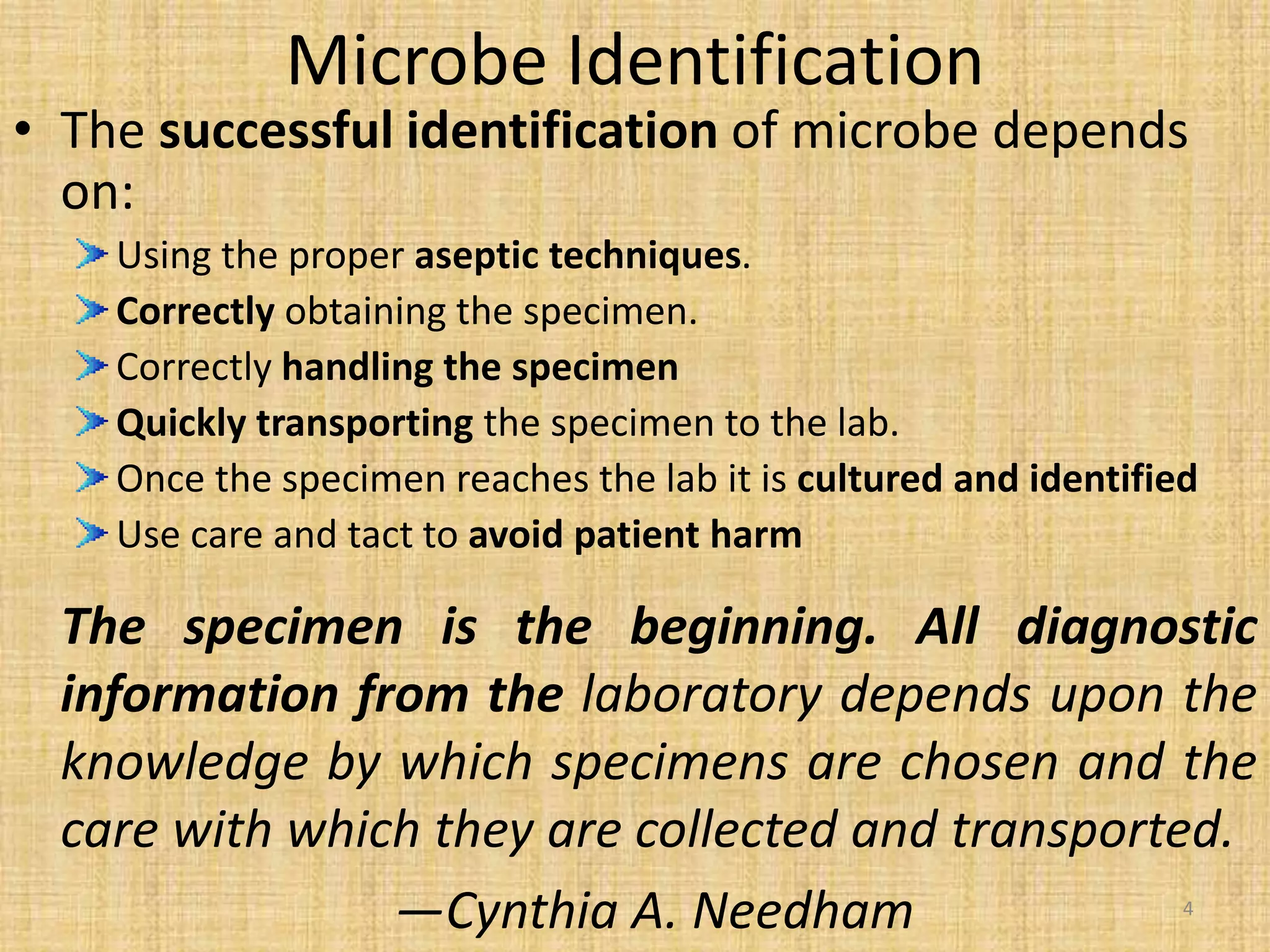
