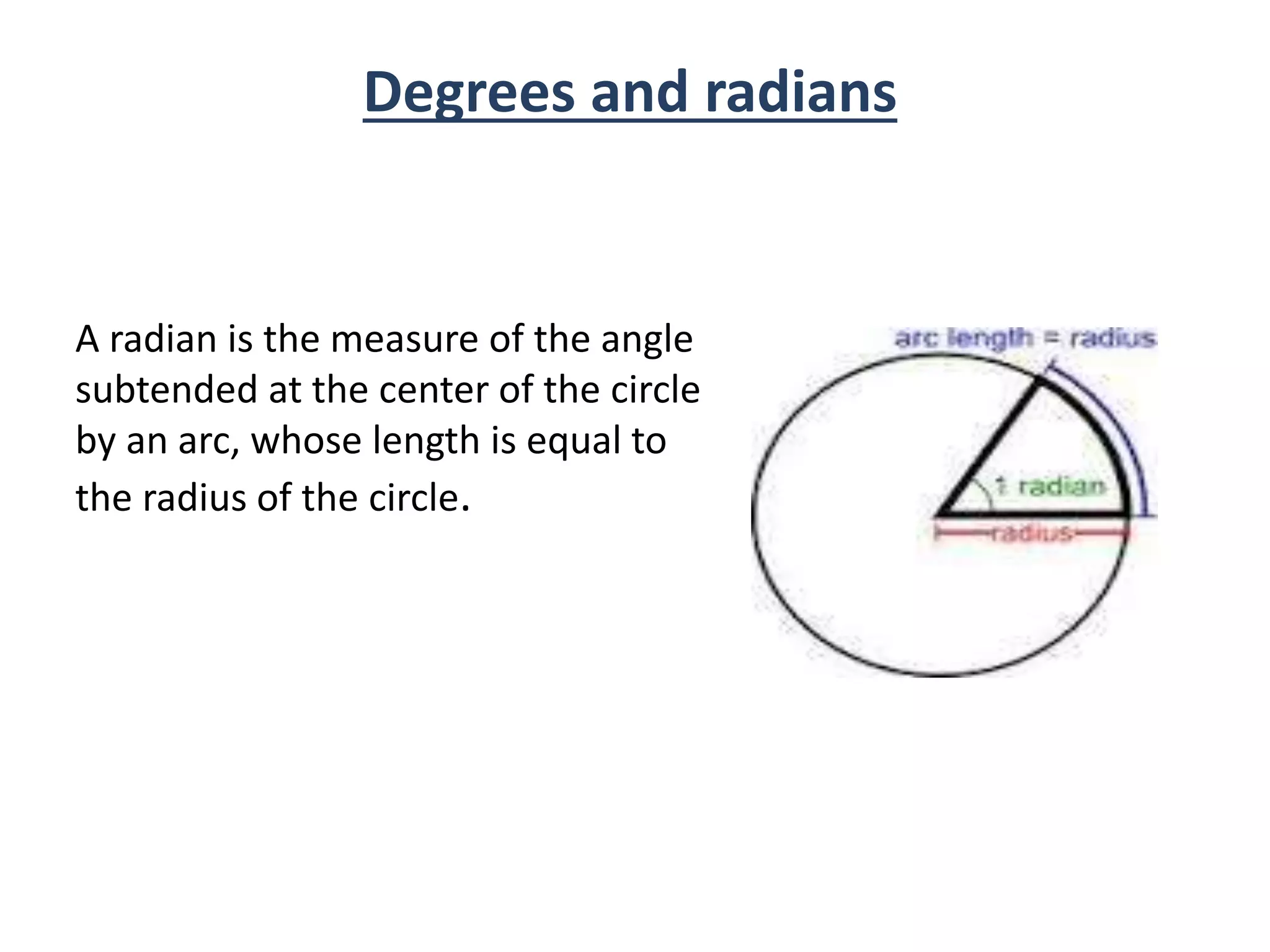
This document introduces trigonometry, including:
- Trigonometry is the measurement of triangles and the relationship between sides and angles, derived from Greek words meaning "three", "angles", and "measurement".
