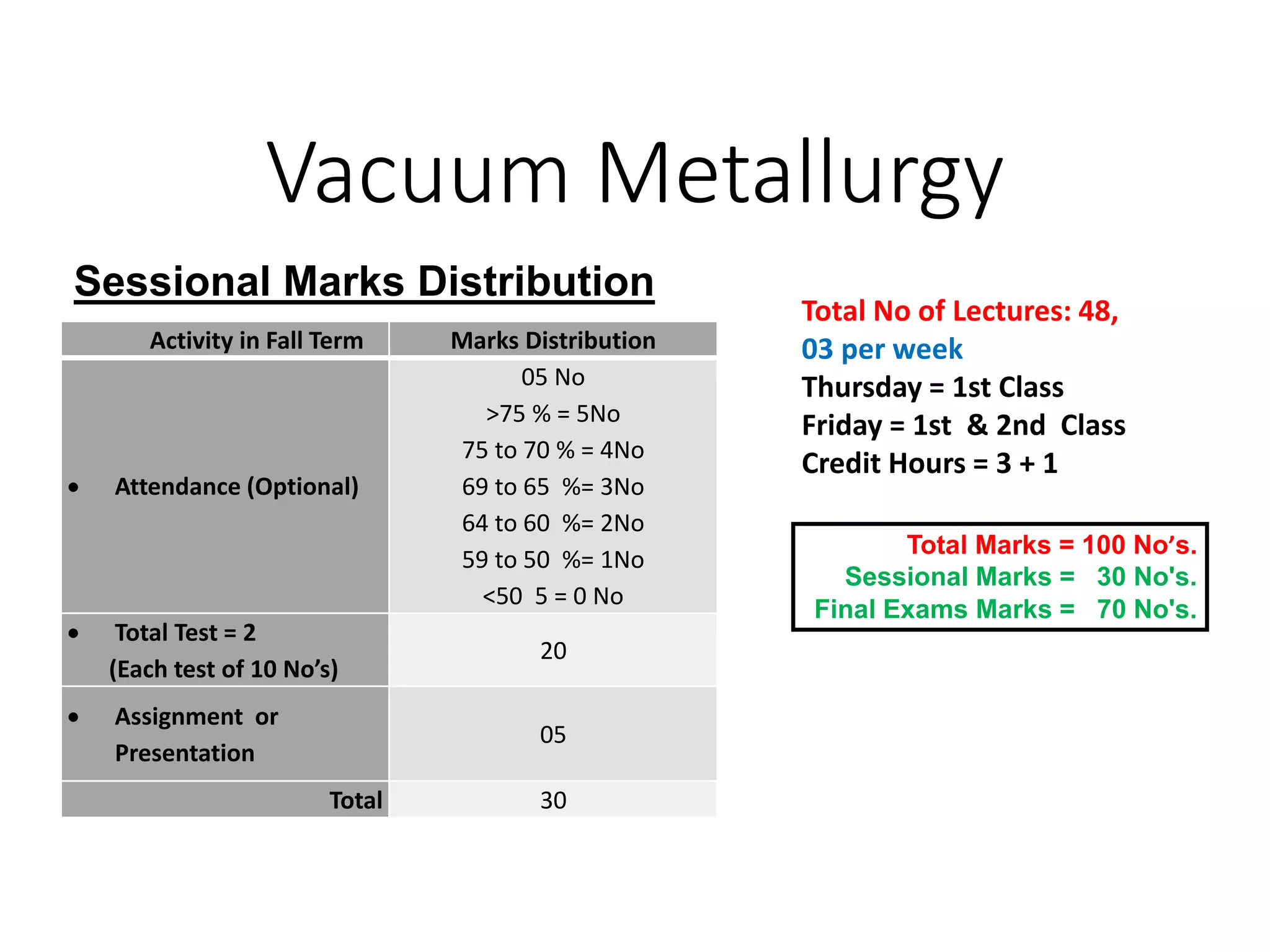
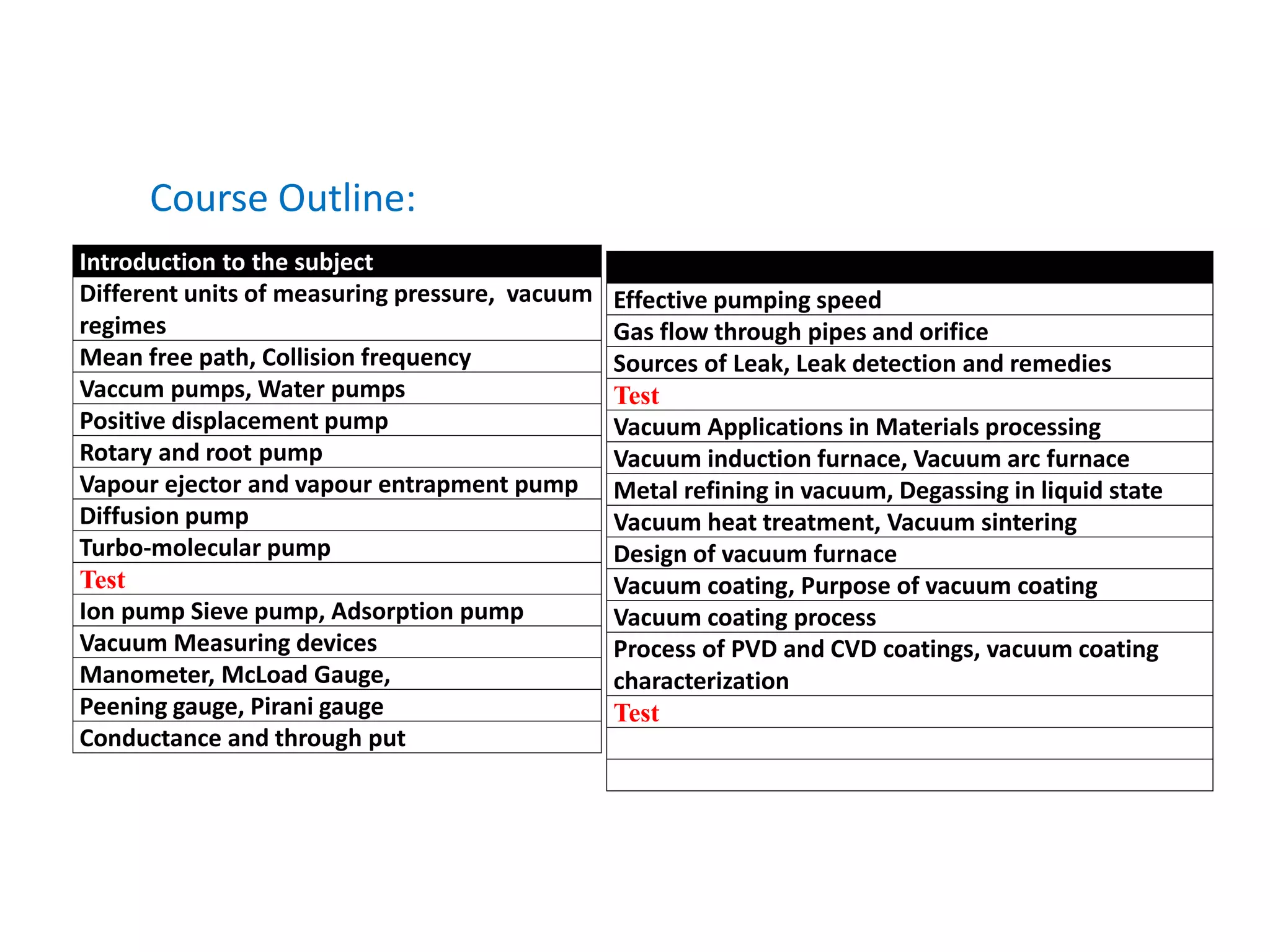
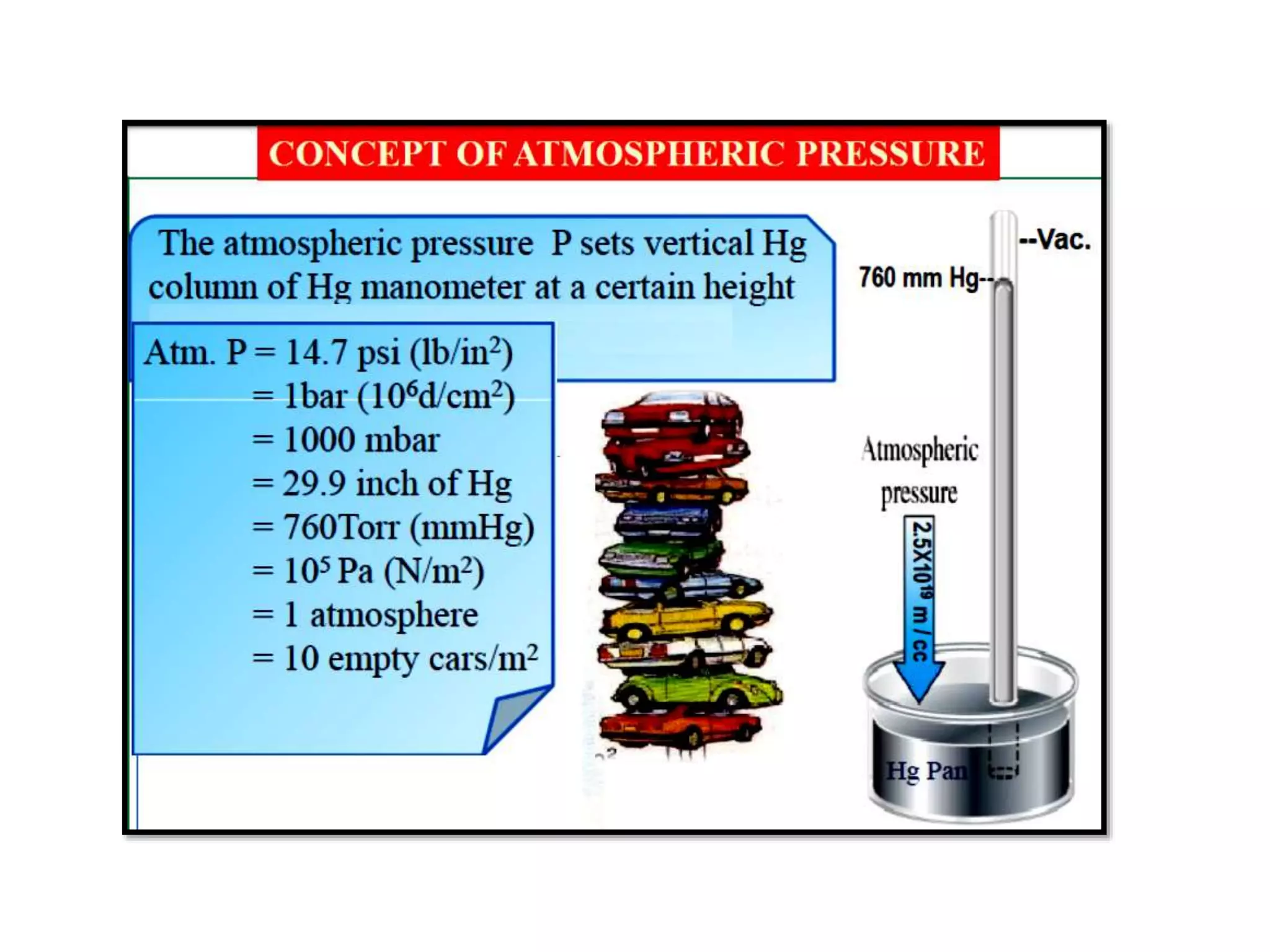