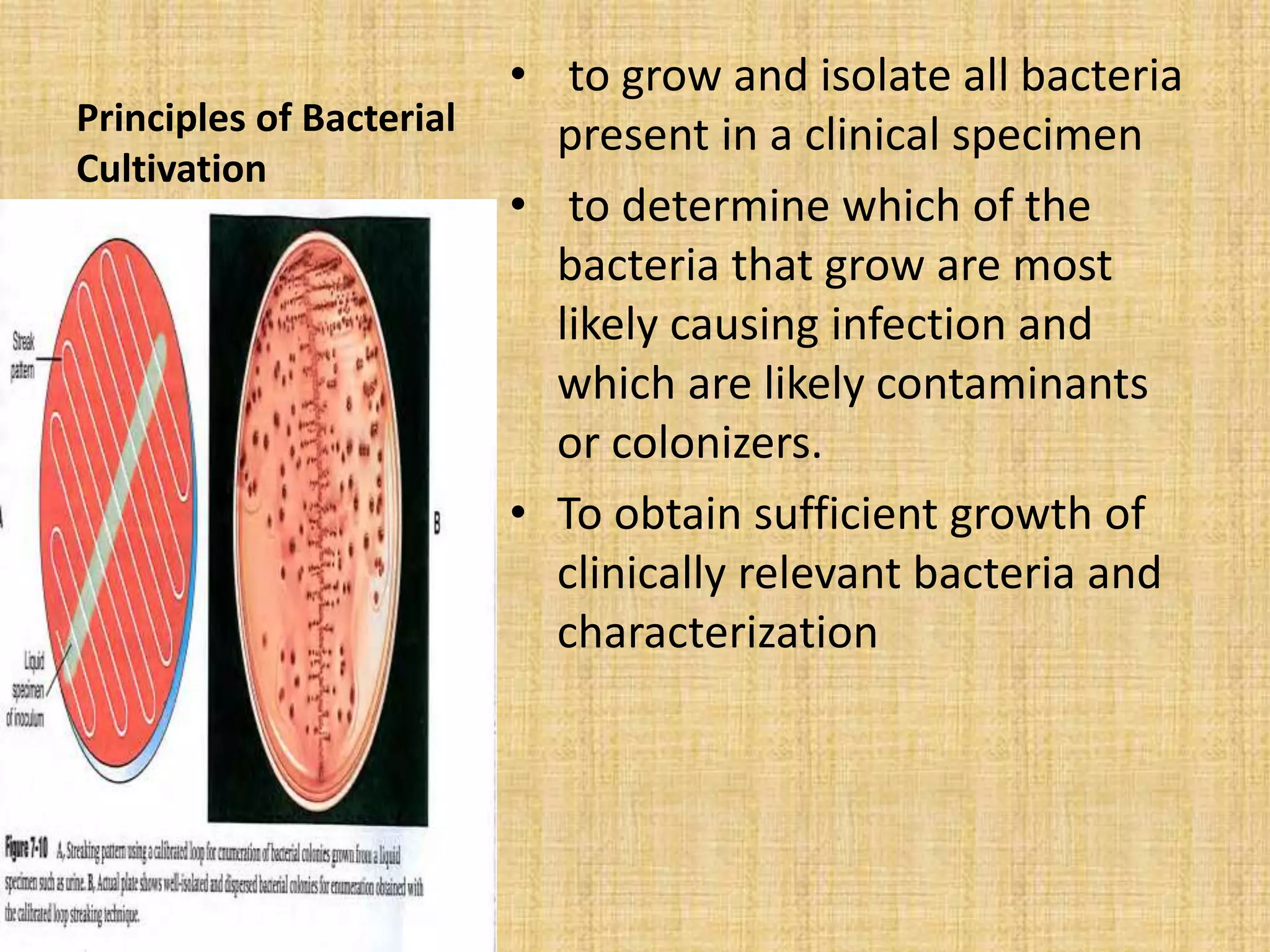
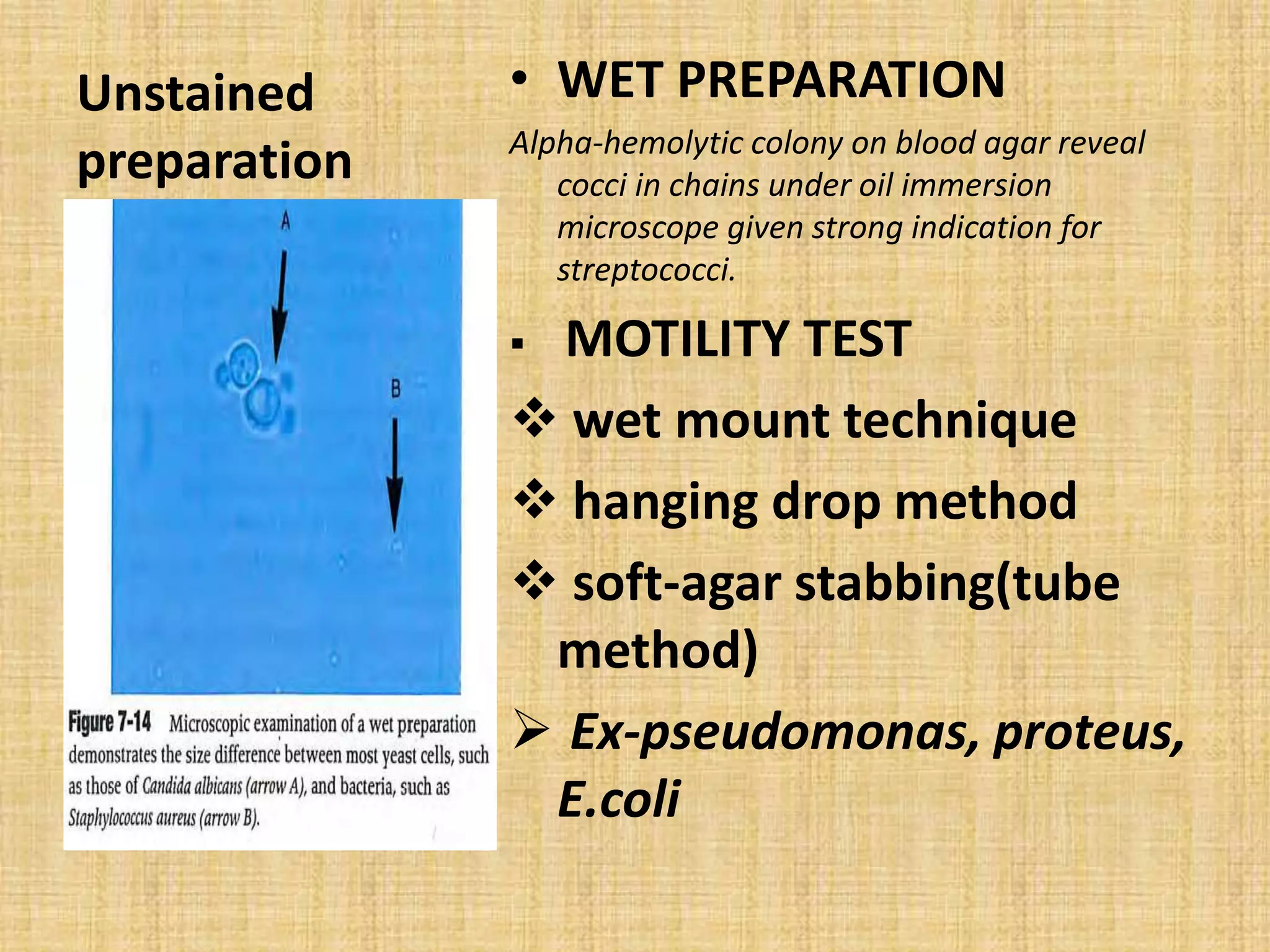
