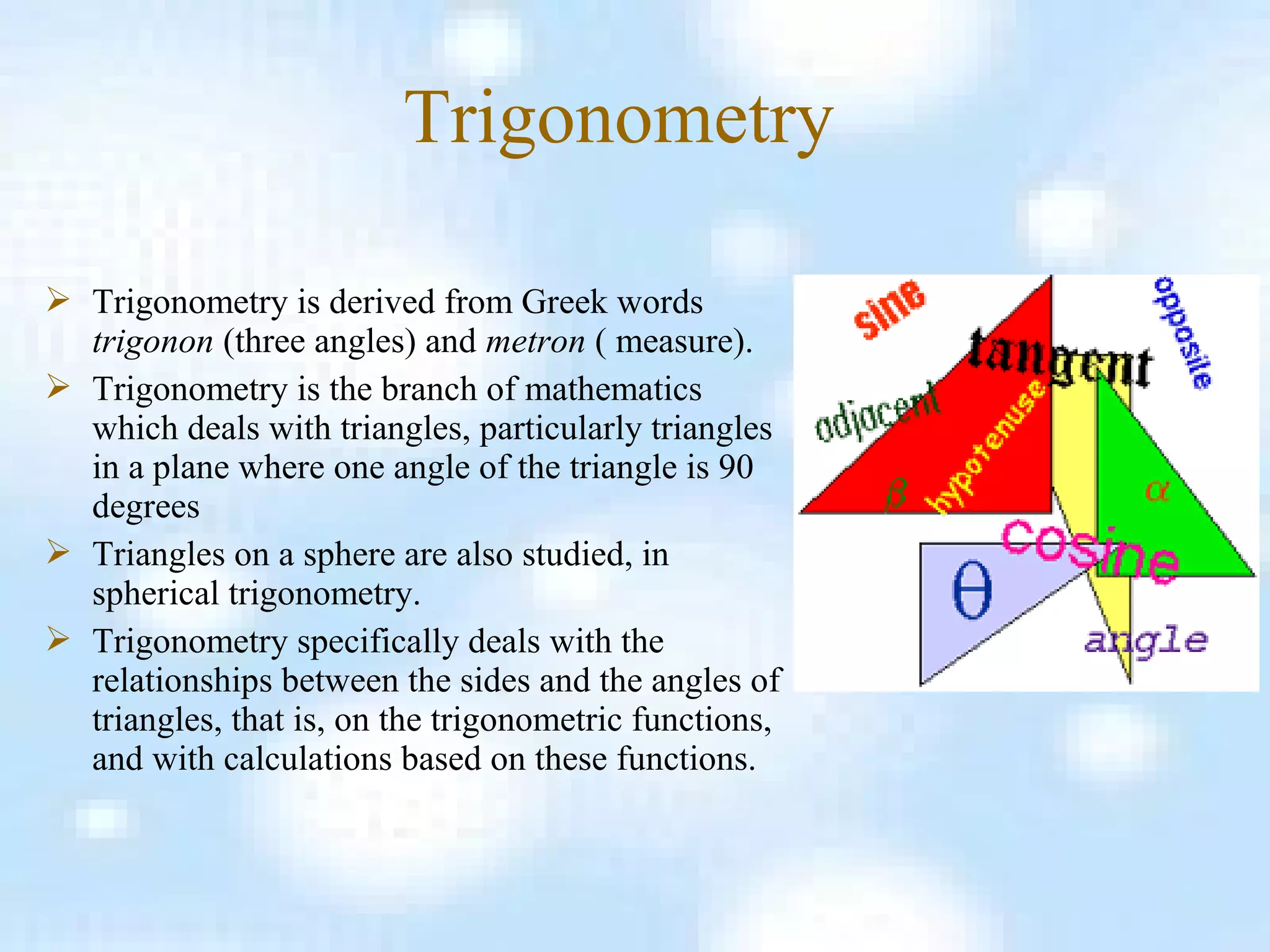
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics focused on the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles, particularly right triangles. It involves concepts such as the Pythagorean theorem and various trigonometric ratios including sine, cosine, and tangent. The document also includes specific values of trigonometric functions for common angles and definitions related to right triangles.