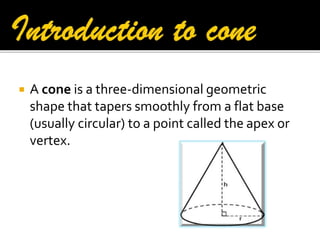
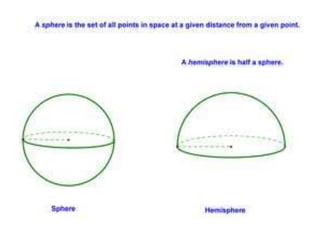
1. The document defines various 3D shapes including cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and hemispheres.
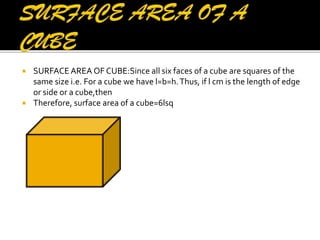
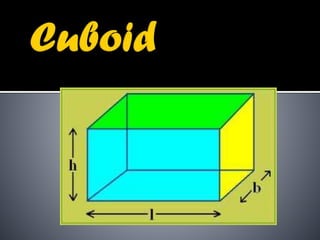
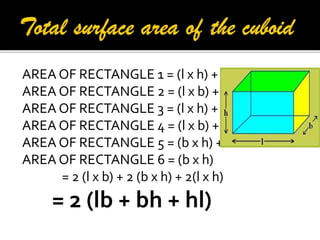
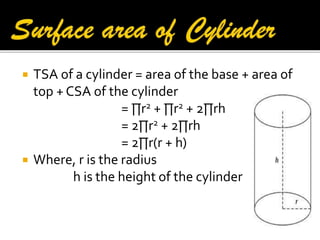
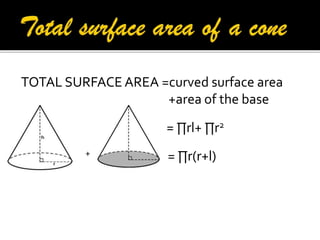
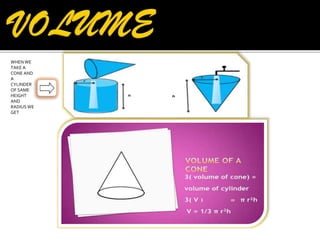
2. It provides the formulas to calculate the surface area and volume of each shape. For cubes, cuboids, cylinders and cones it gives the formulas for total surface area. For spheres and hemispheres it provides the formulas for total surface area, curved surface area, and volume.
3. The document was created collaboratively by several students, with each person responsible for explaining different shapes.