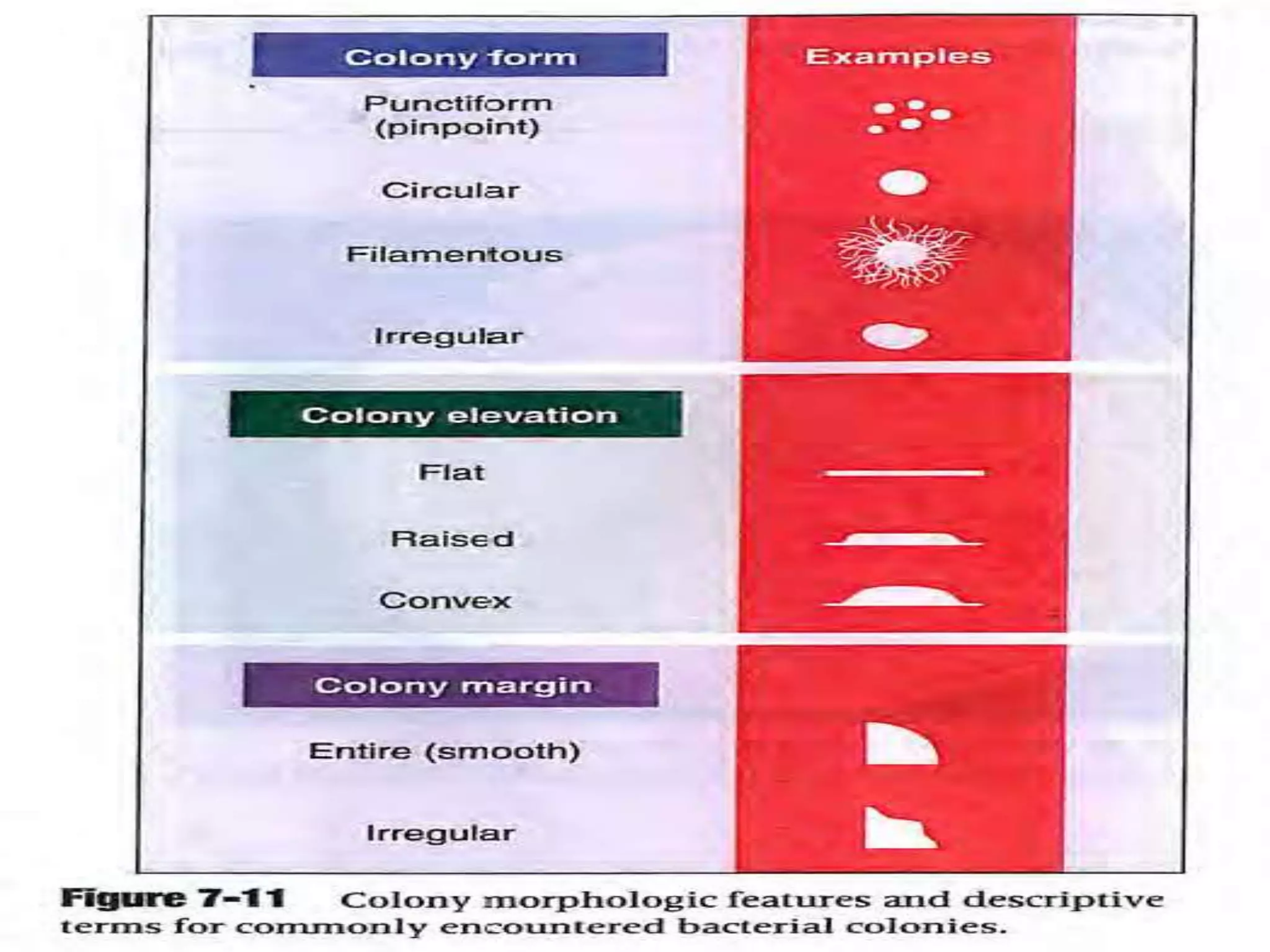