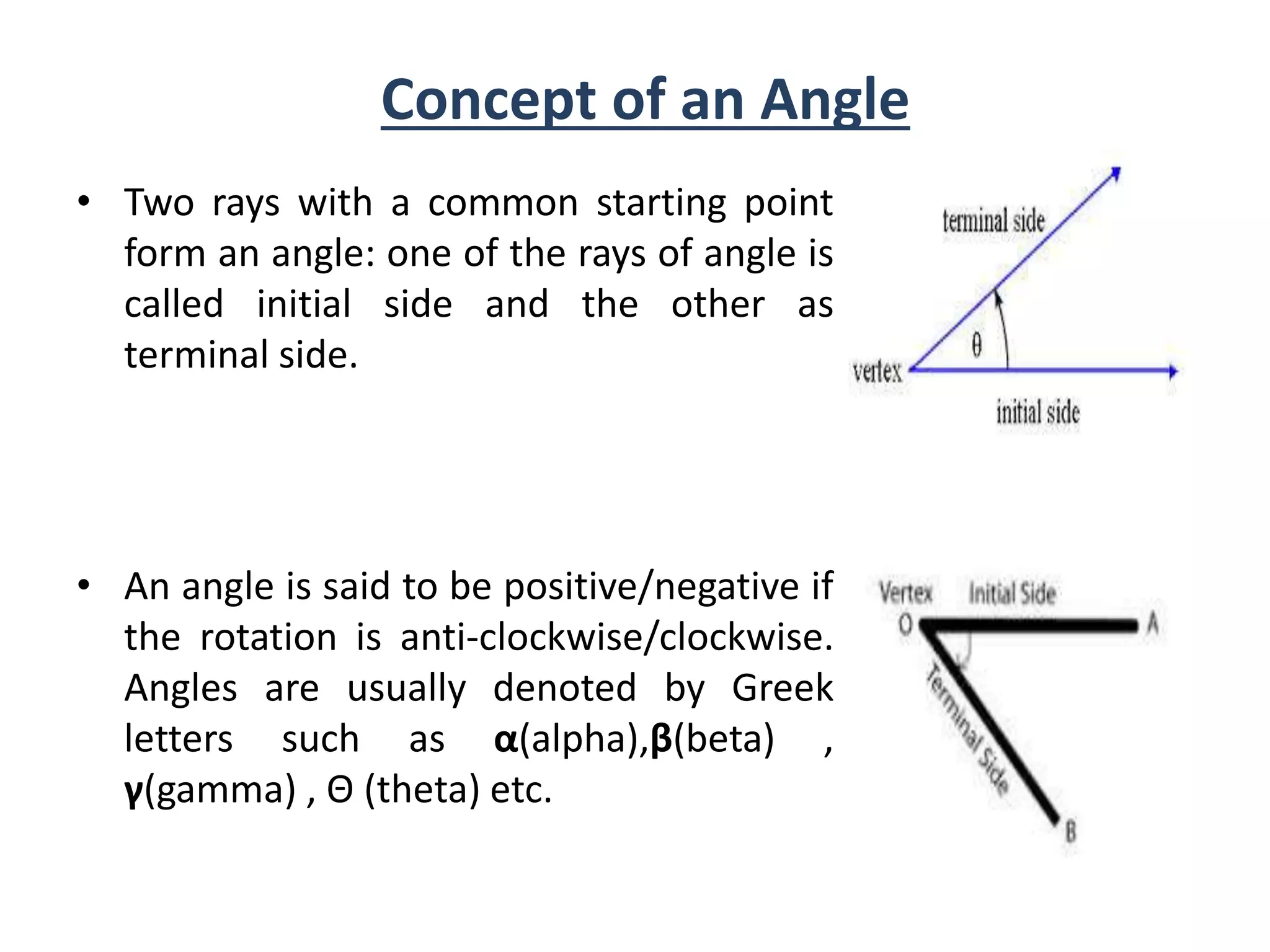
- Angles are formed by two rays with a common starting point and can be positive or negative depending on direction of rotation.
