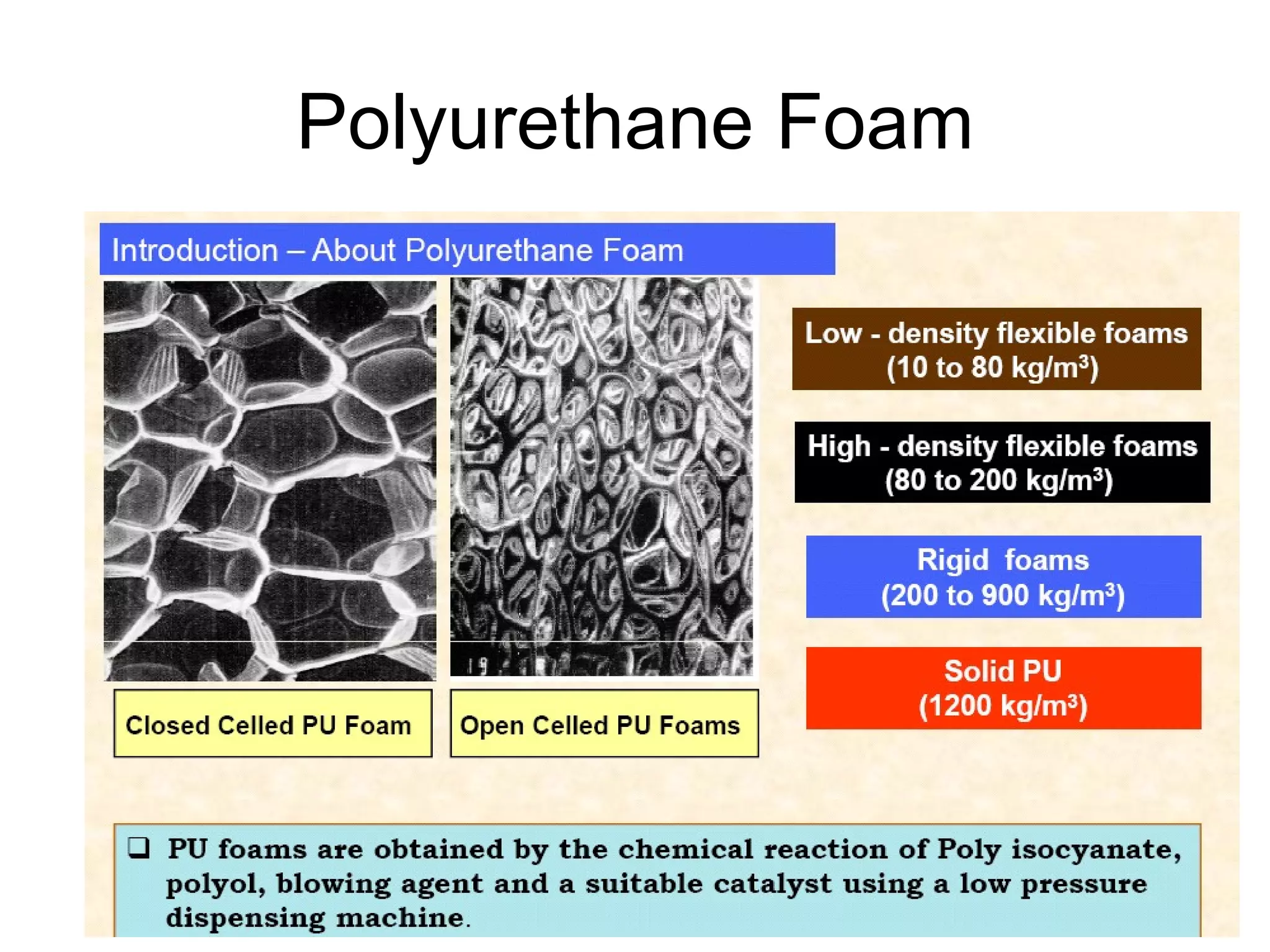
1. Metallic foam is a cellular metallic material with a porous structure and lower density than solid metal.
2. Metal foams are prepared using a liquid metallurgy route where a foaming agent is added to a metal melt, releasing gases during solidification to form pores. Common foaming agents include titanium hydride, zirconium hydride, calcium carbonate, and sodium carbonate.