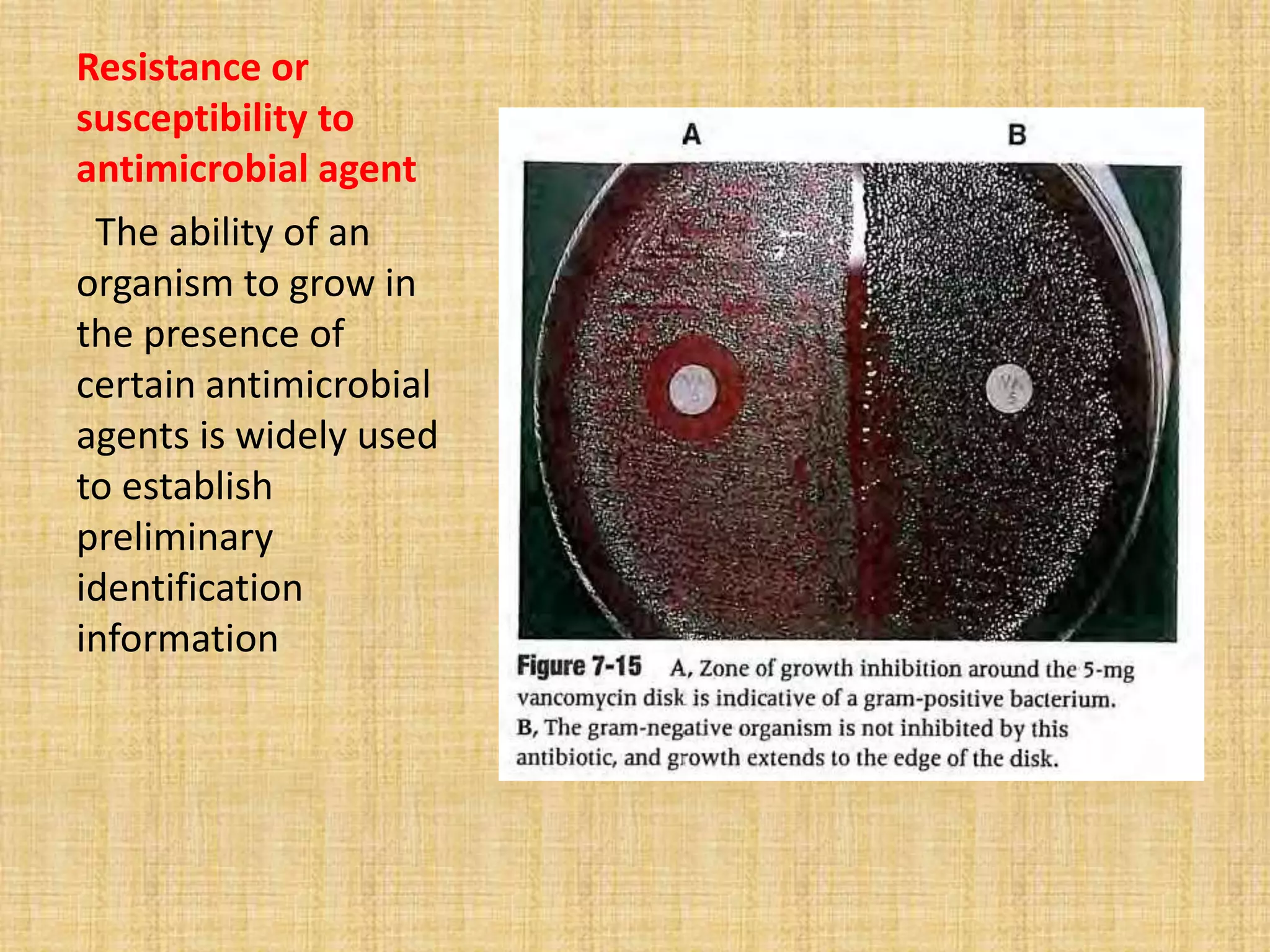
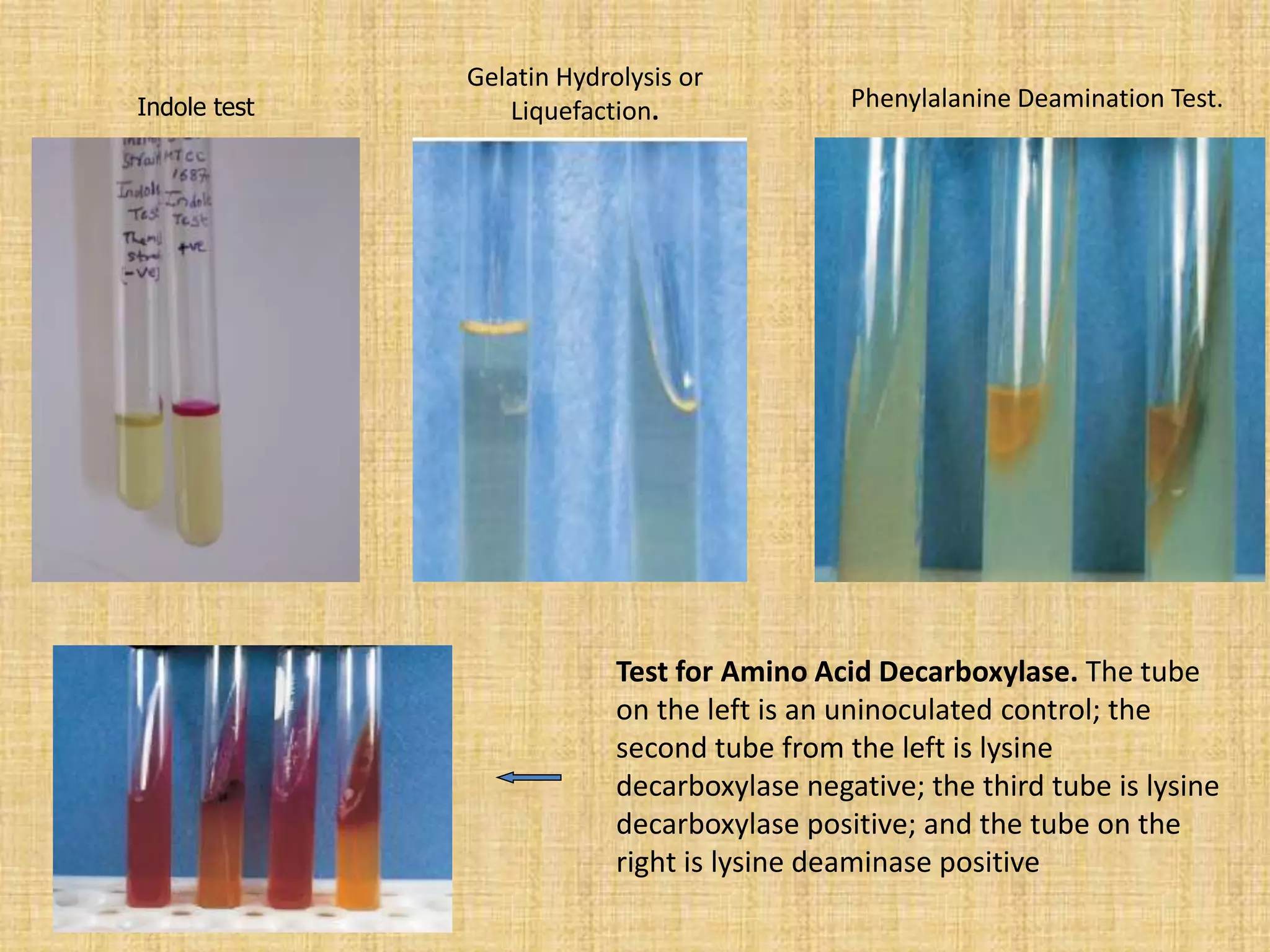
