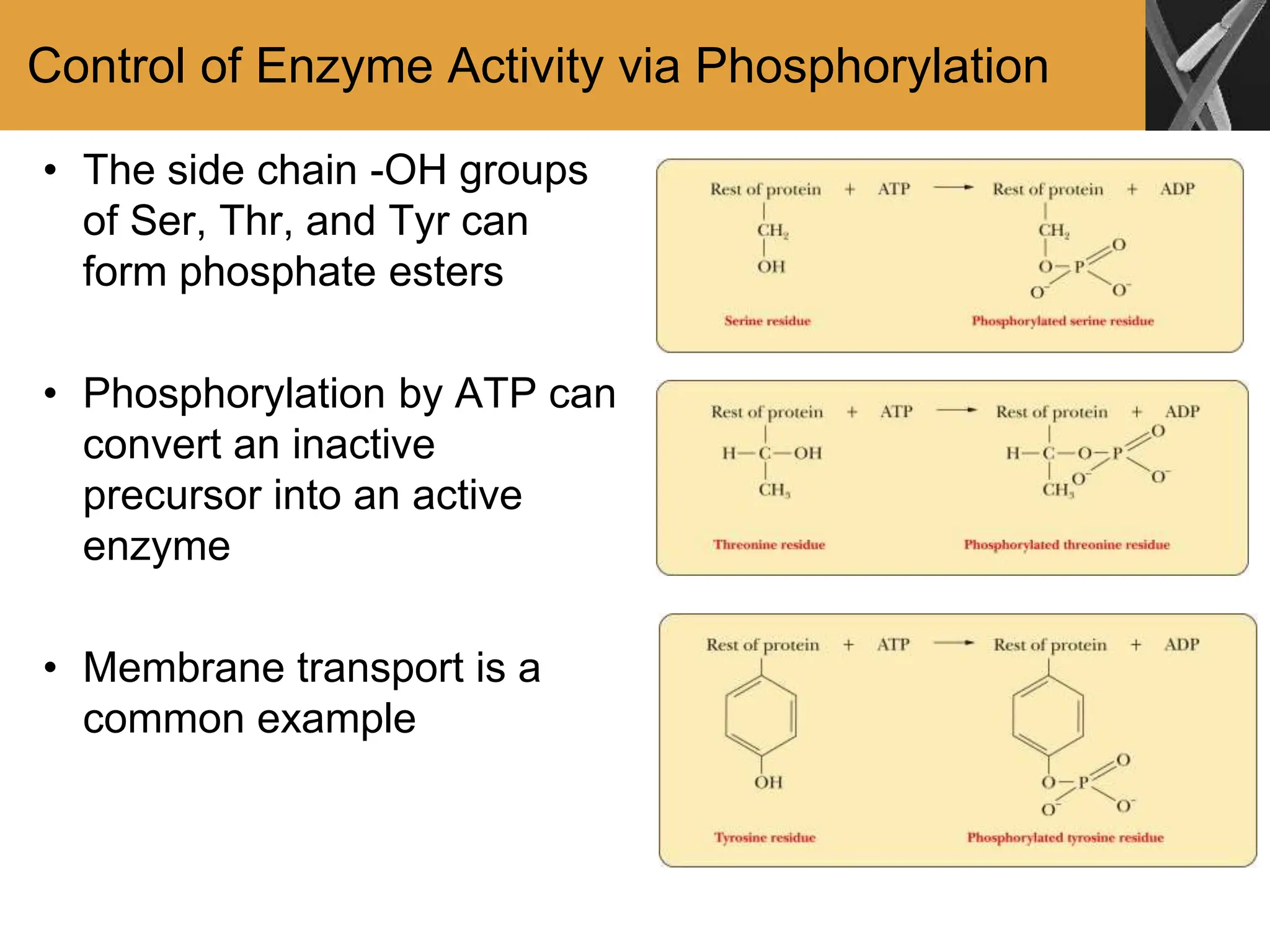
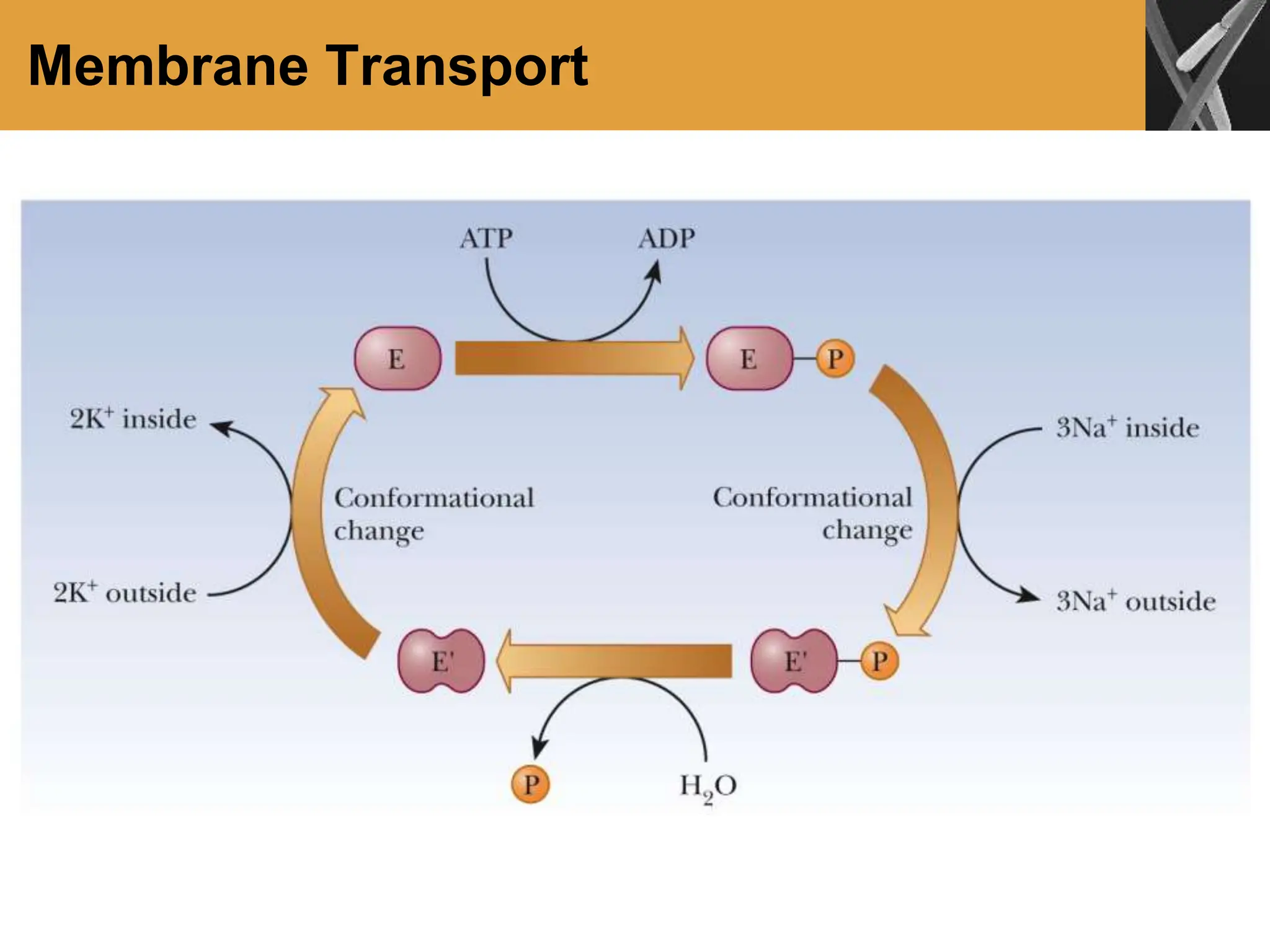
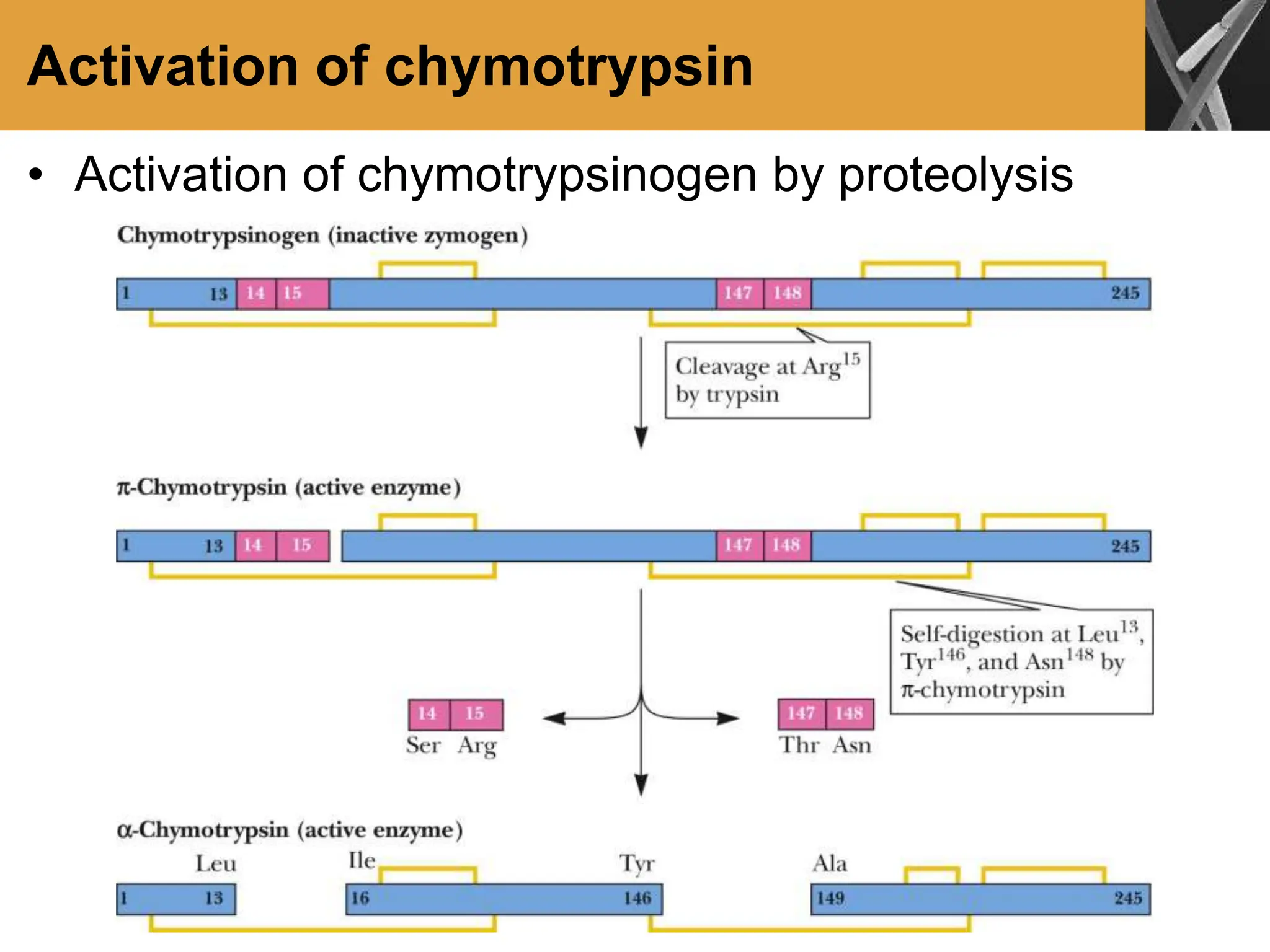
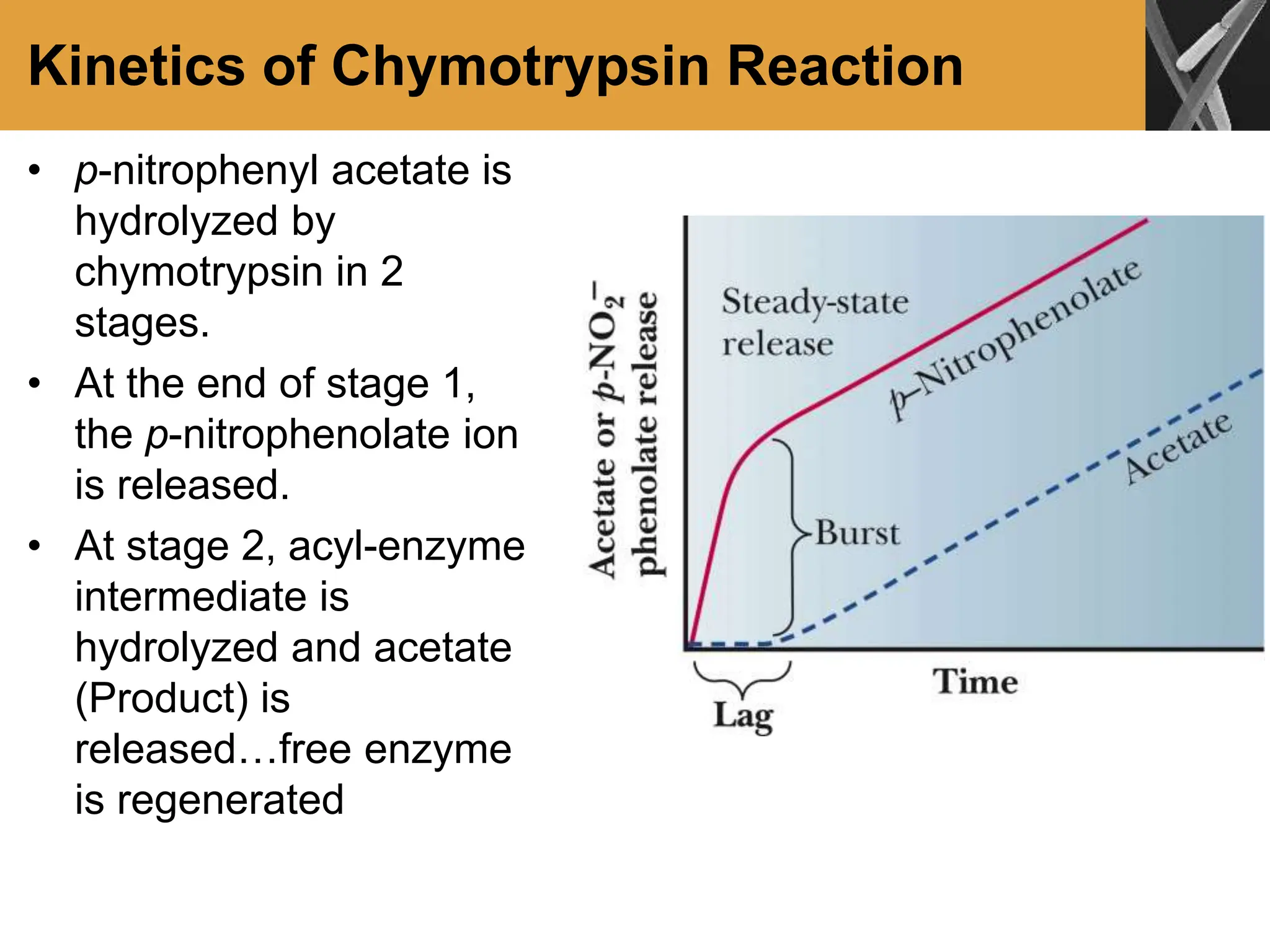