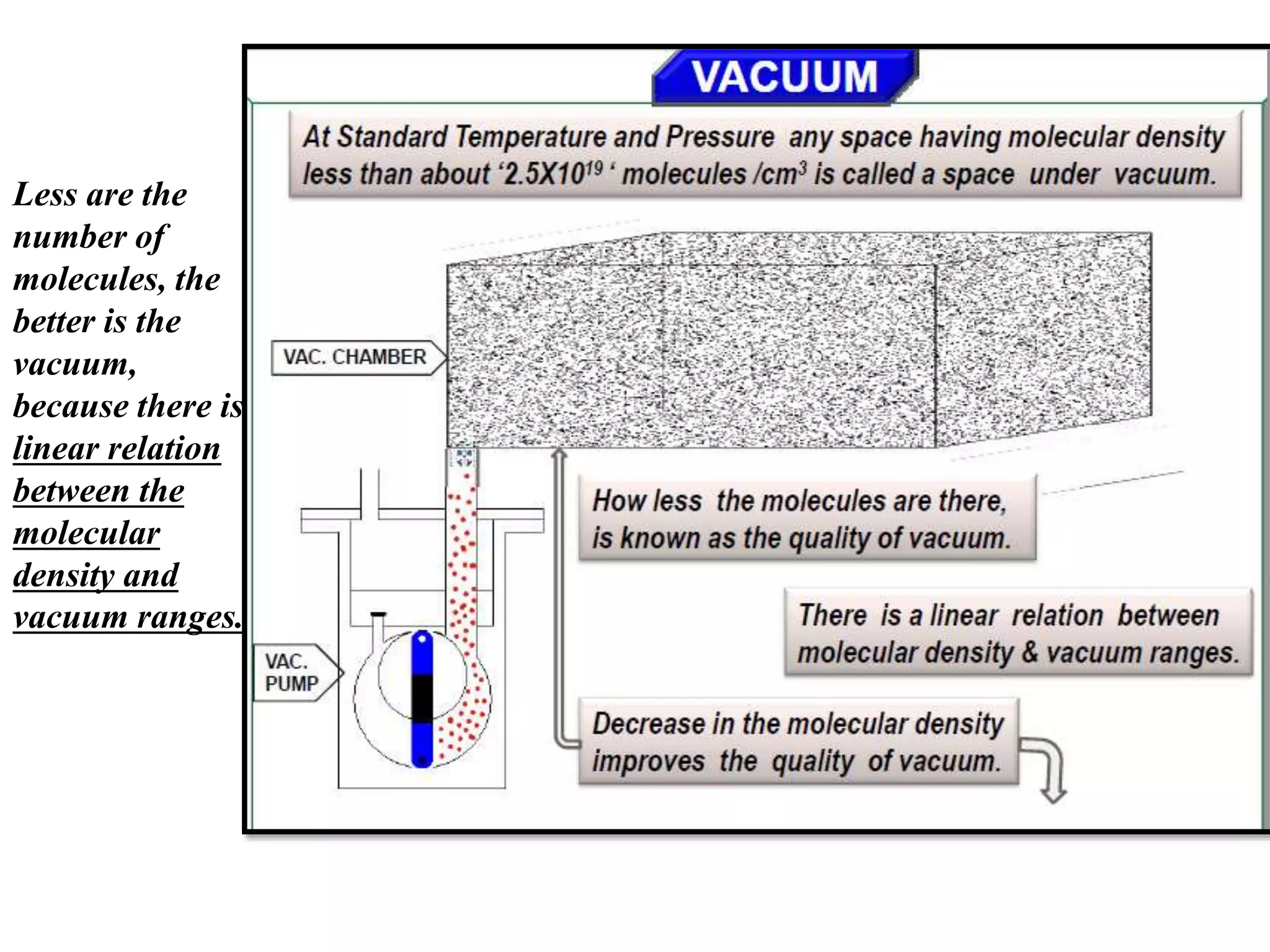
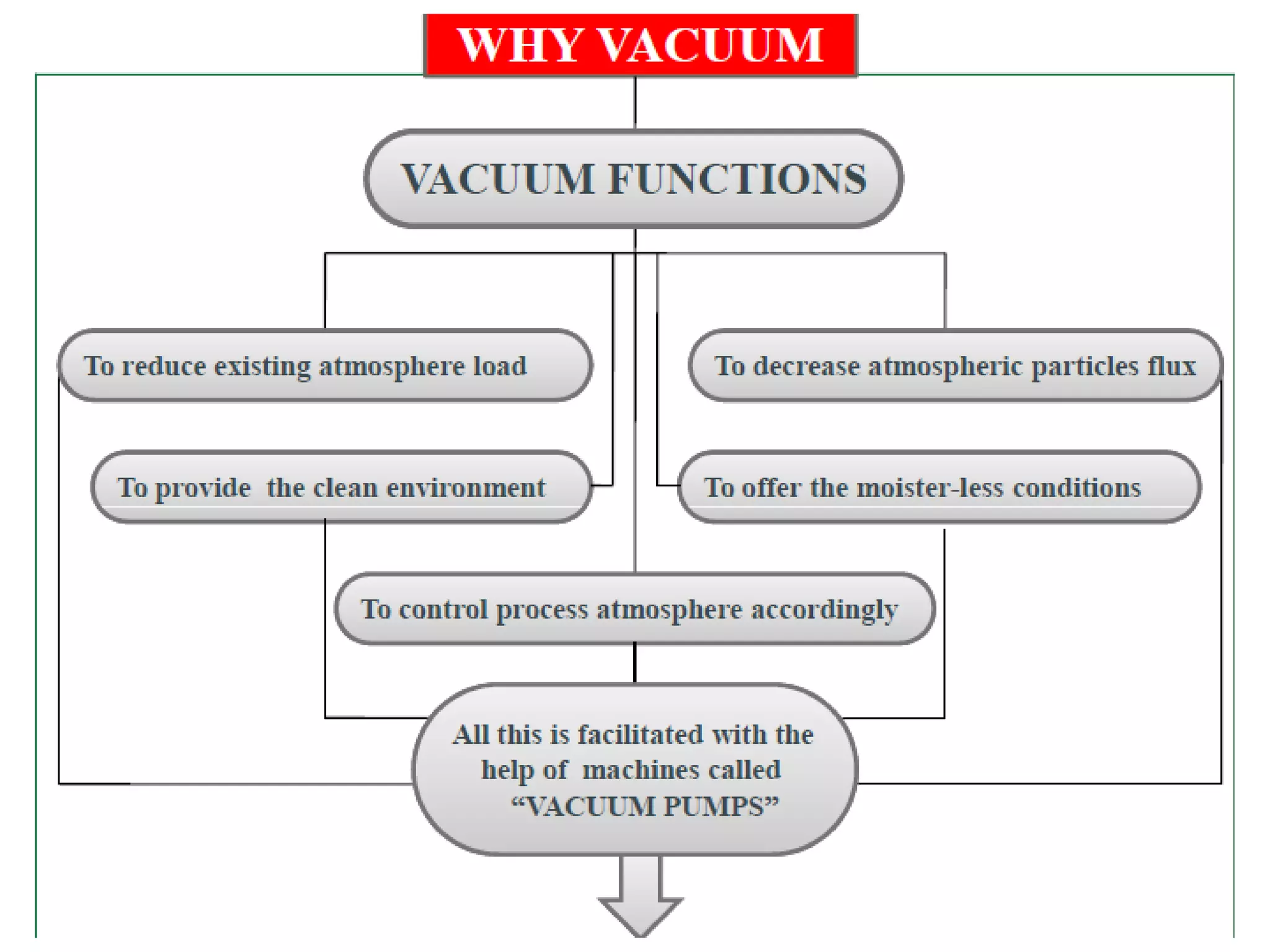
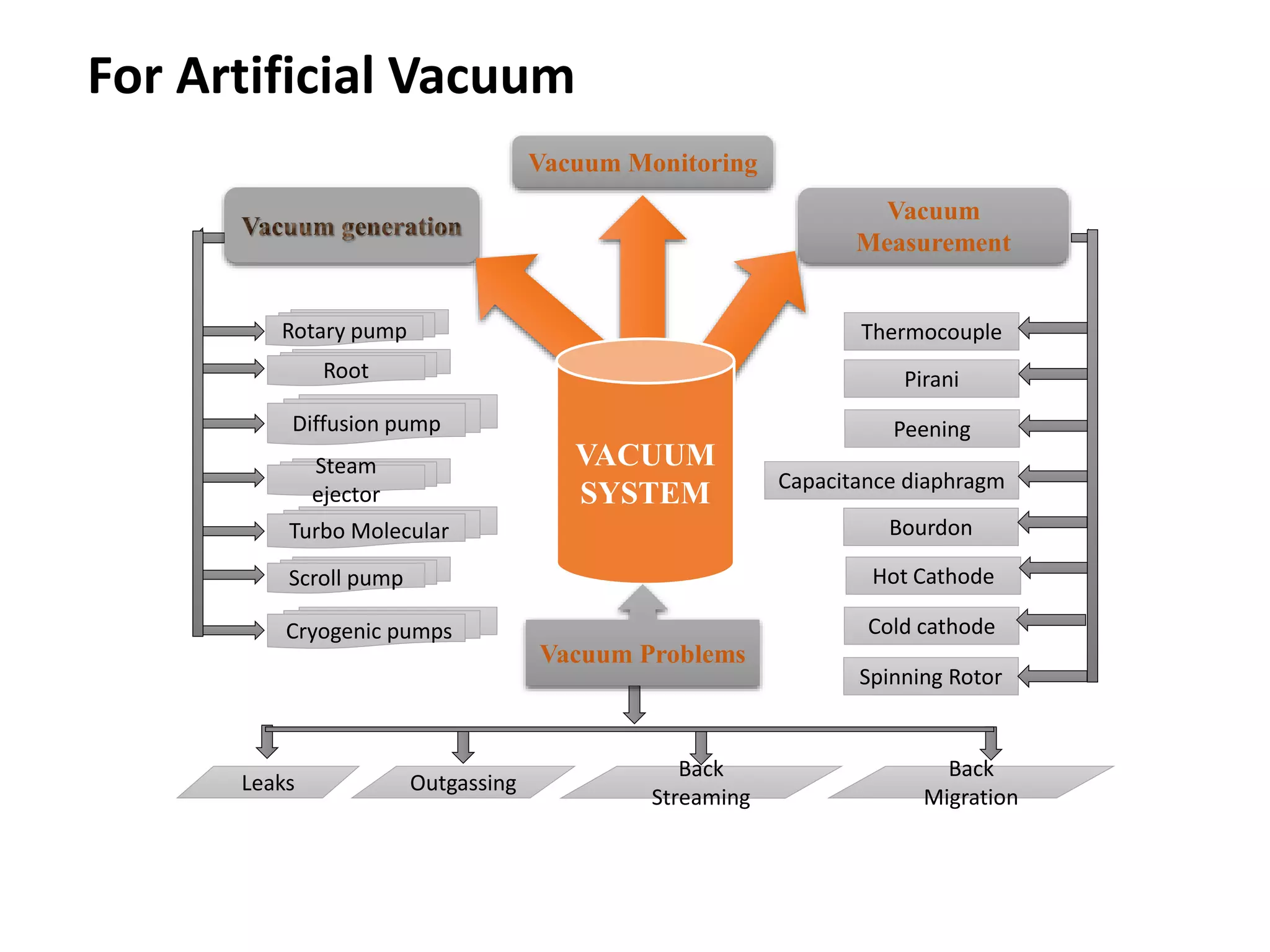
