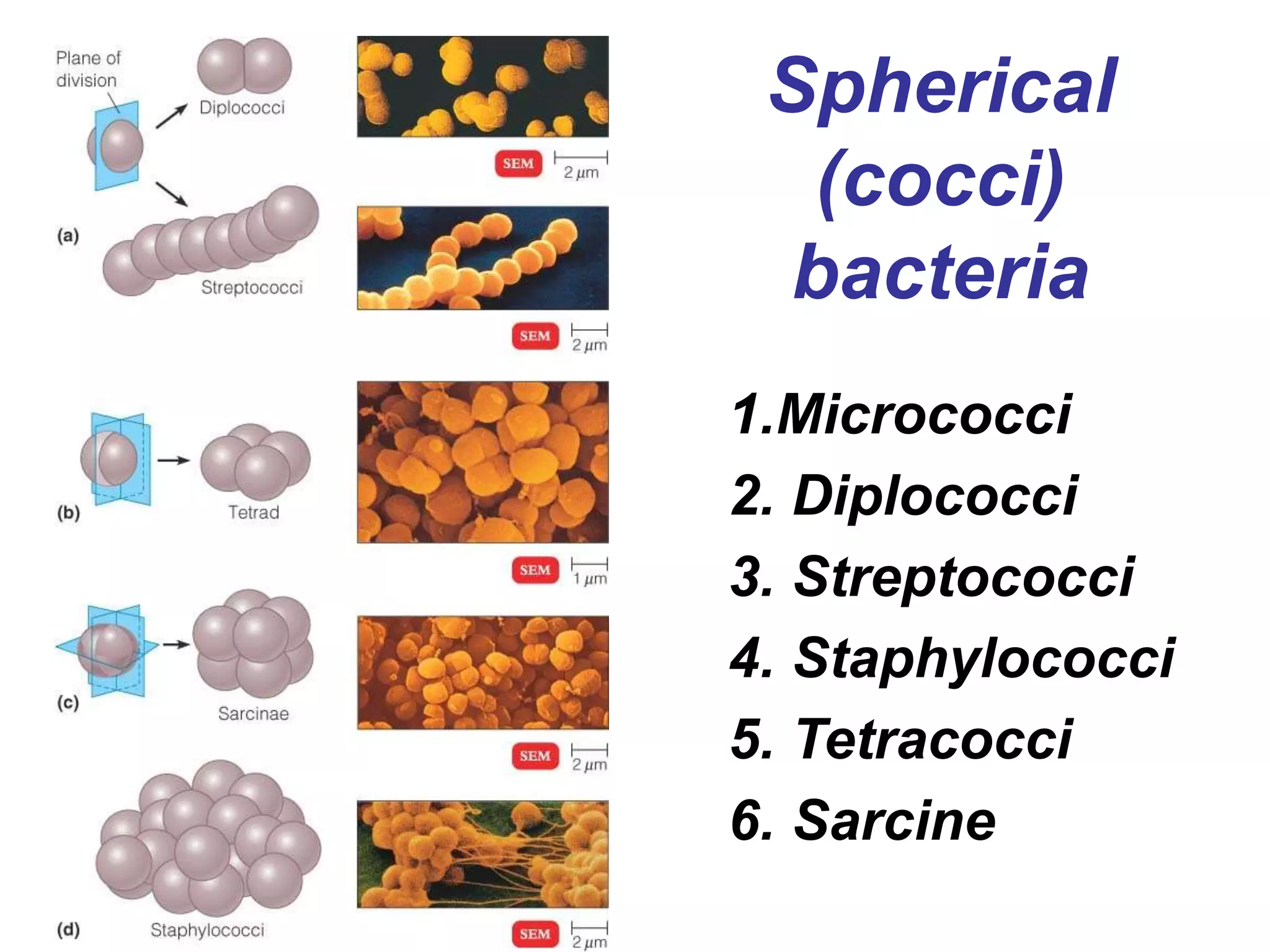
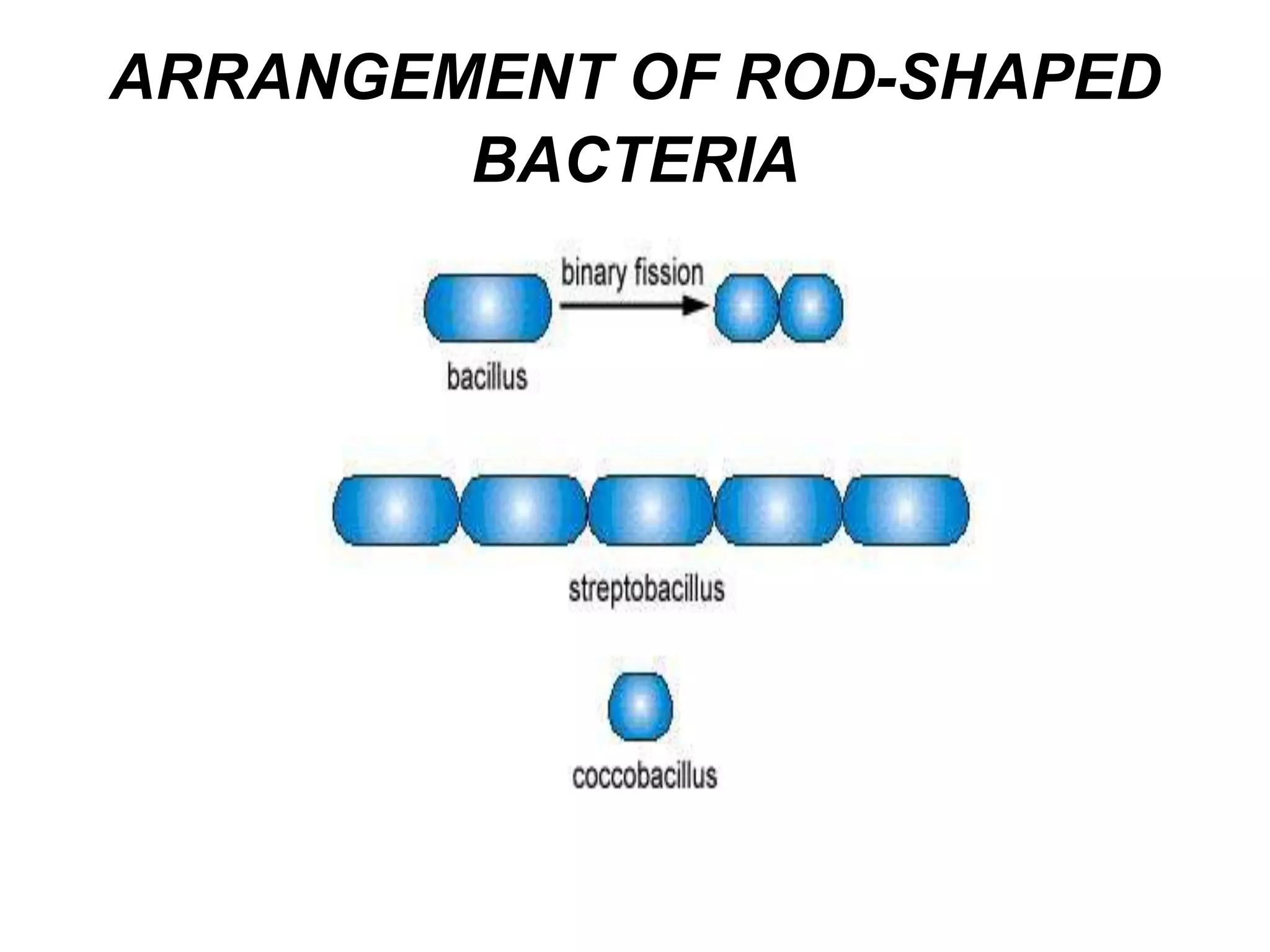