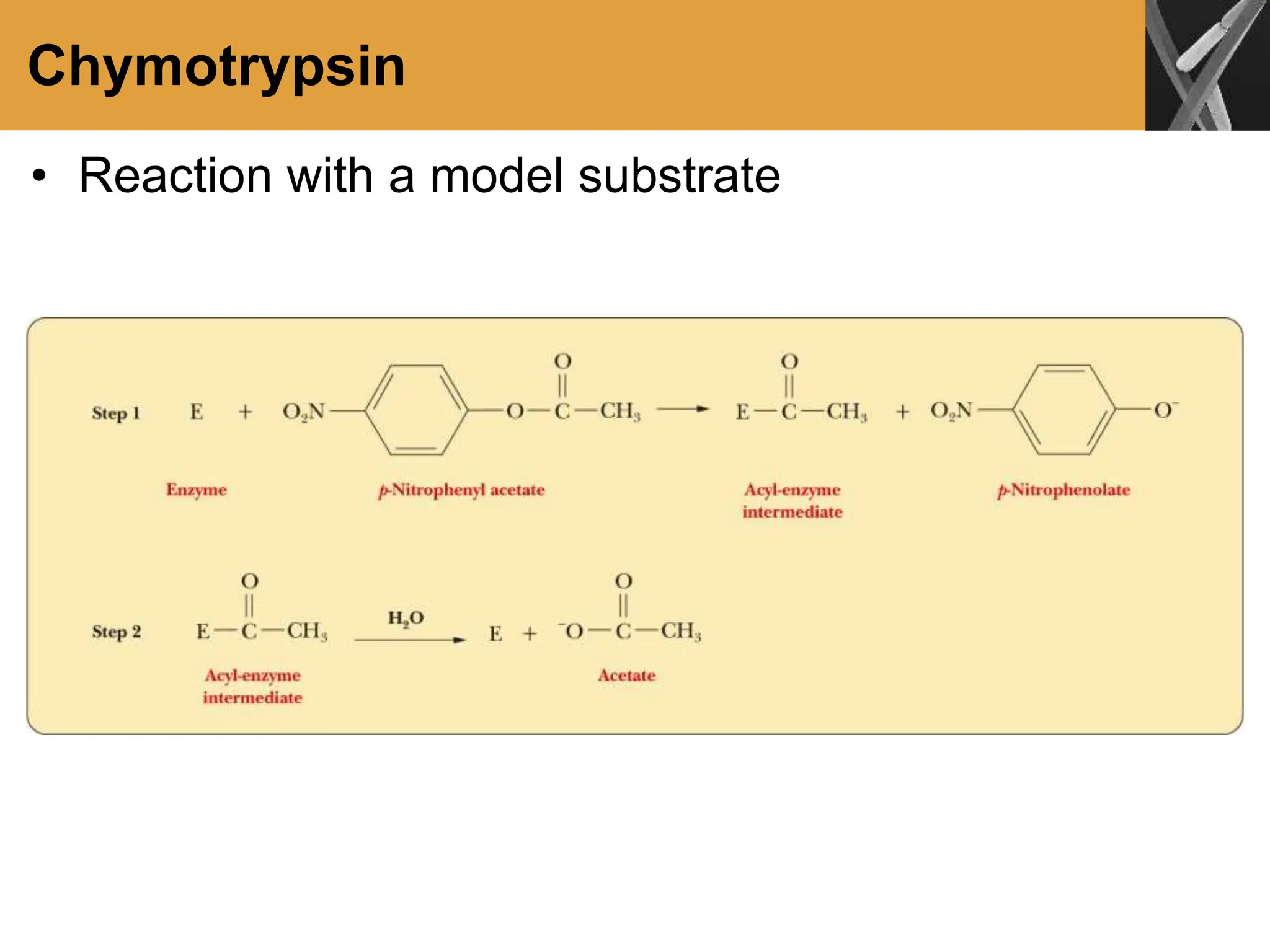
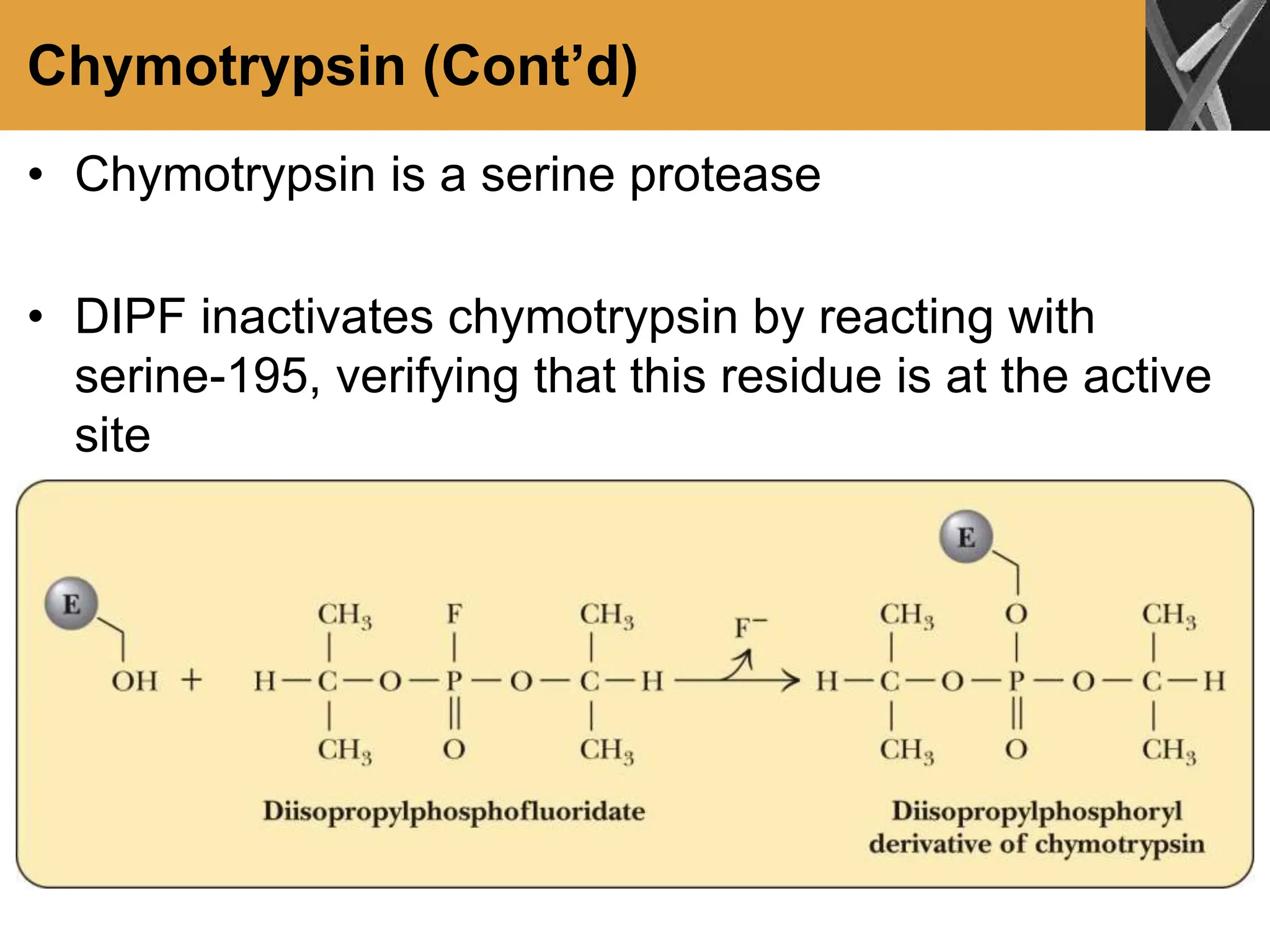
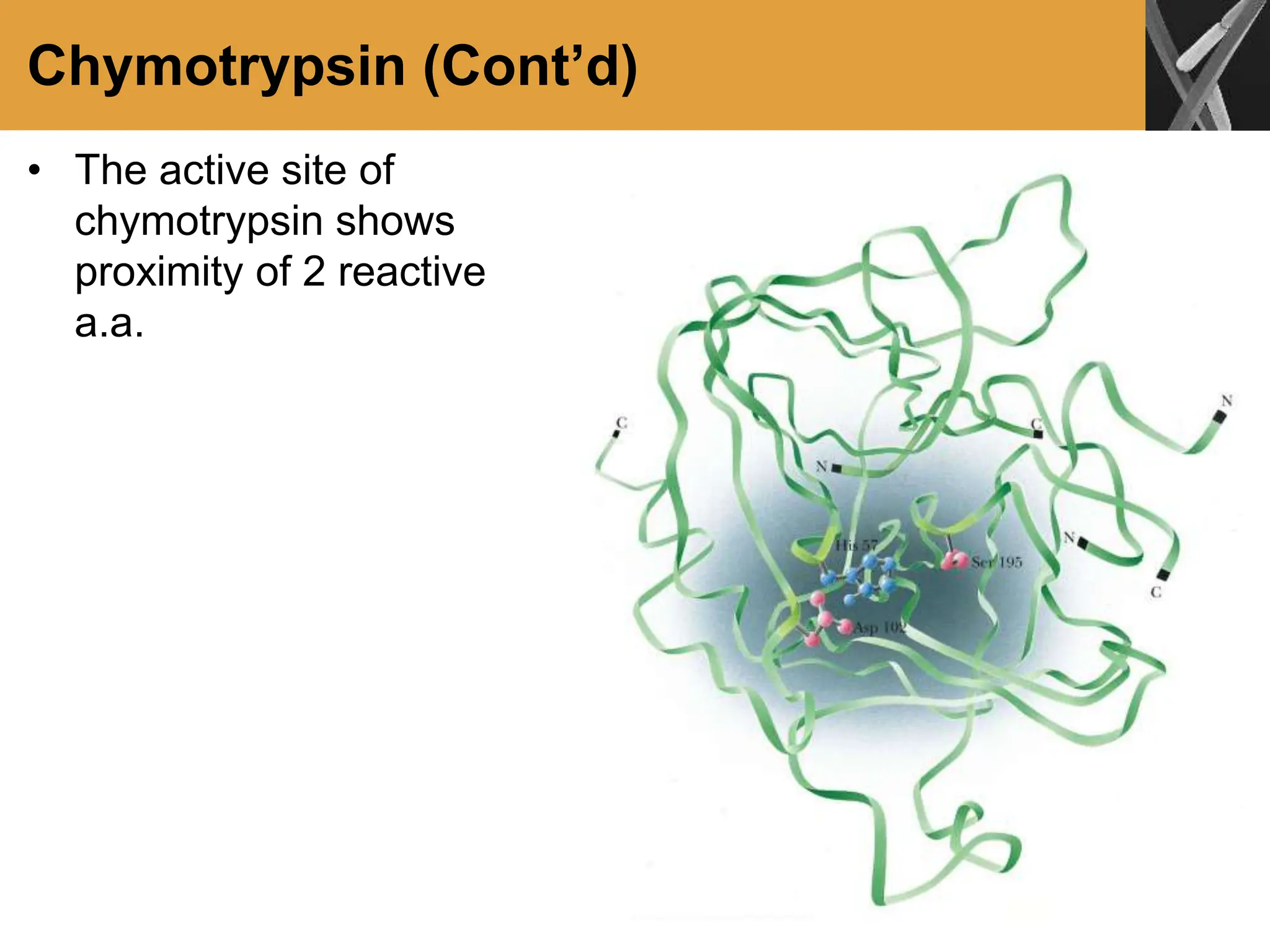