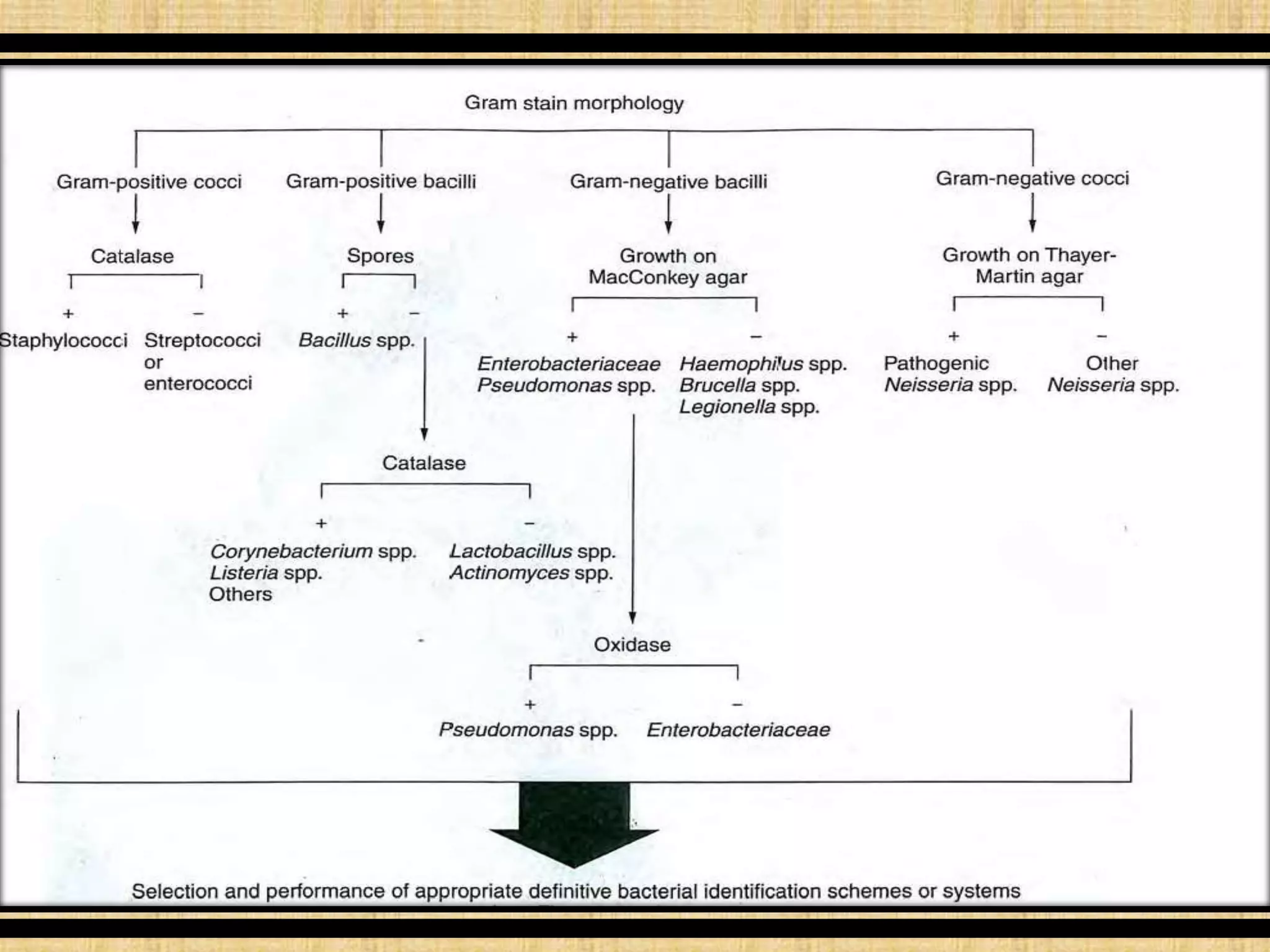