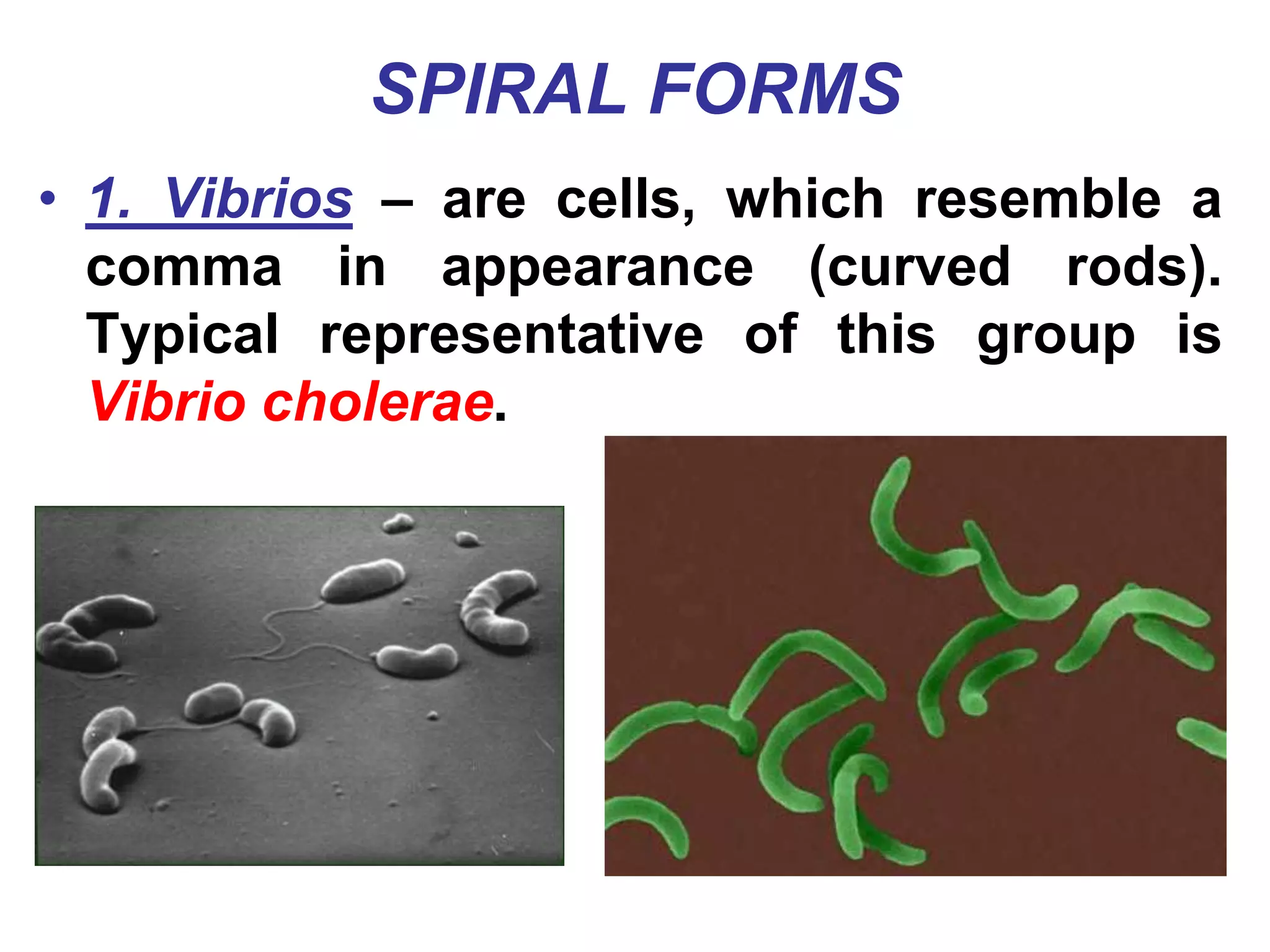
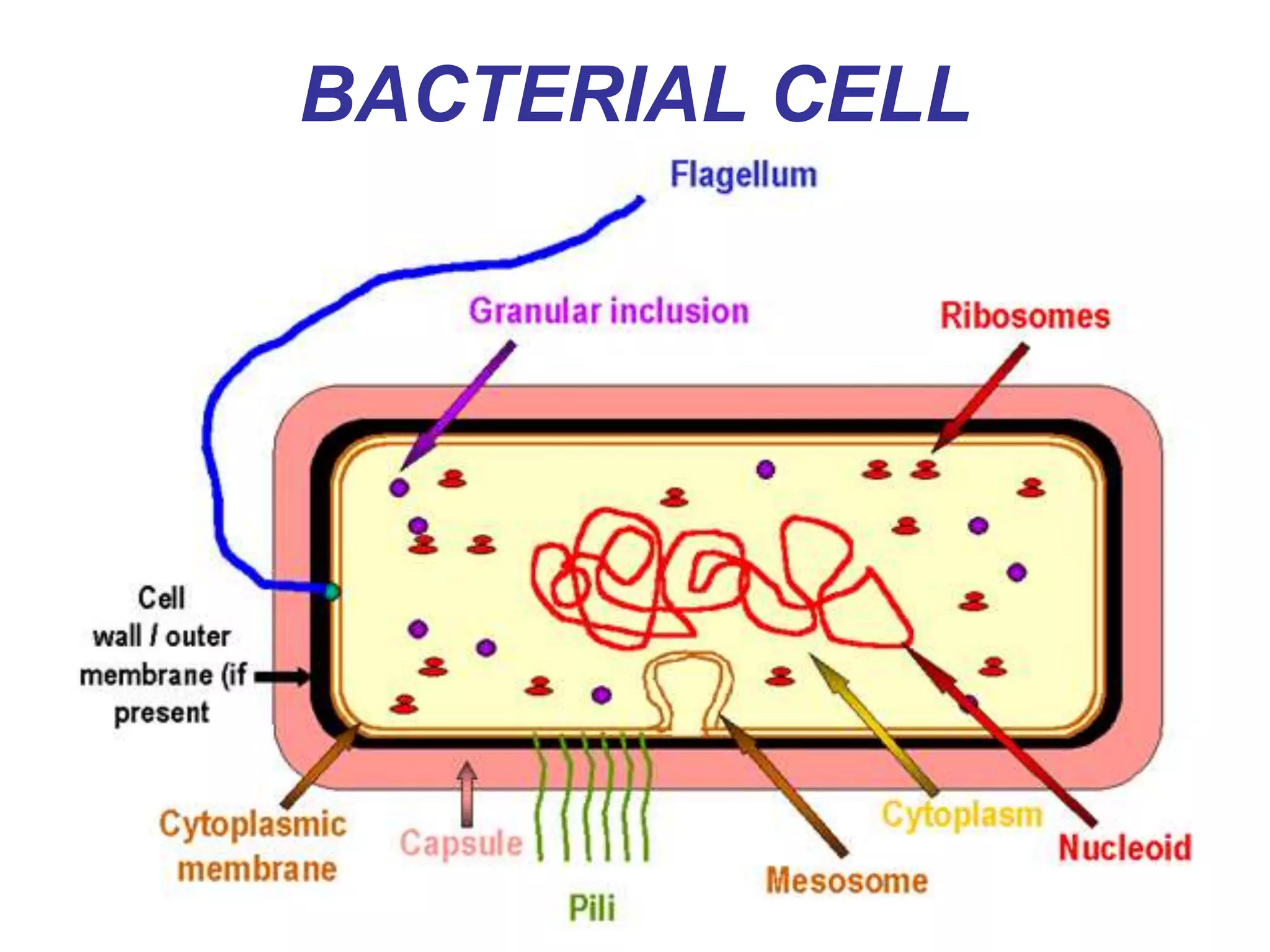
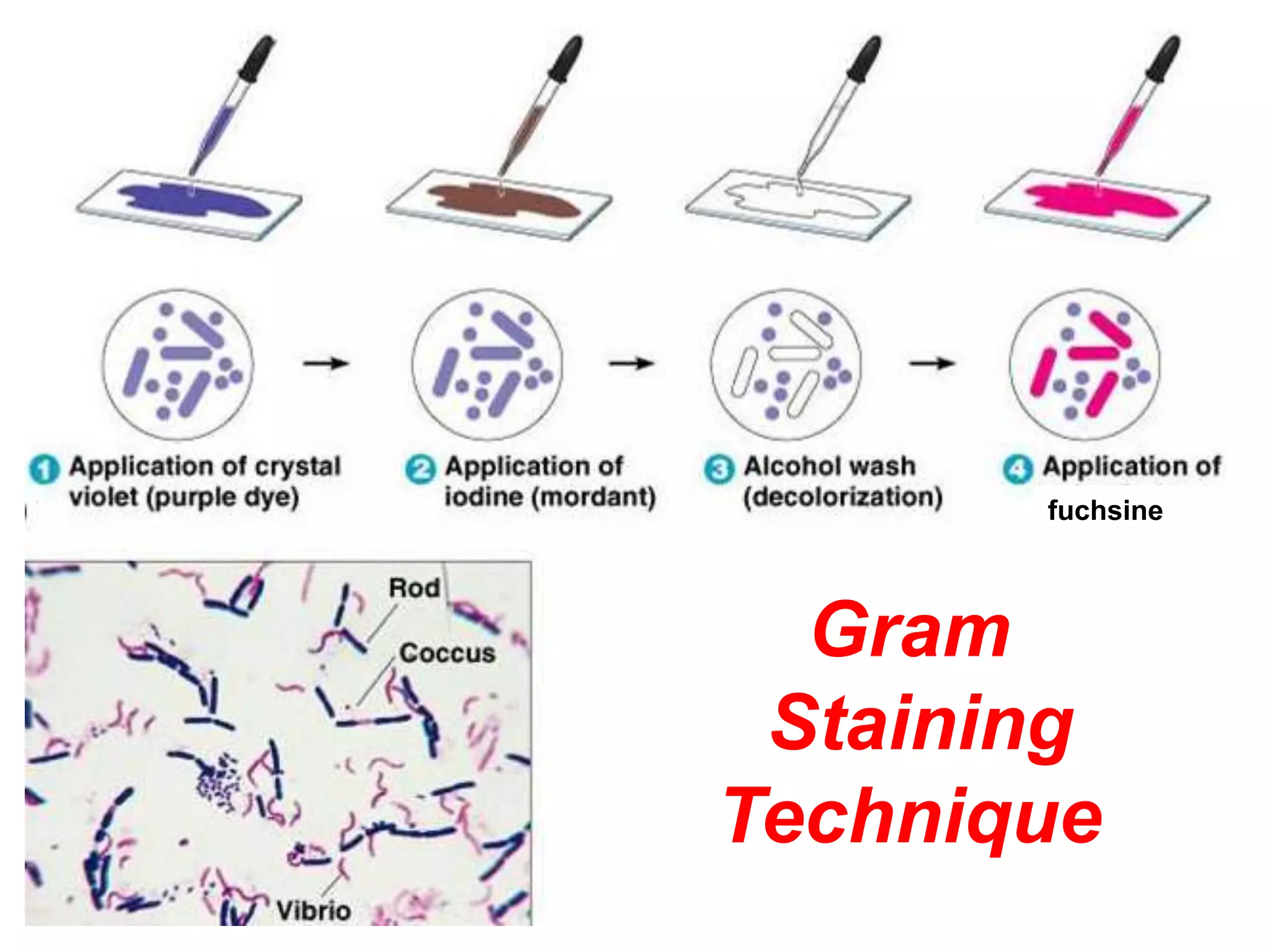