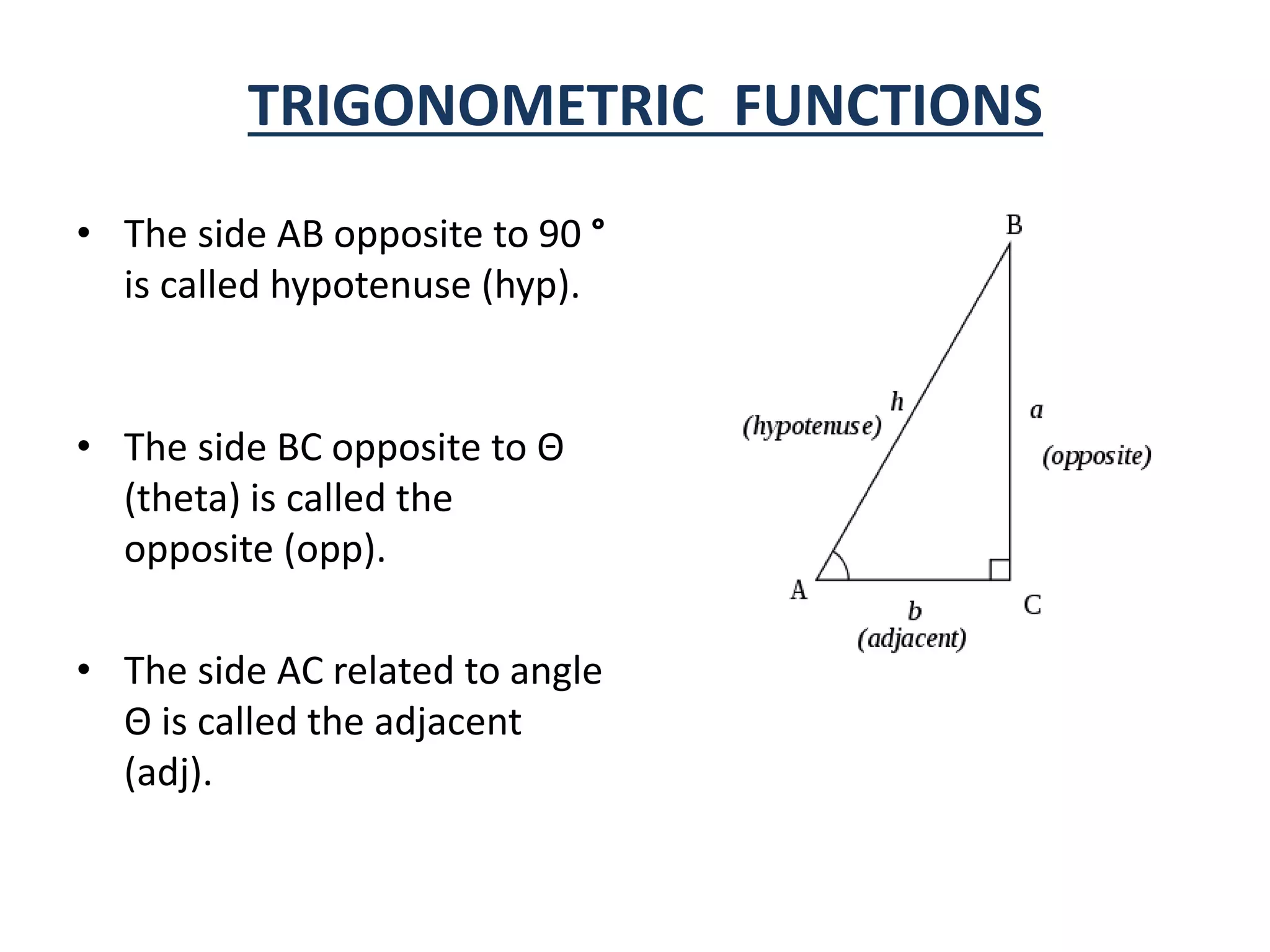
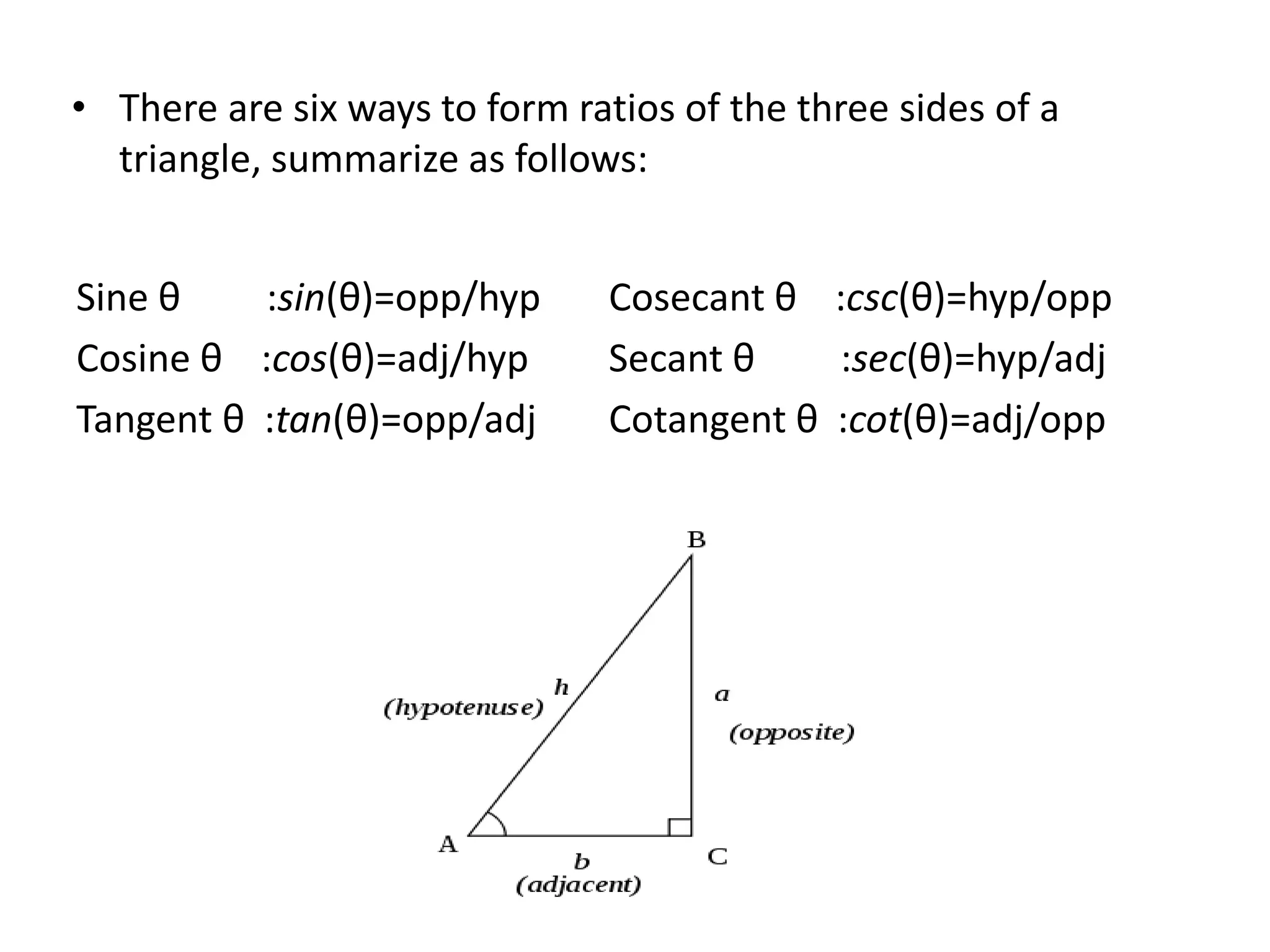
- Trigonometric functions relate ratios of sides of a right triangle to an angle and include sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant.