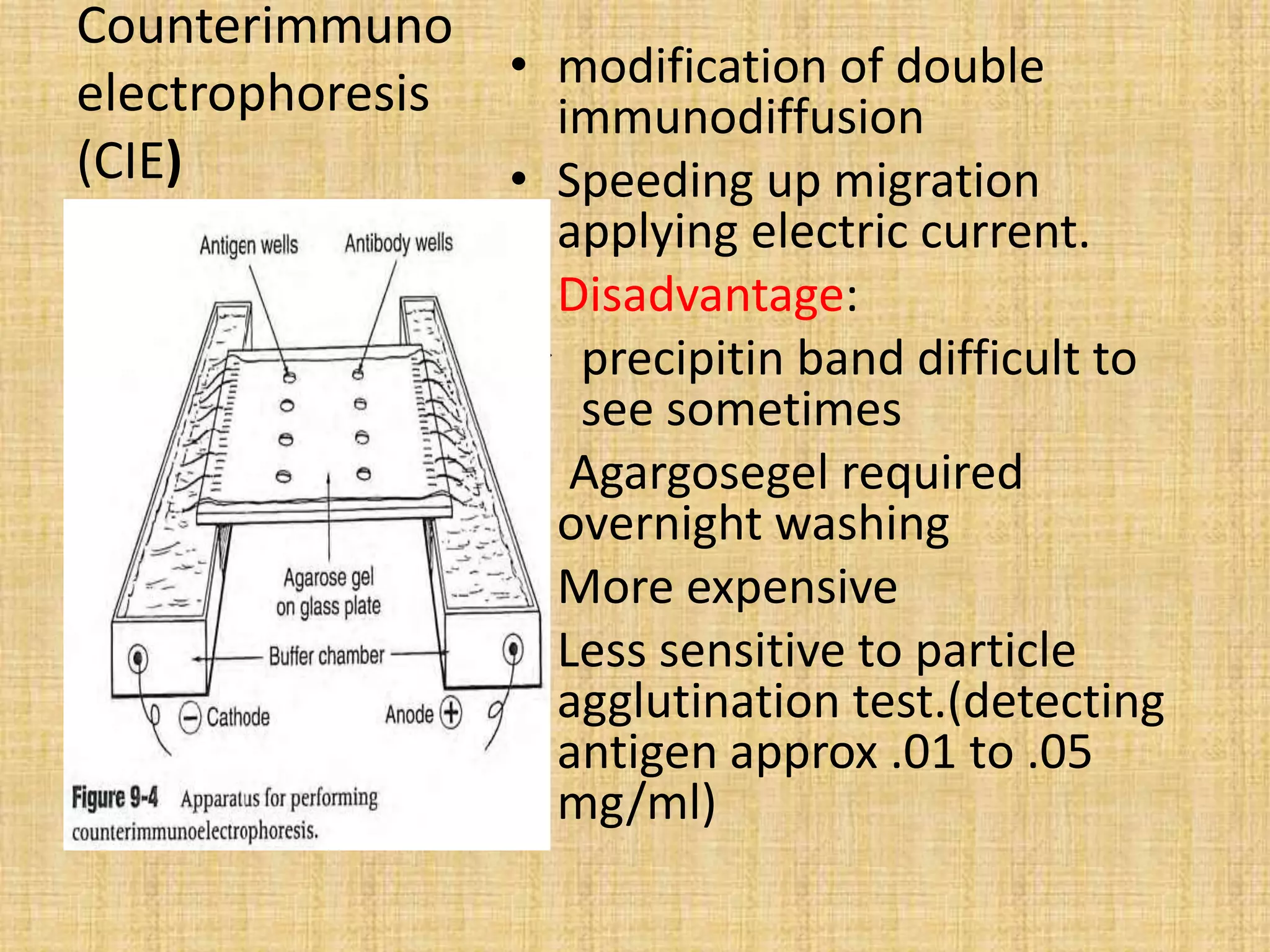
