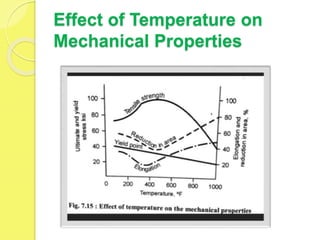
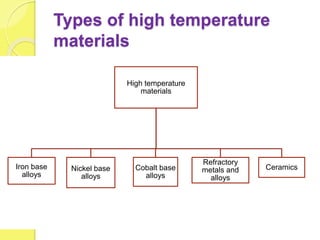
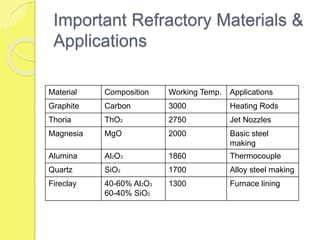
This document discusses the mechanical properties and types of high-temperature materials used in engineering, including iron, nickel, and cobalt-based alloys, as well as refractory ceramics. It highlights the importance of these materials in high-temperature applications due to their resistance to oxidation, corrosion, and creep. Additionally, it outlines the composition and specific applications of various refractory and ceramic materials.