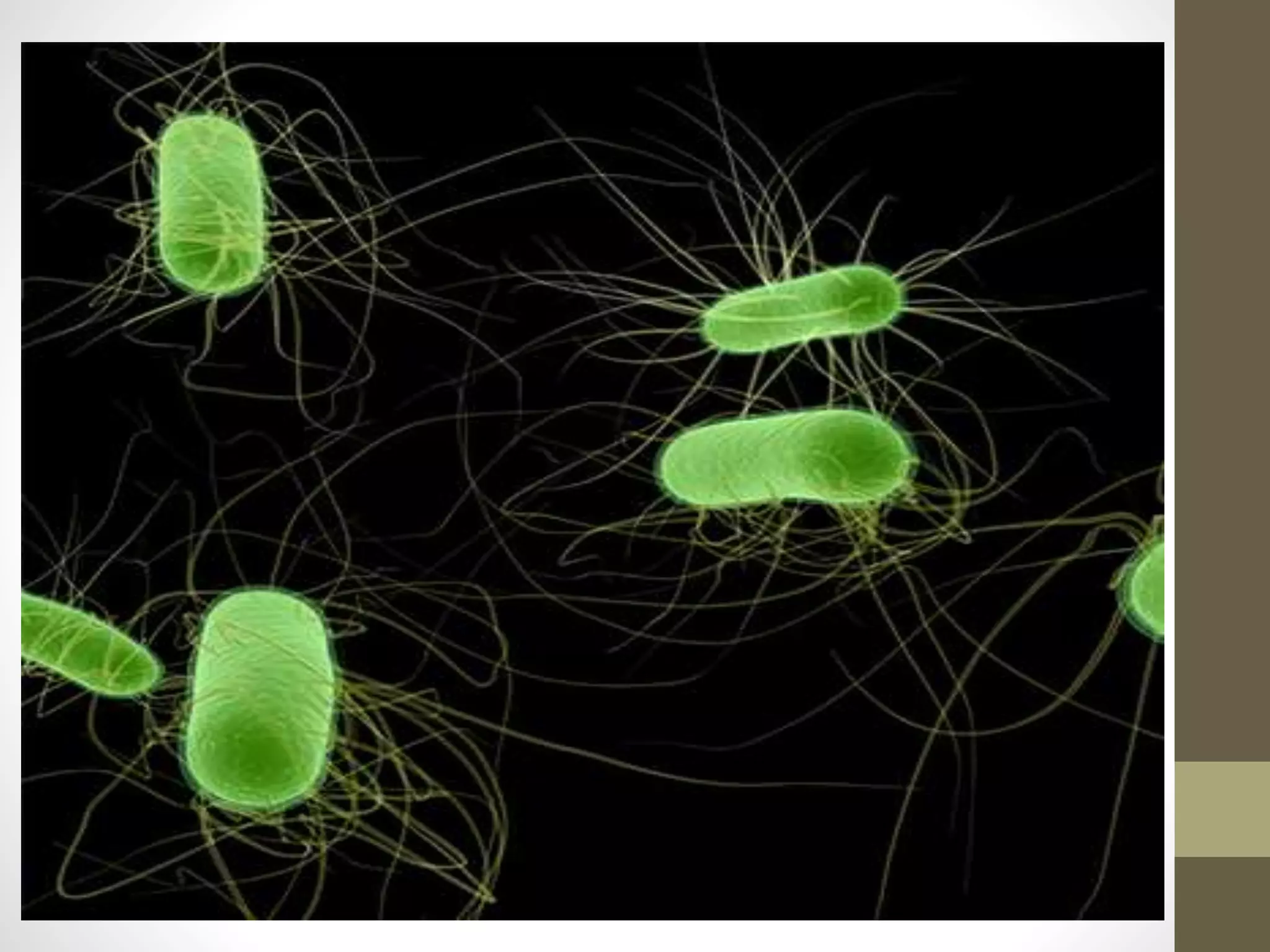
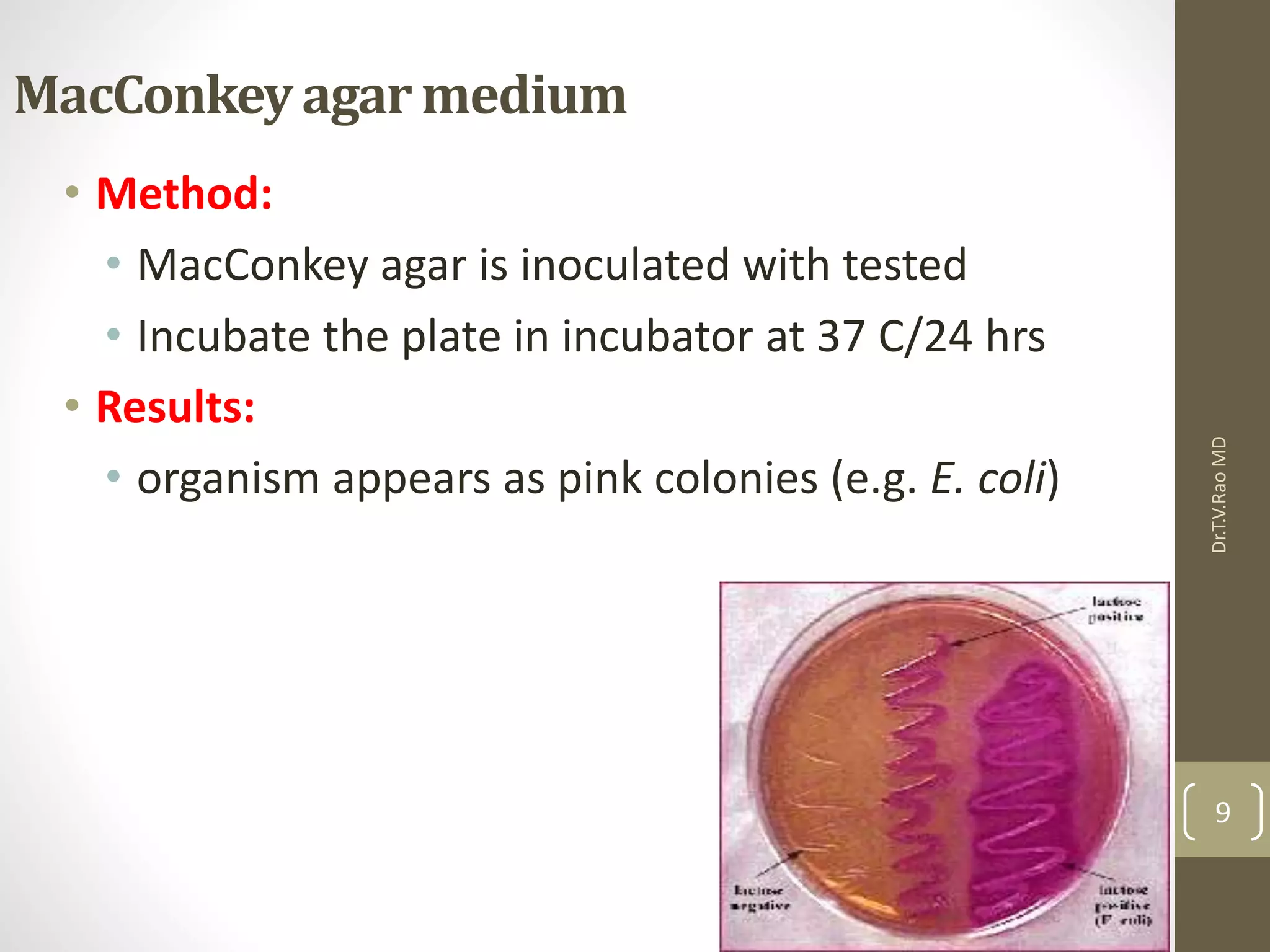
Eschericia coli is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. It can cause several types of infections including urinary tract infections, enteric infections like traveler's diarrhea, and other rare infections. Laboratory diagnosis involves microscopic examination of samples showing gram-negative bacilli, as well as culture-based identification using selective media and biochemical tests to confirm lactose fermentation and other properties. Treatment depends on the severity and type of infection, ranging from supportive care to antibiotics for serious complications.