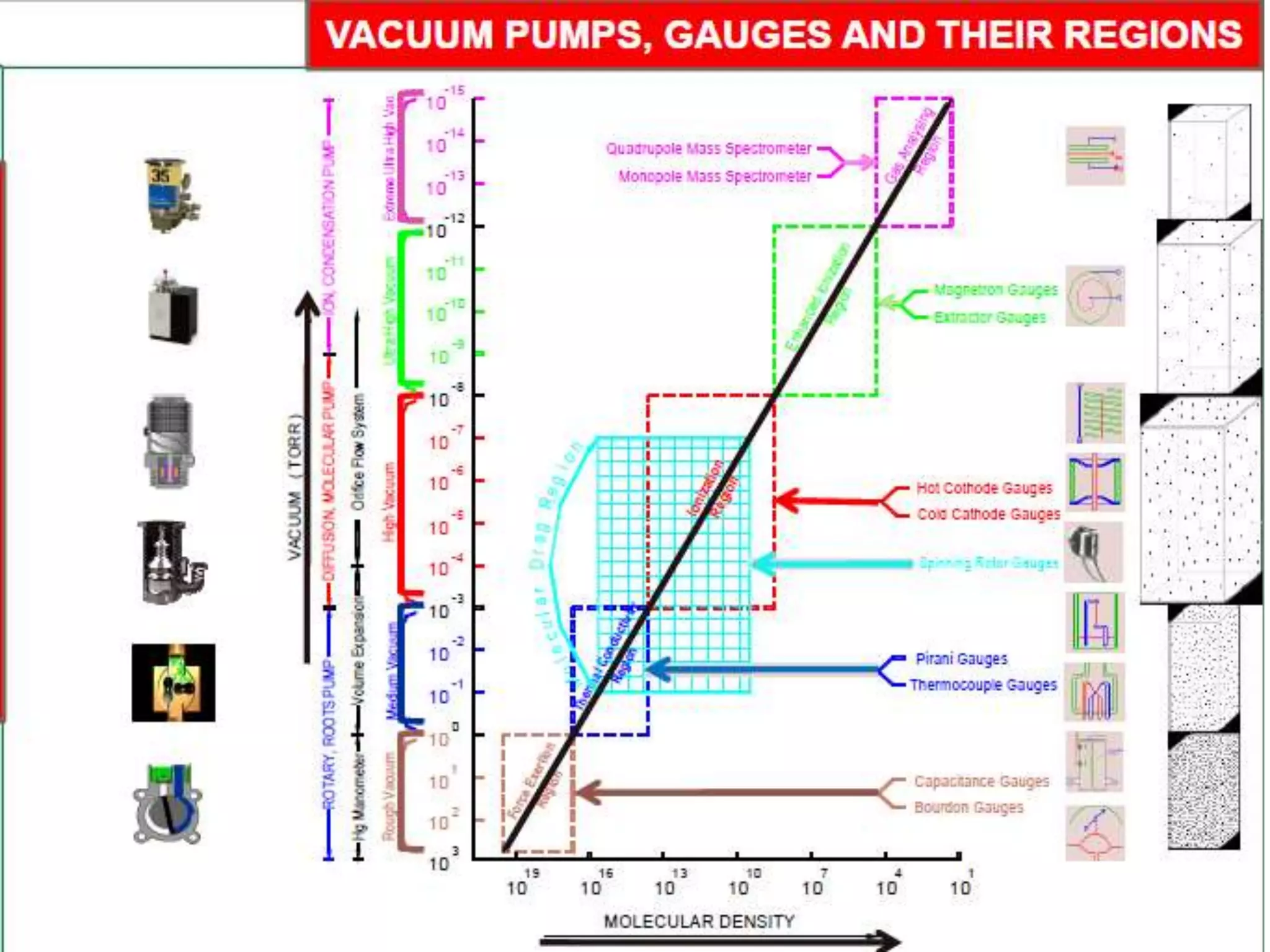
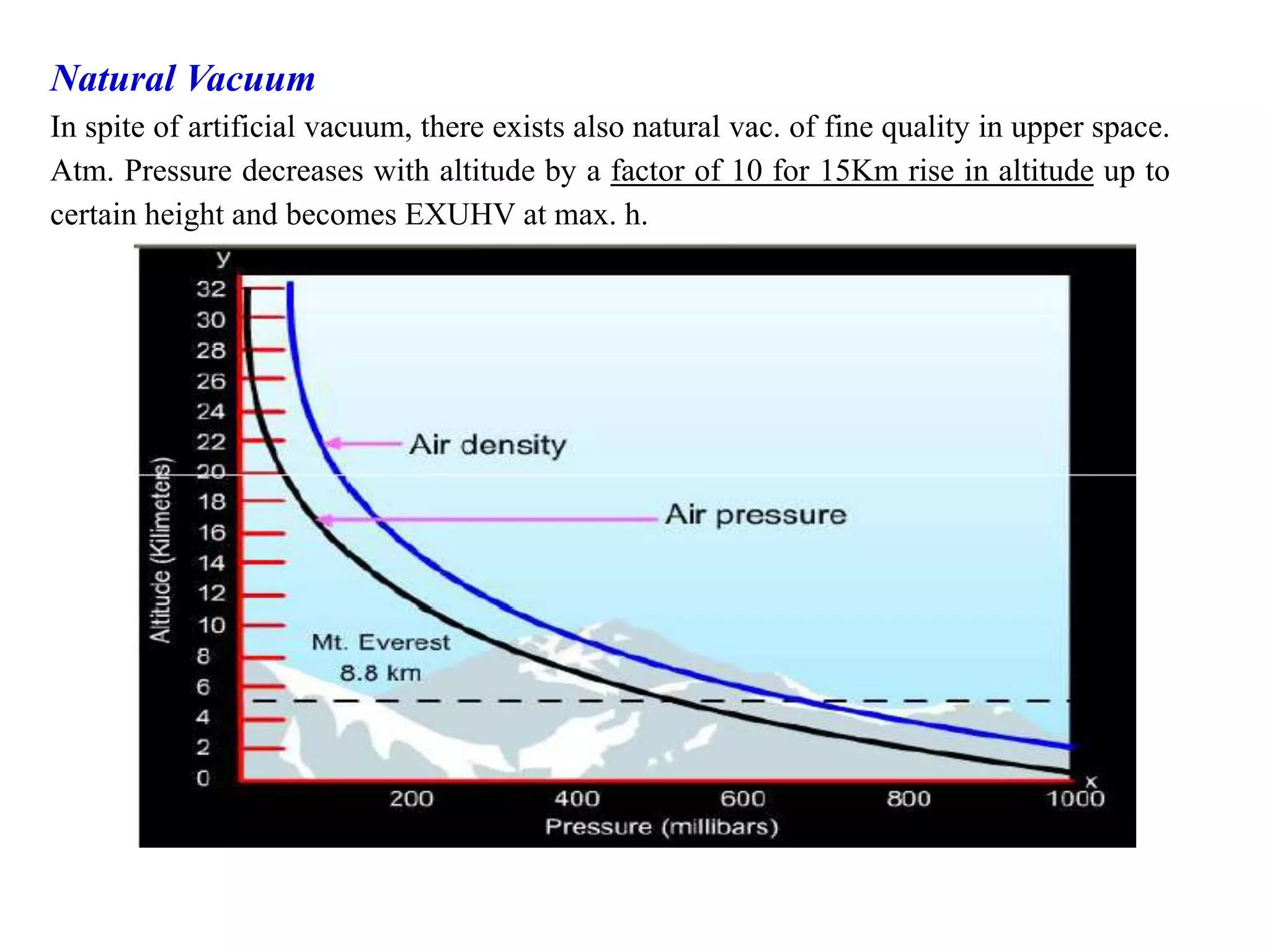
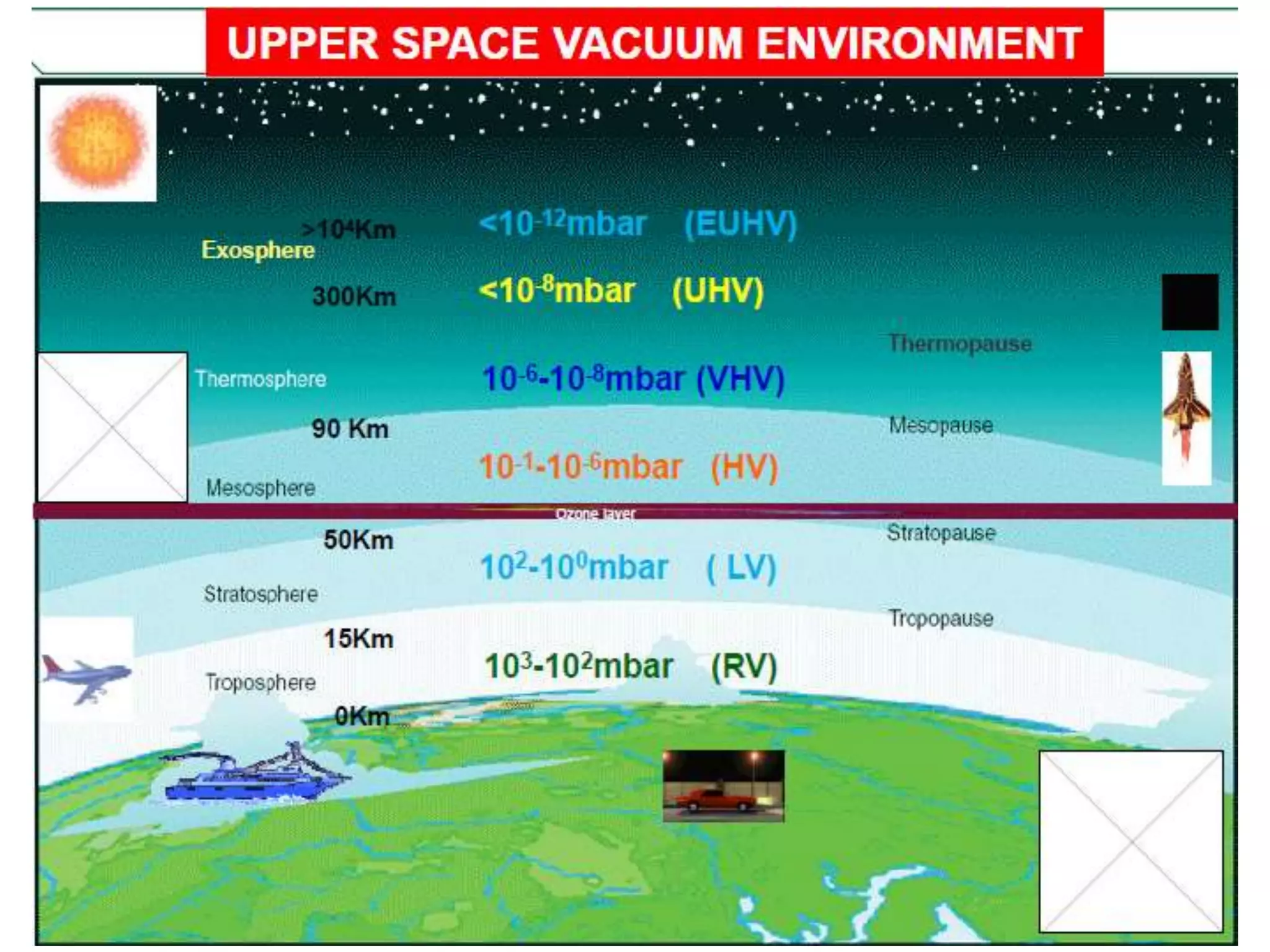