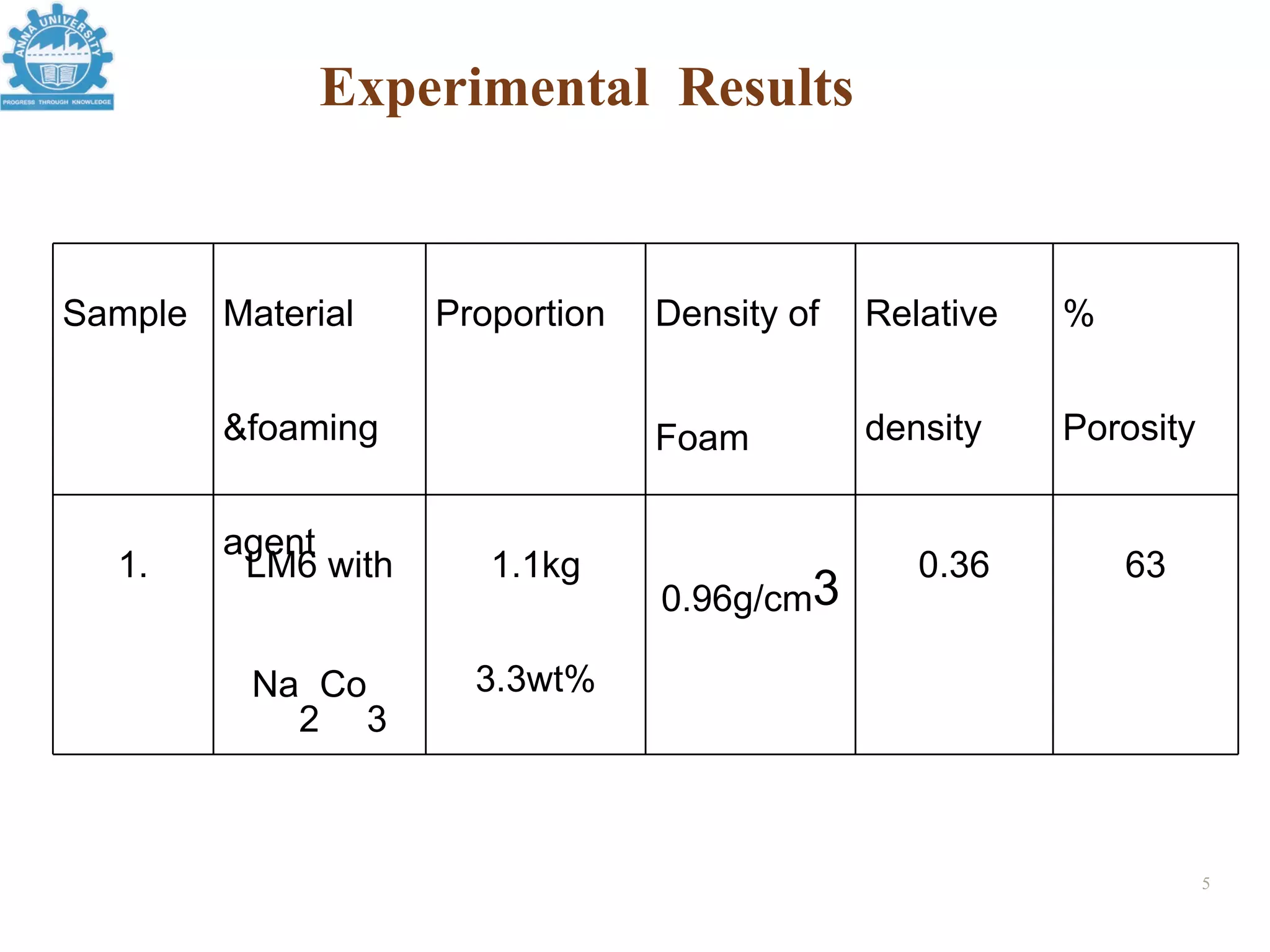
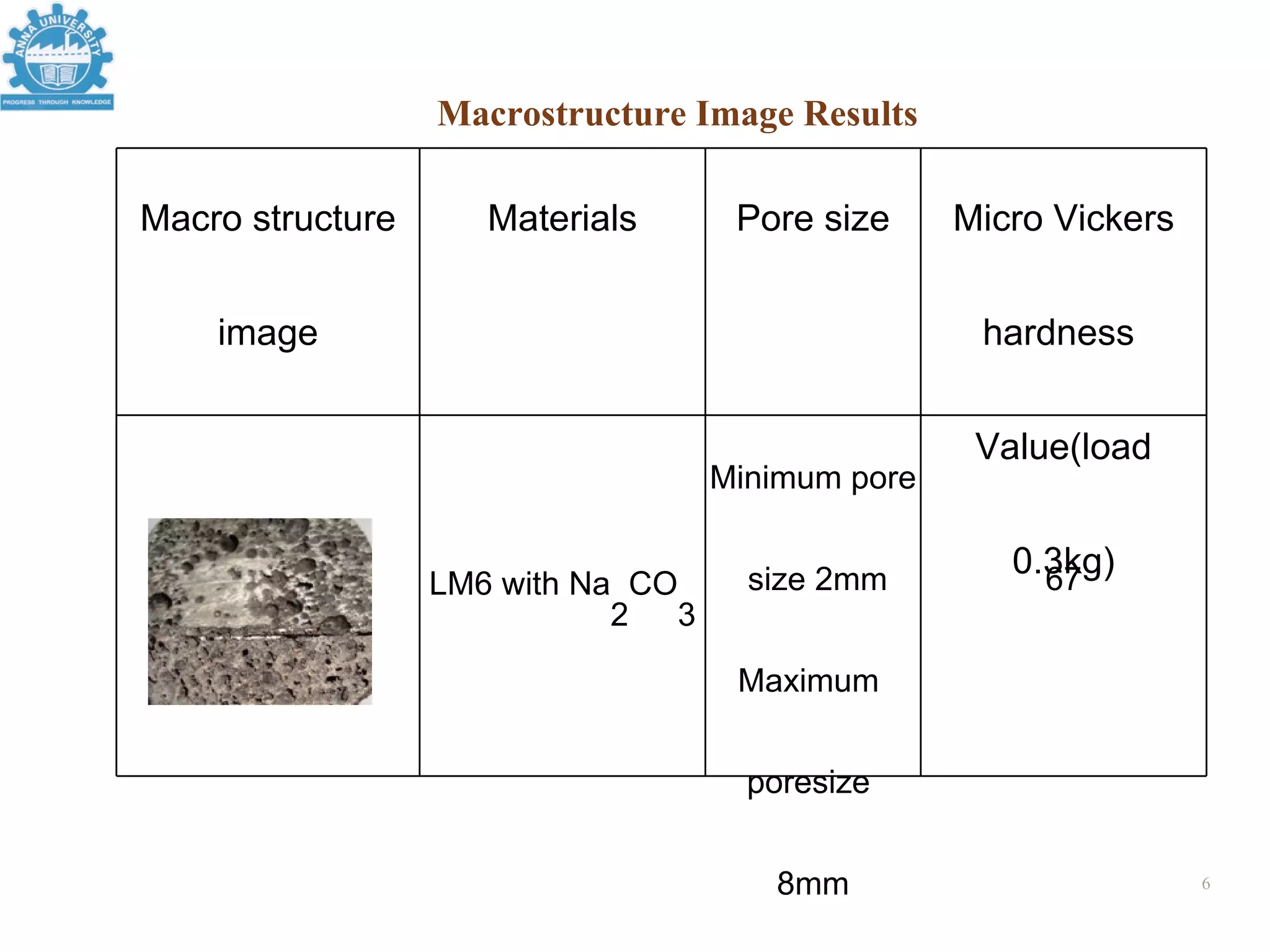