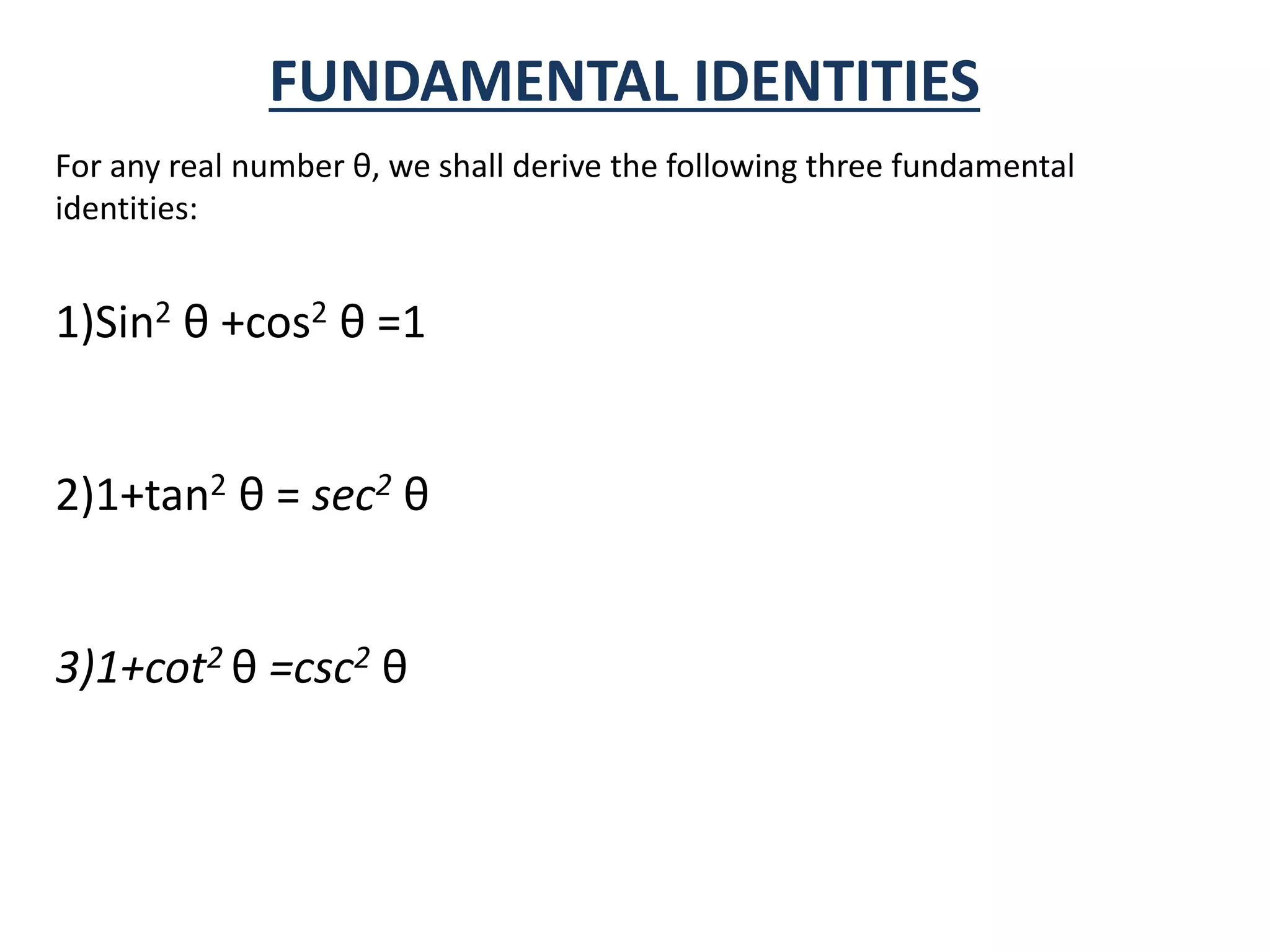
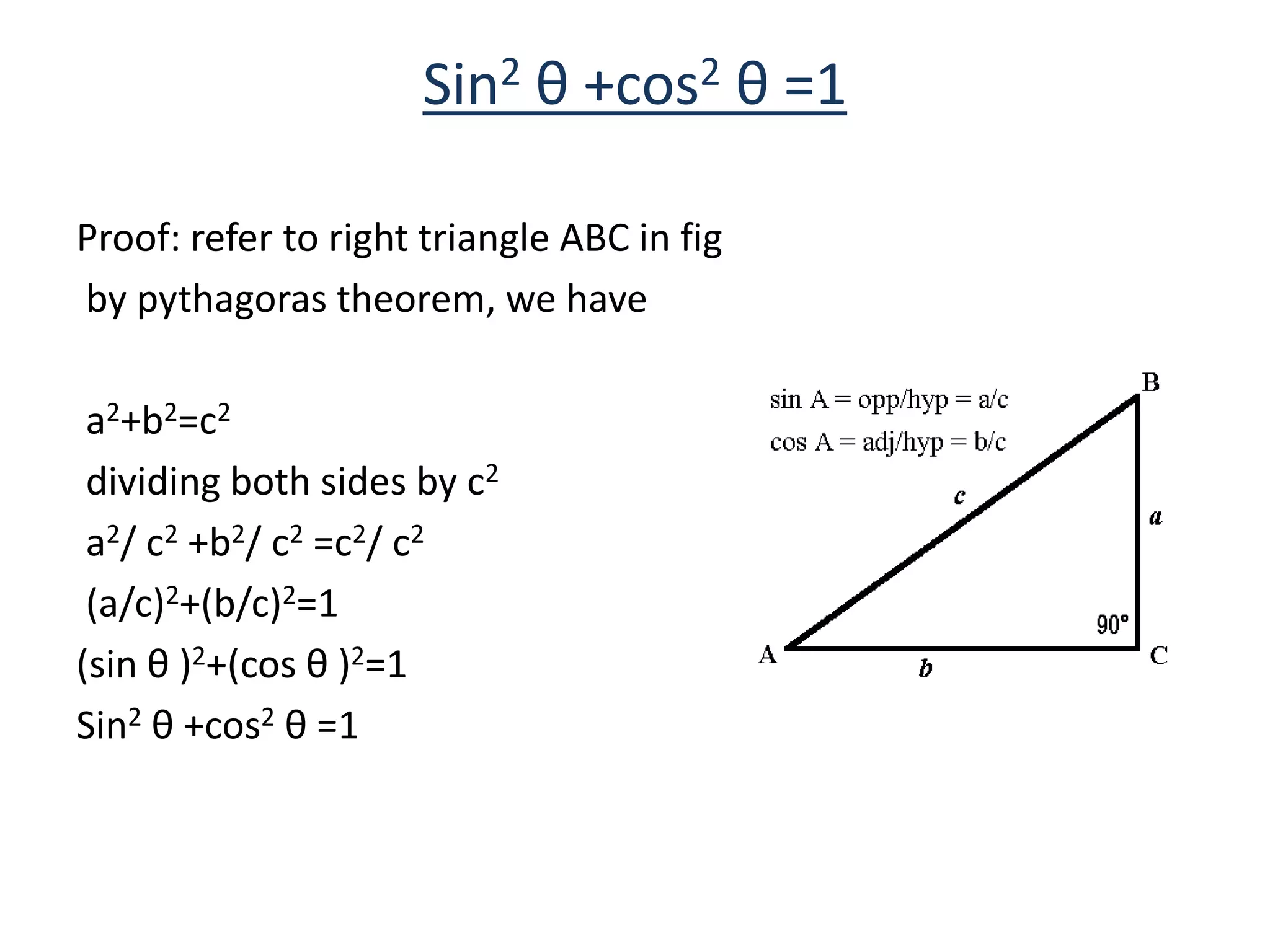
- Fundamental trigonometric identities are derived, including that sine squared plus cosine squared equals one.