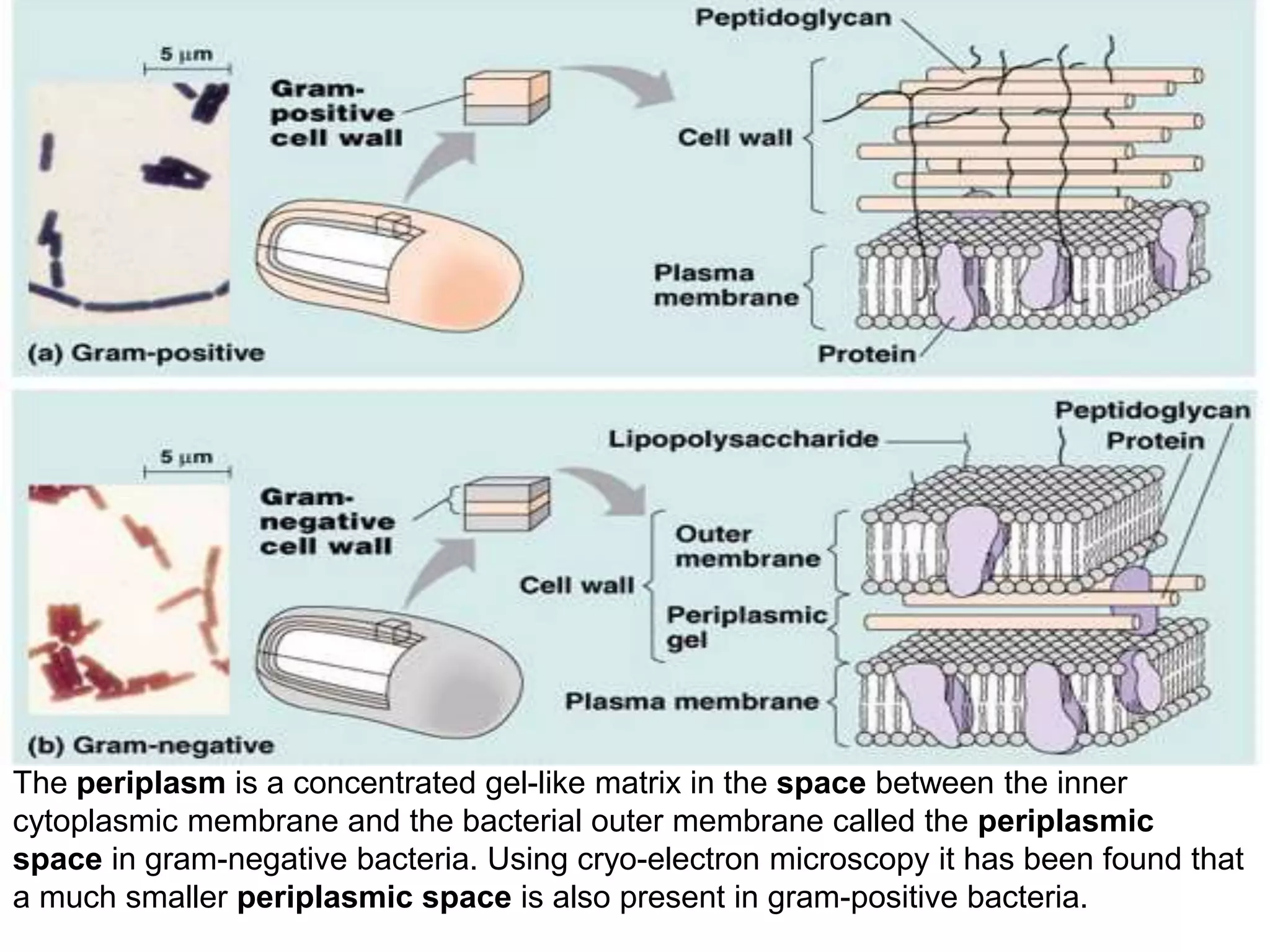
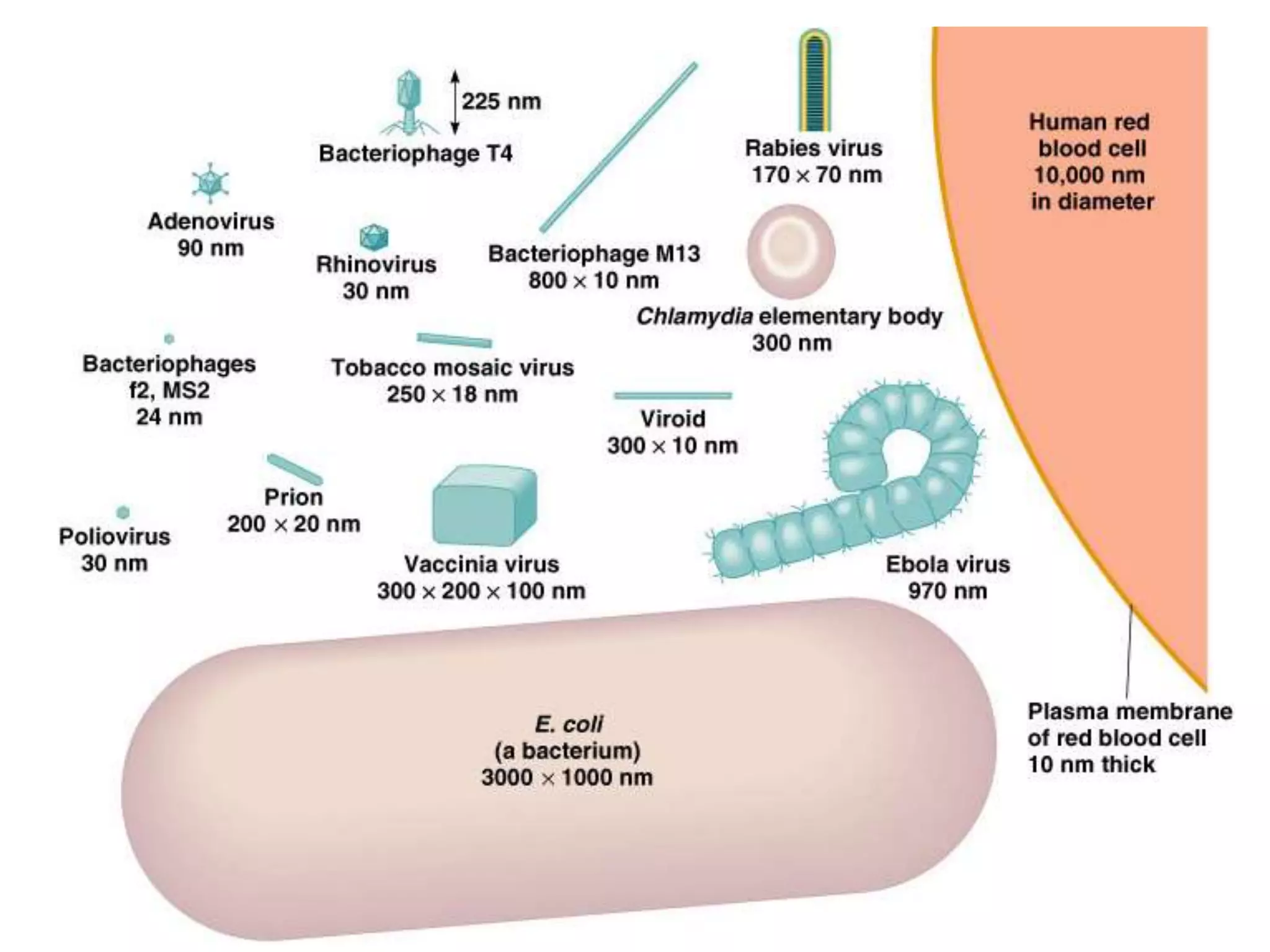