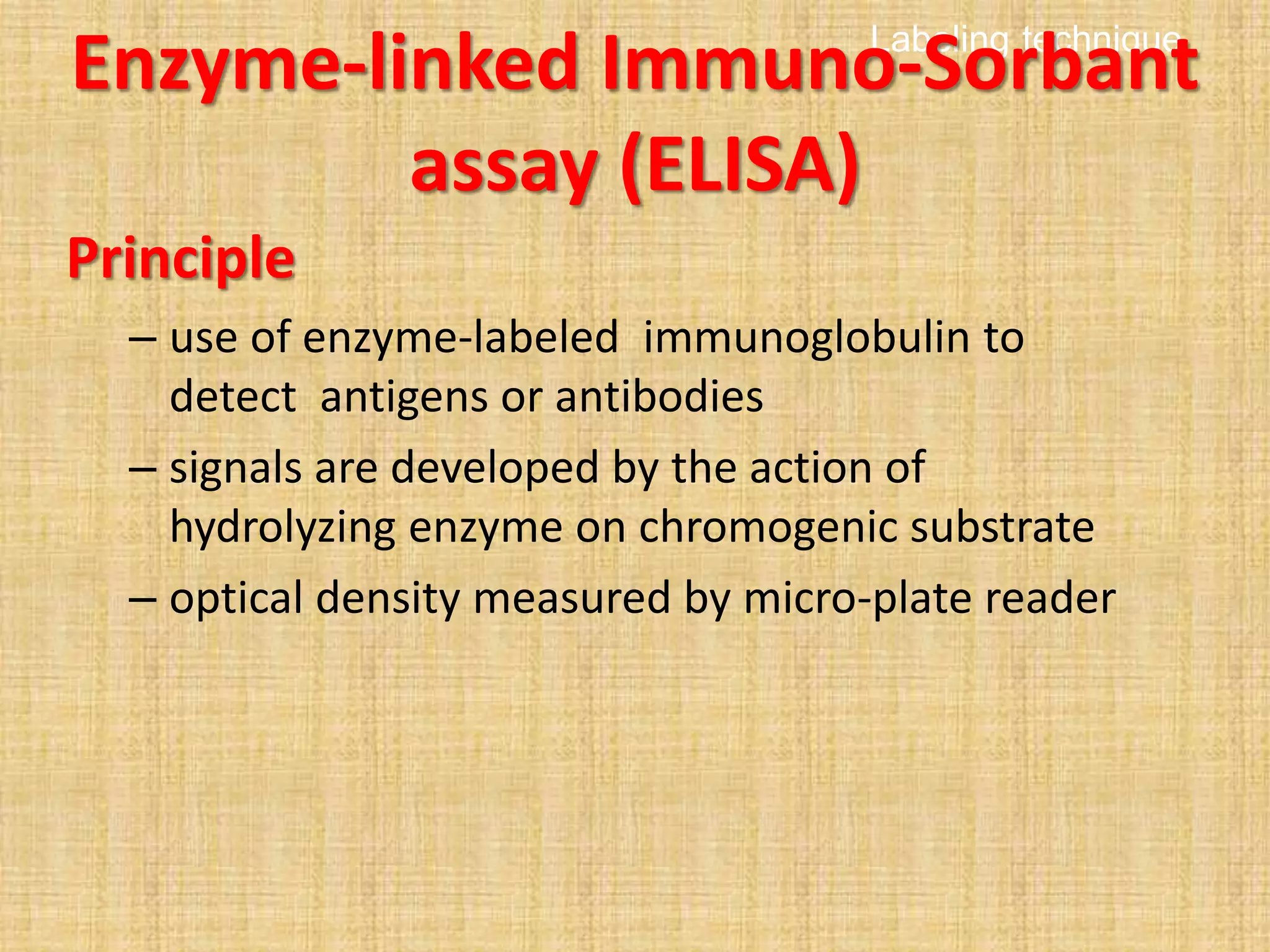
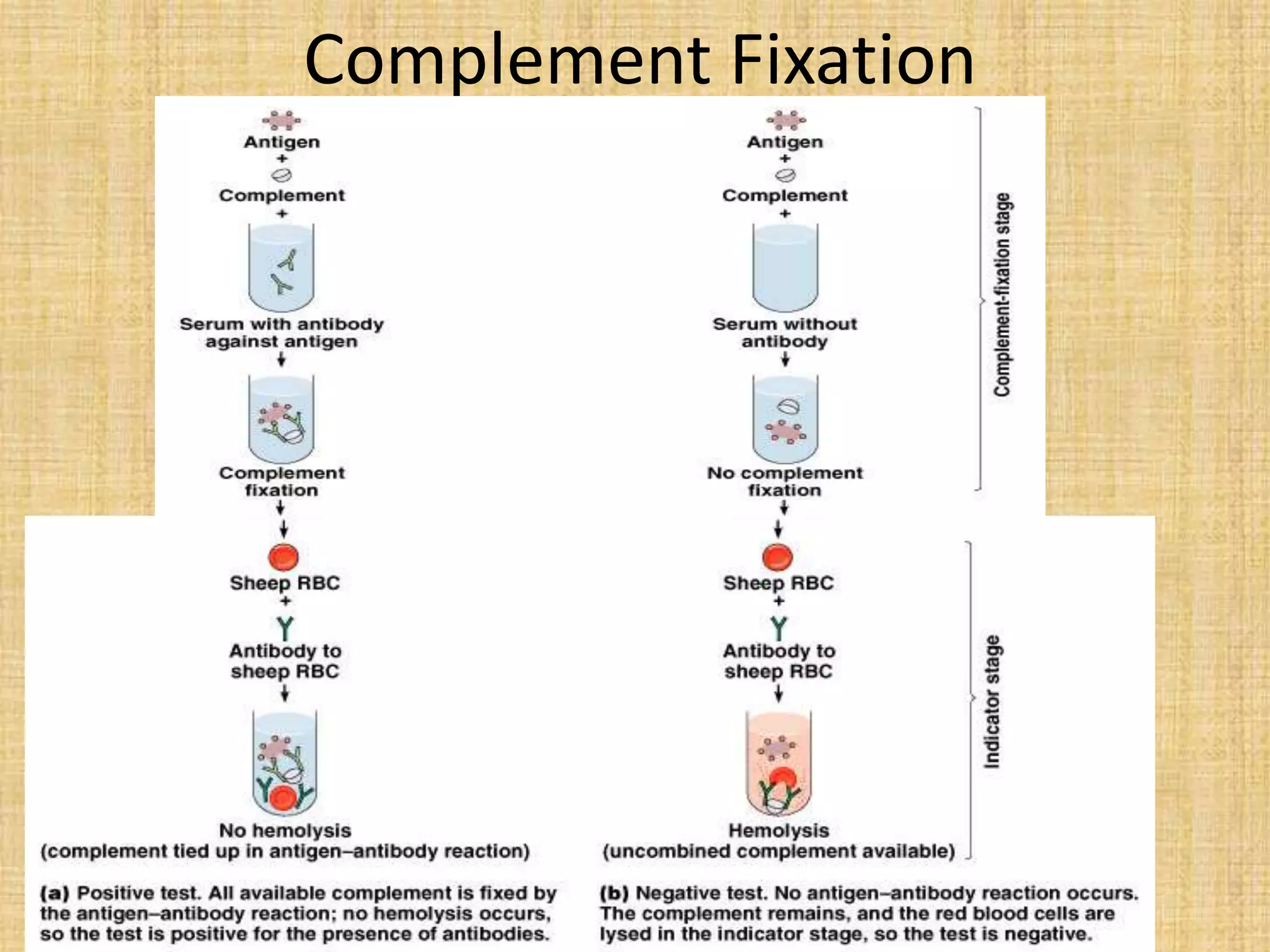