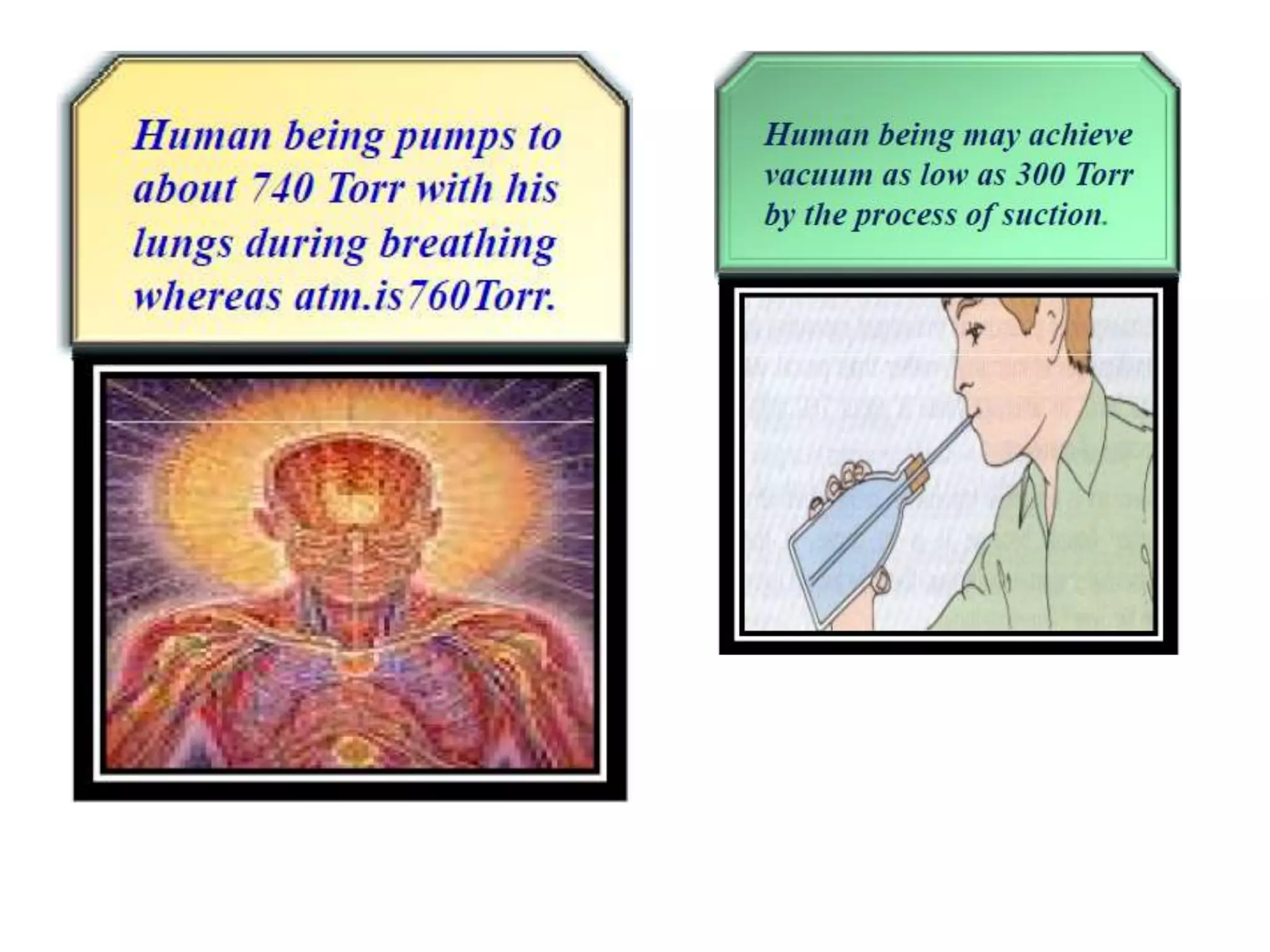
This document provides information about a course on Vacuum Metallurgy taught by Engr. Muhammad Ali Siddiqui. It includes details about the instructor's qualifications, an outline of course topics such as different types of vacuum, vacuum measurement devices, vacuum applications in materials processing, and introduction to concepts like natural versus artificial vacuum. The document also provides the course credit hours, sessional marks distribution which includes attendance, tests, assignments, and the breakdown of final marks between sessional and exams.