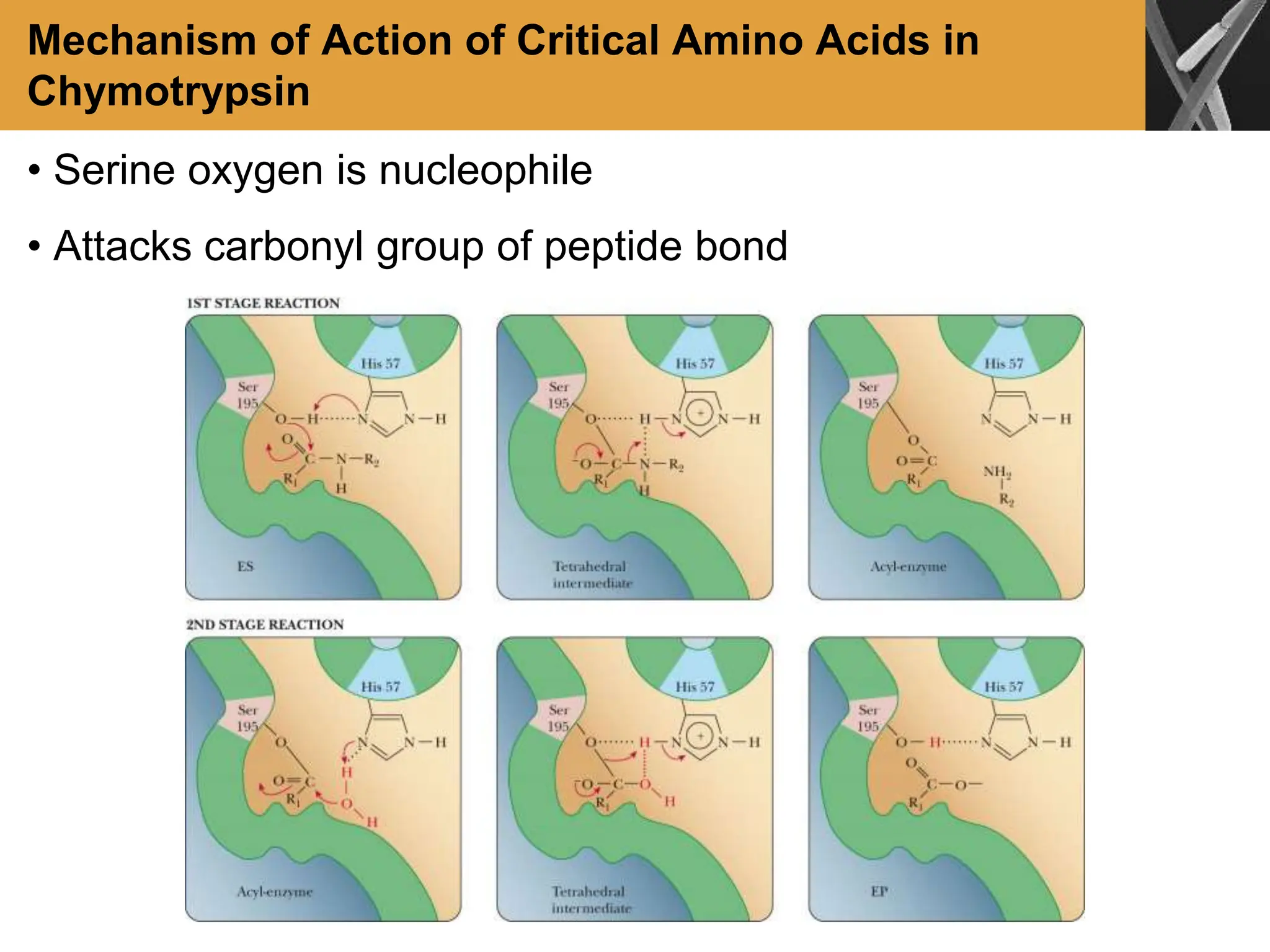
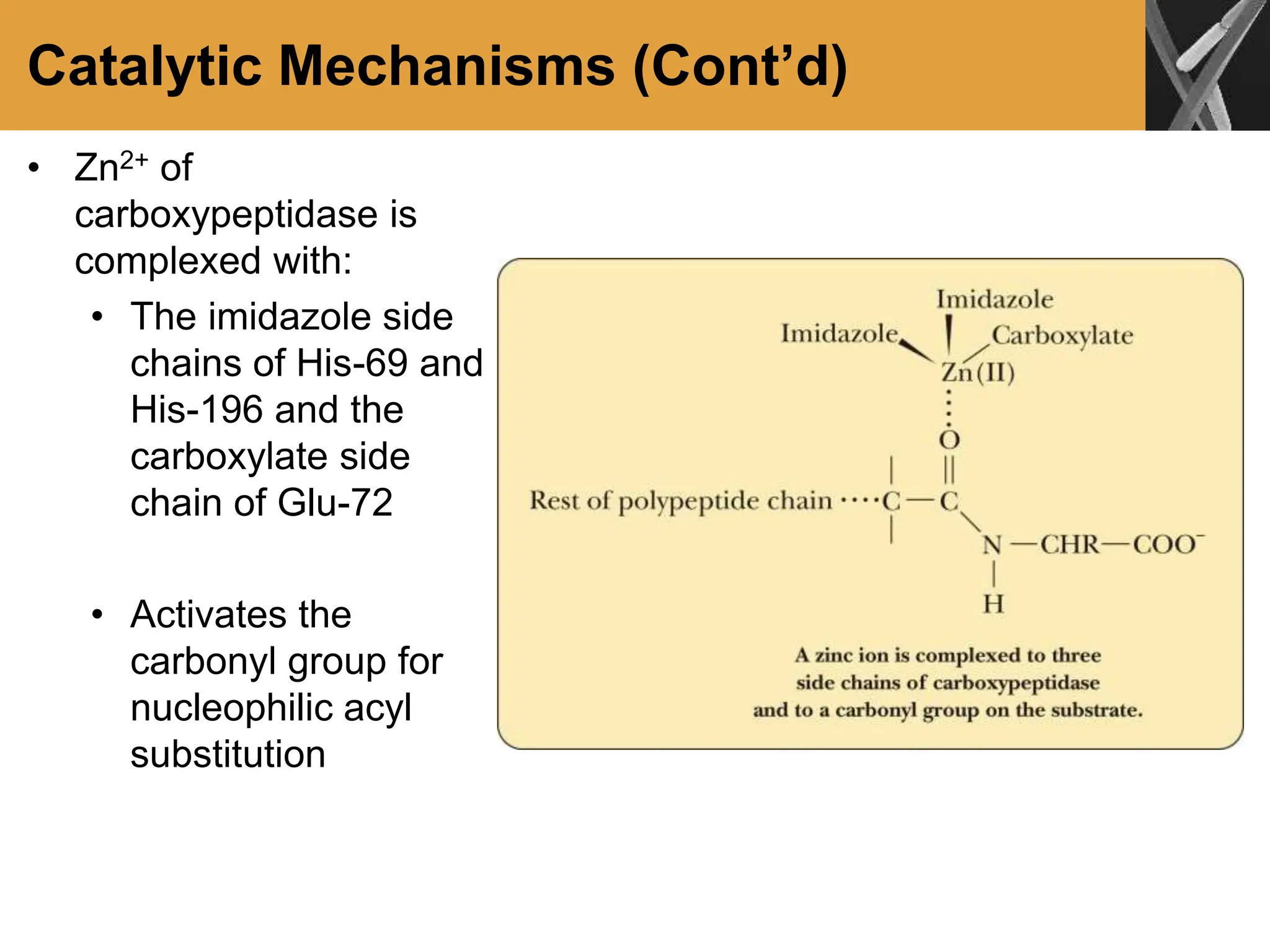
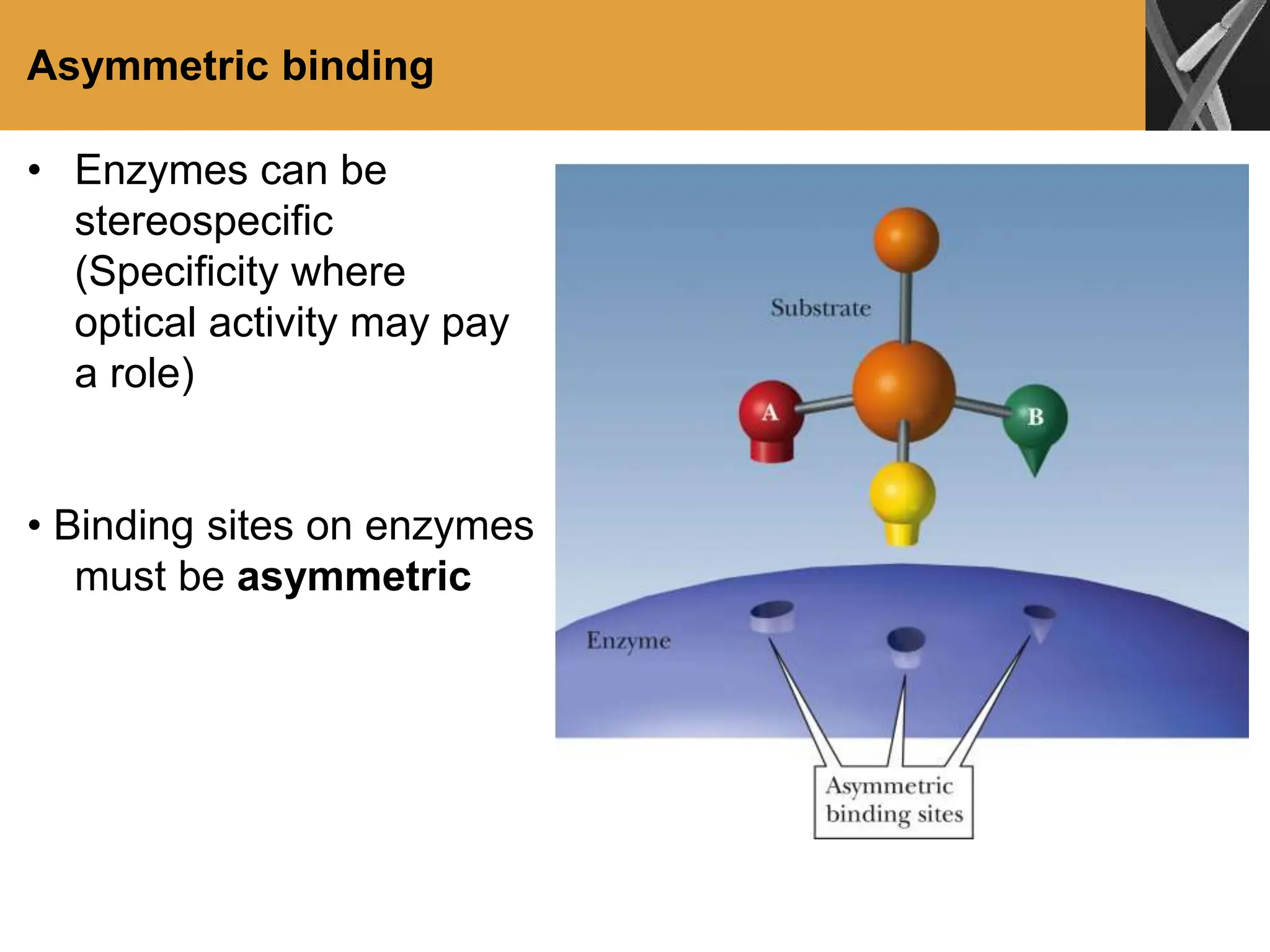
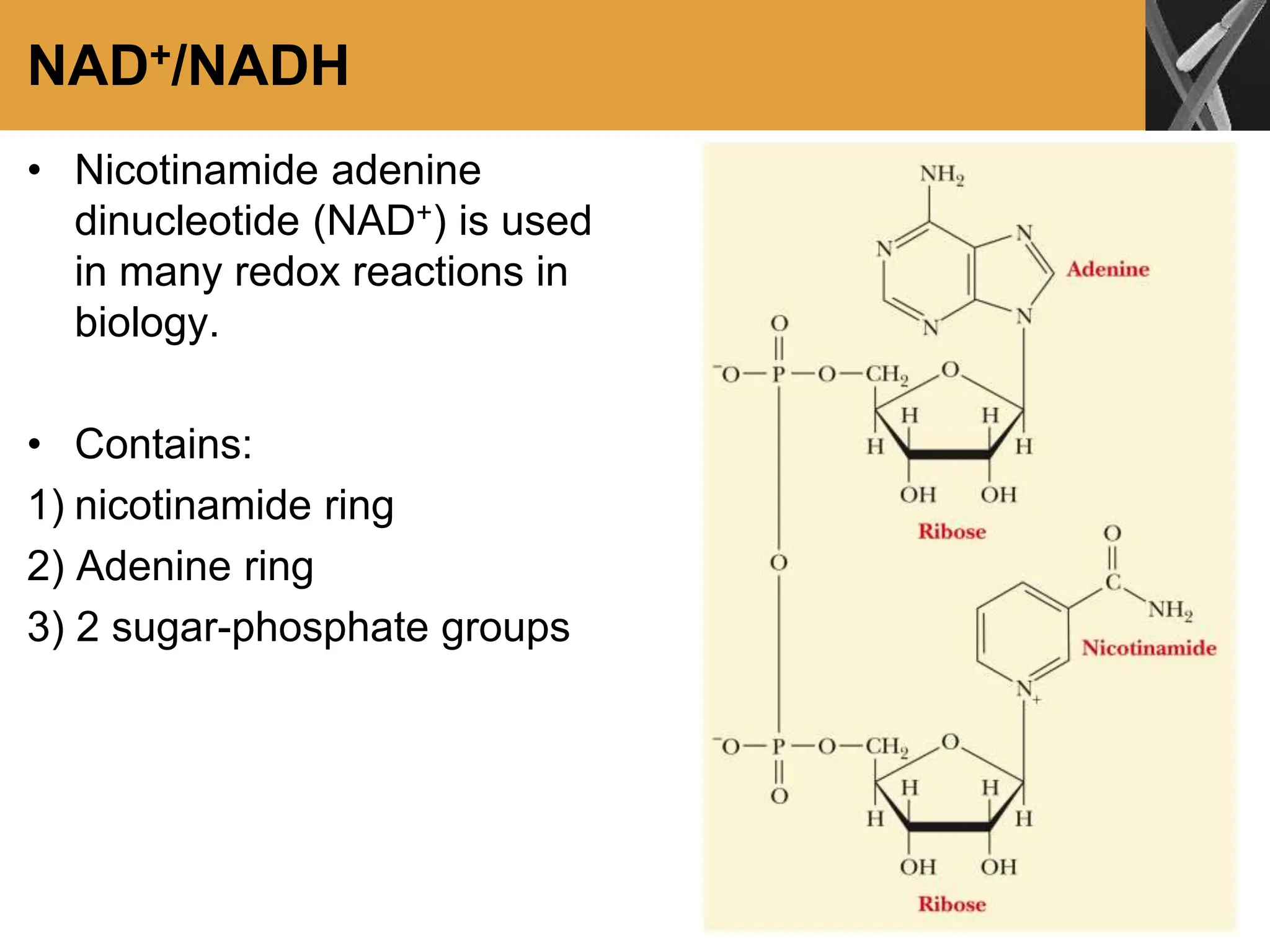