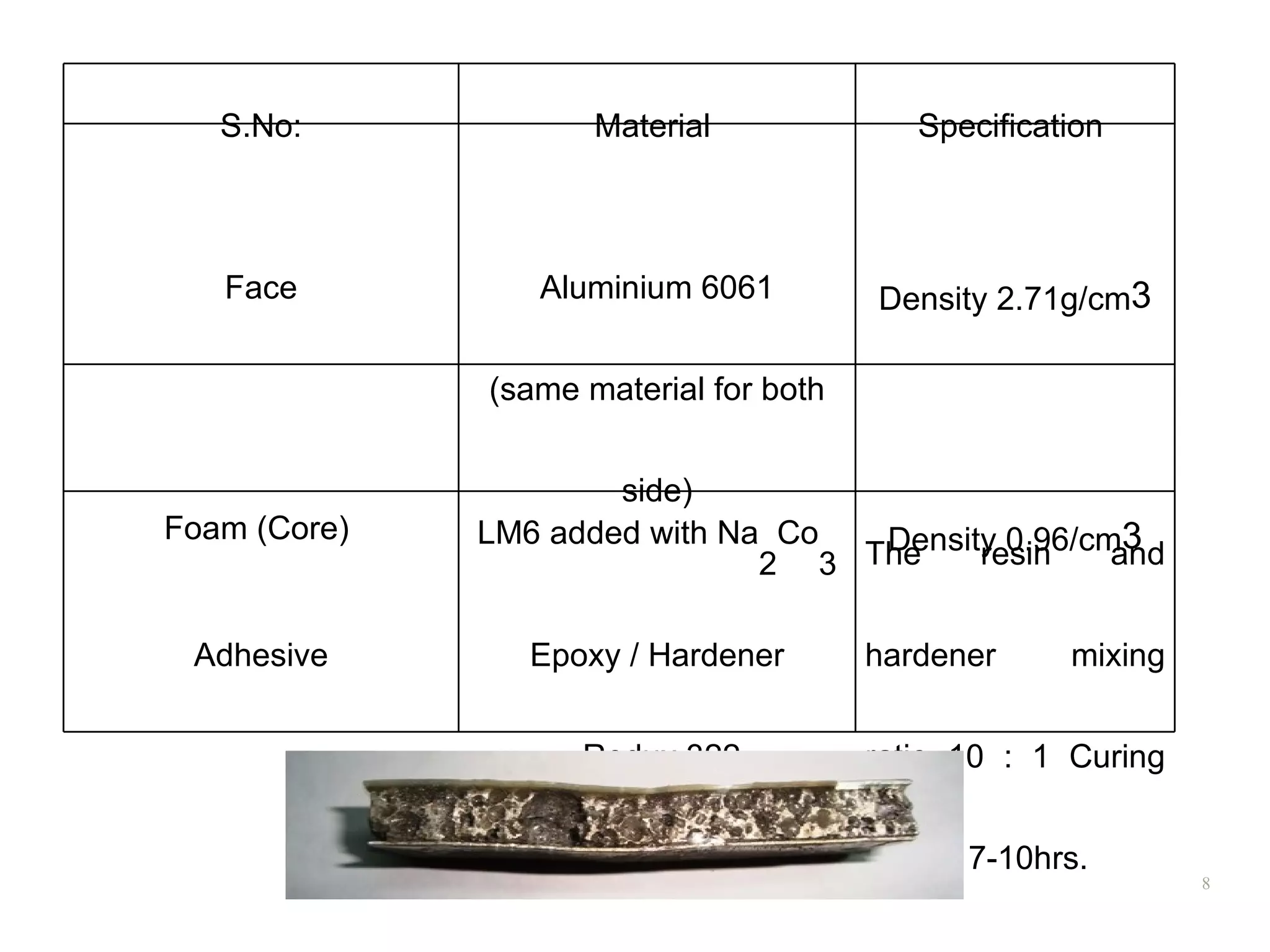
3. An example process uses an aluminum alloy melt with 3.3% sodium carbonate as the foaming agent, producing a foam with 63% porosity and a density of 0.96 g/cc.