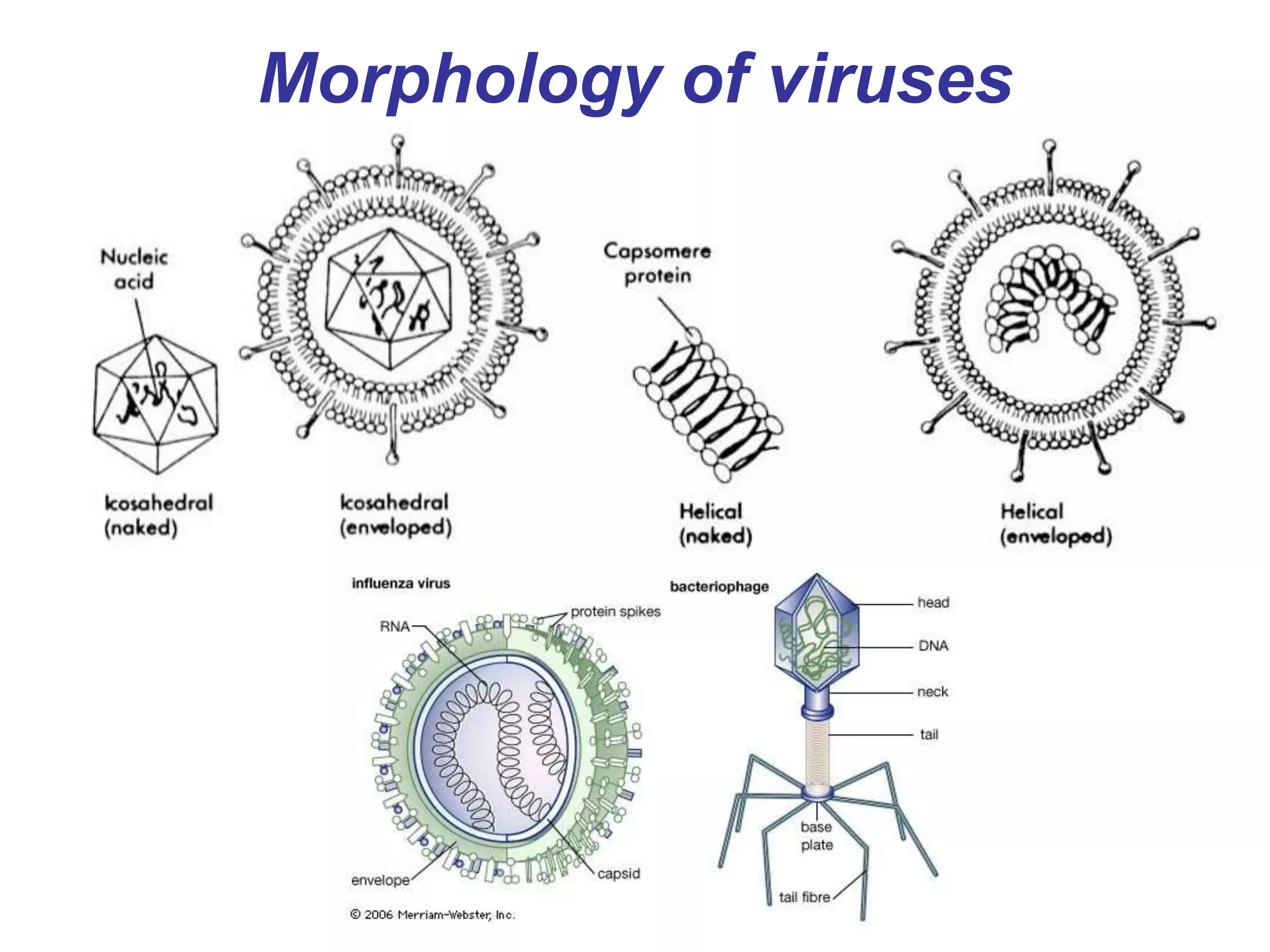
The document provides an overview of medical microbiology, which studies the agents of infectious diseases and their impact on humans. It covers the classification, morphology, and reproduction methods of various microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, rickettsiae, and chlamydia, along with diagnostic laboratory methods. Additionally, it discusses the structure and properties of these microorganisms, including their cellular organization and response to antibiotics.