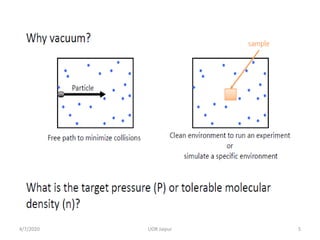
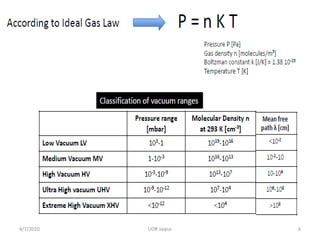
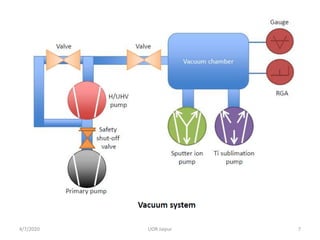
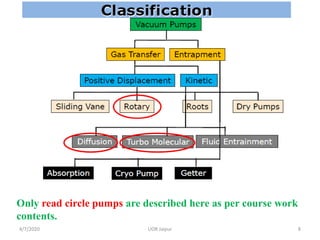
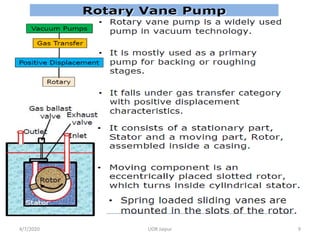
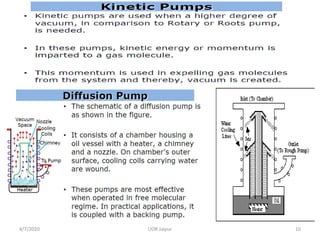
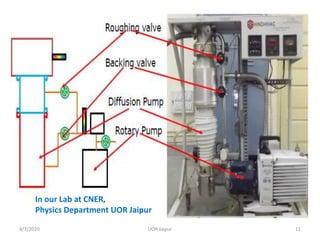
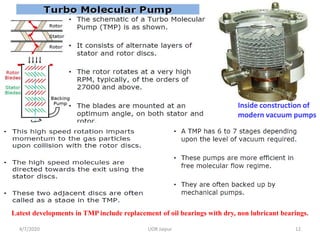
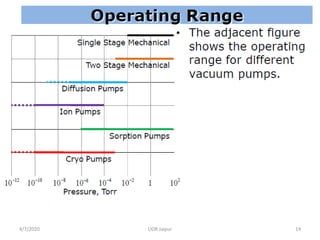
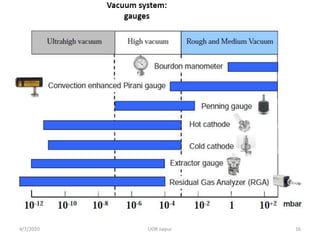
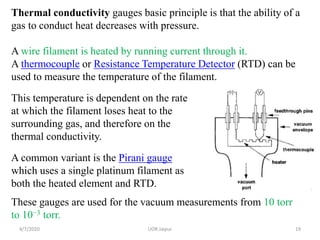
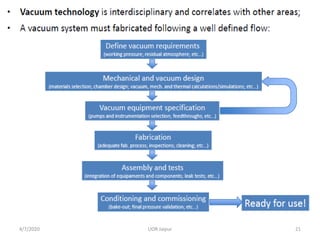
This document discusses experimental techniques for vacuum technology research. It begins by defining vacuum and describing how vacuum can be produced in the laboratory using a mercury test tube and glass container. It then discusses different types of vacuum pumps used to create vacuum, including rotary vane pumps and turbomolecular pumps. The document outlines various vacuum measurement techniques like mechanical gauges, thermal conductivity gauges, and ionization gauges and how they work in different pressure ranges from atmospheric pressure down to ultra-high vacuum. It concludes by thanking the reader for their time and inviting feedback to improve the presentation.