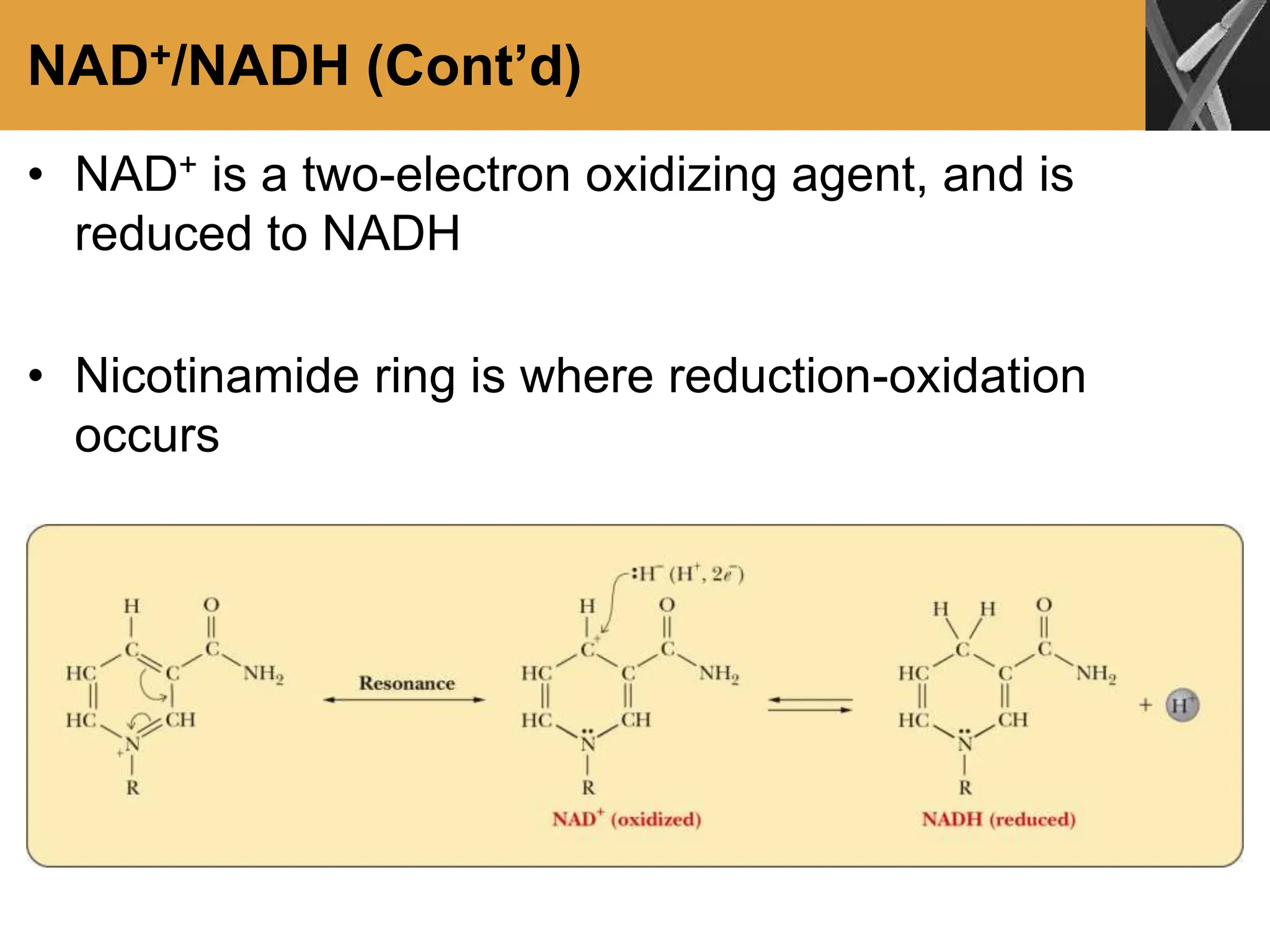
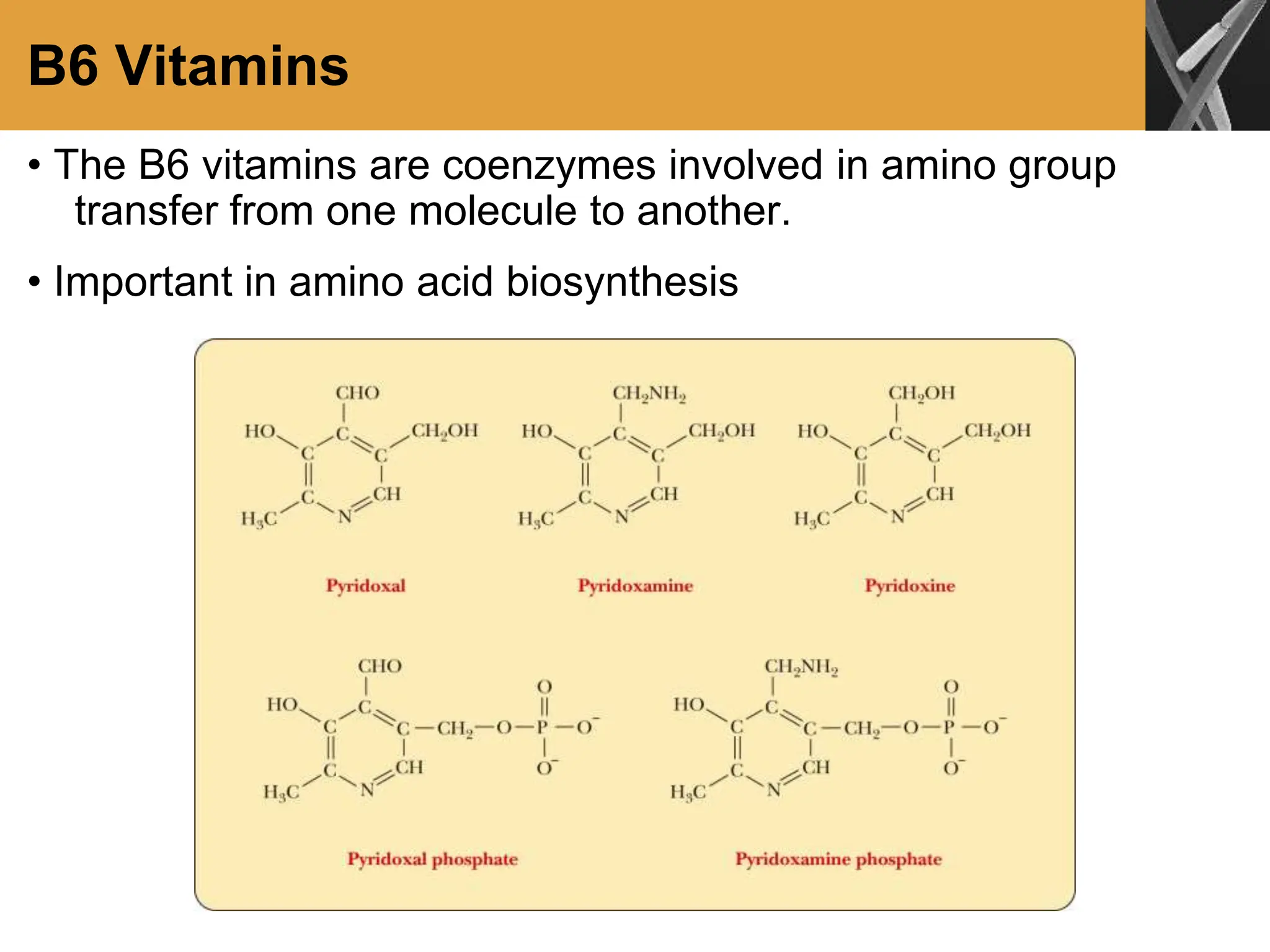
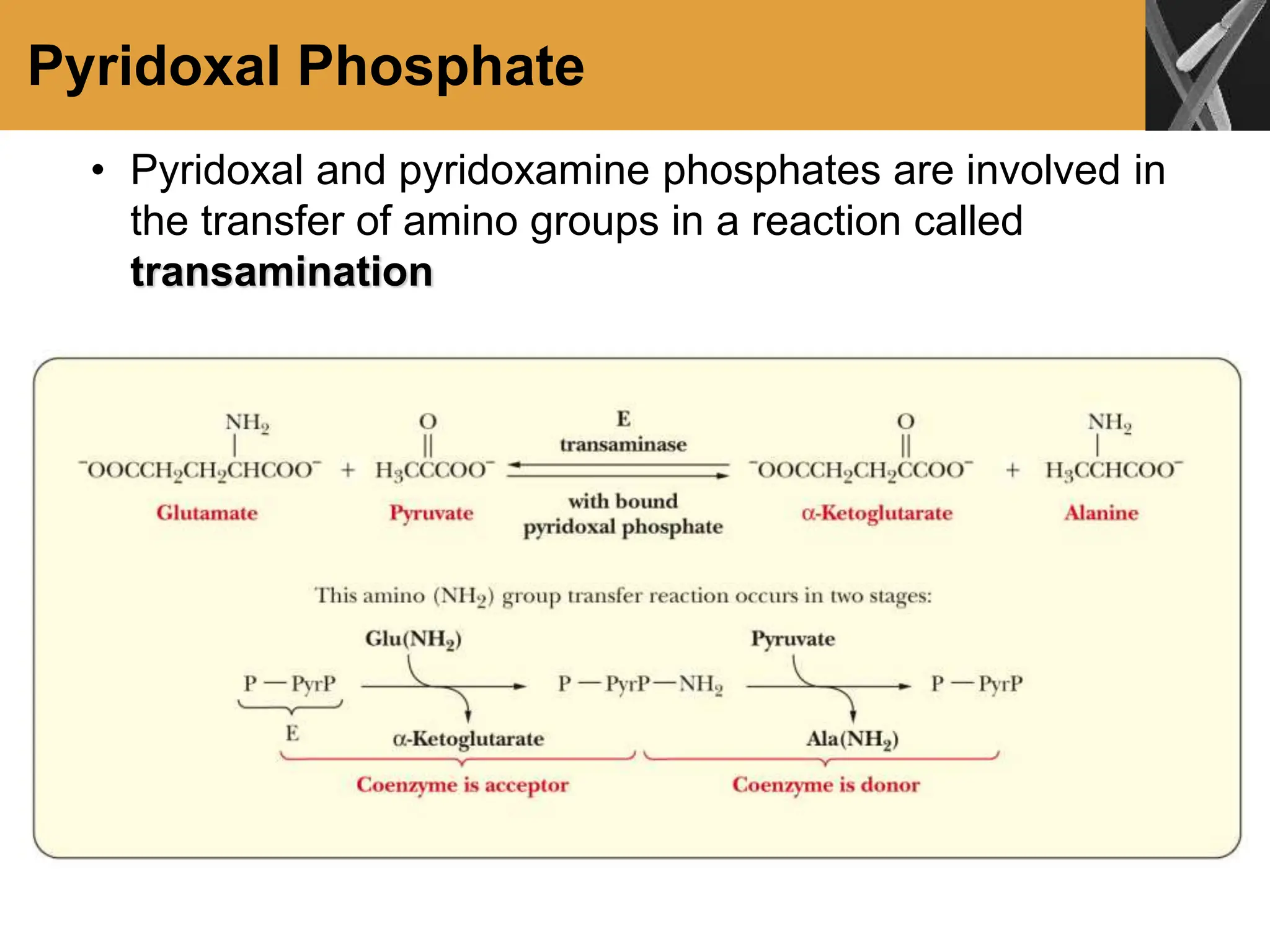
This document discusses allosteric enzymes and their regulation. It begins by defining allosteric enzymes as oligomeric enzymes whose activity is affected by binding of other substances that alter the enzyme's conformation. A key example discussed is aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase), which shows feedback inhibition. The document then examines models of allosteric regulation, including the concerted model and sequential model. It also discusses other mechanisms of enzyme regulation, such as phosphorylation, proteolytic activation of zymogens, and the use of coenzymes like NAD+/NADH in redox reactions.