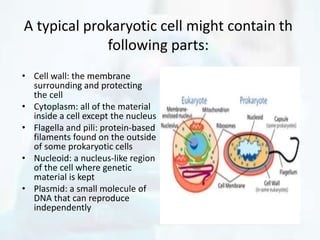
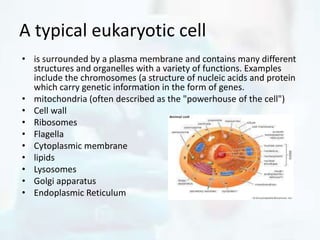
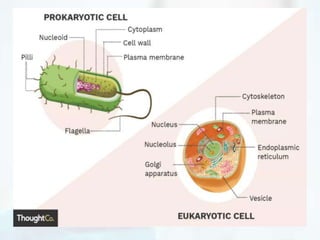
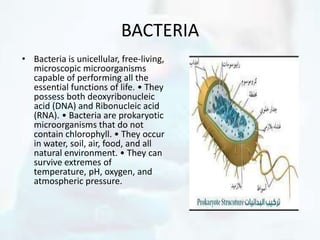
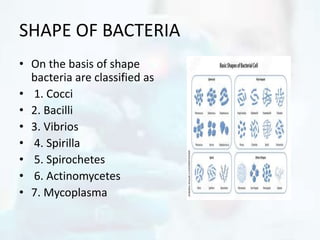
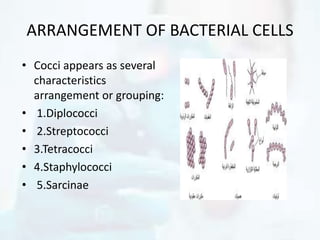
The document explores the morphology and classification of bacteria, detailing the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, with a focus on their structures, reproduction, and biological functions. It also describes various types of bacteria based on shape and arrangement, microscopy techniques for studying bacteria, and staining methods to enhance visibility under a microscope. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview of bacteria's biological characteristics and their role in the environment.