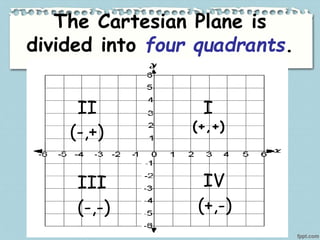
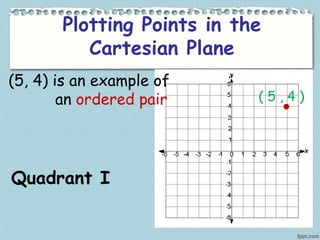
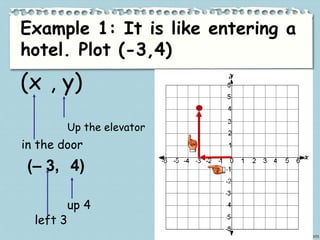
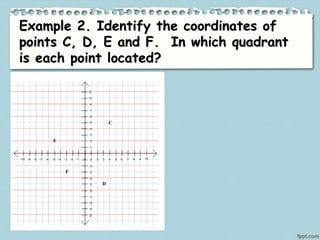
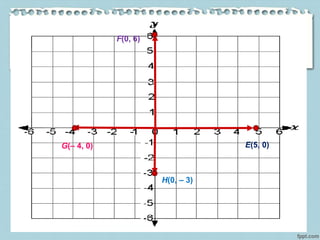
This document provides information about various landmarks and their locations: Rizal Park in Manila, New York City in the USA, the Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Merlion in Singapore, and the Basilica of Saint Peter in Rome. It then instructs the reader to locate each of these places on a map according to their latitude and longitude. The document explains how Cartesian coordinates use a grid system with x and y axes to precisely locate points on a plane or map. It provides examples of plotting points in the Cartesian plane's four quadrants and identifying points' coordinates. The document distinguishes between points that lie within the quadrants versus along the axes. It concludes with an activity asking the reader to identify quadrant locations for