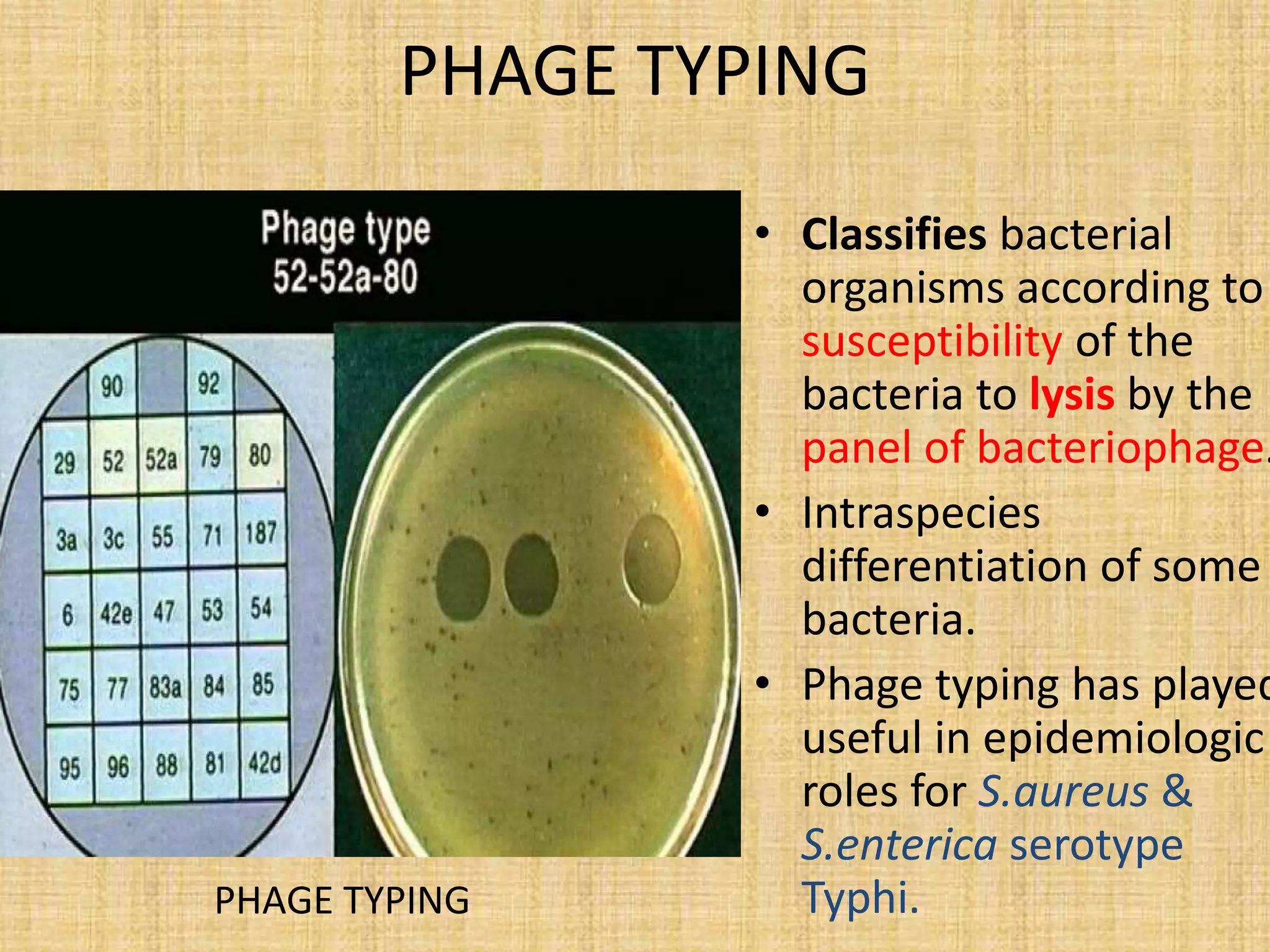
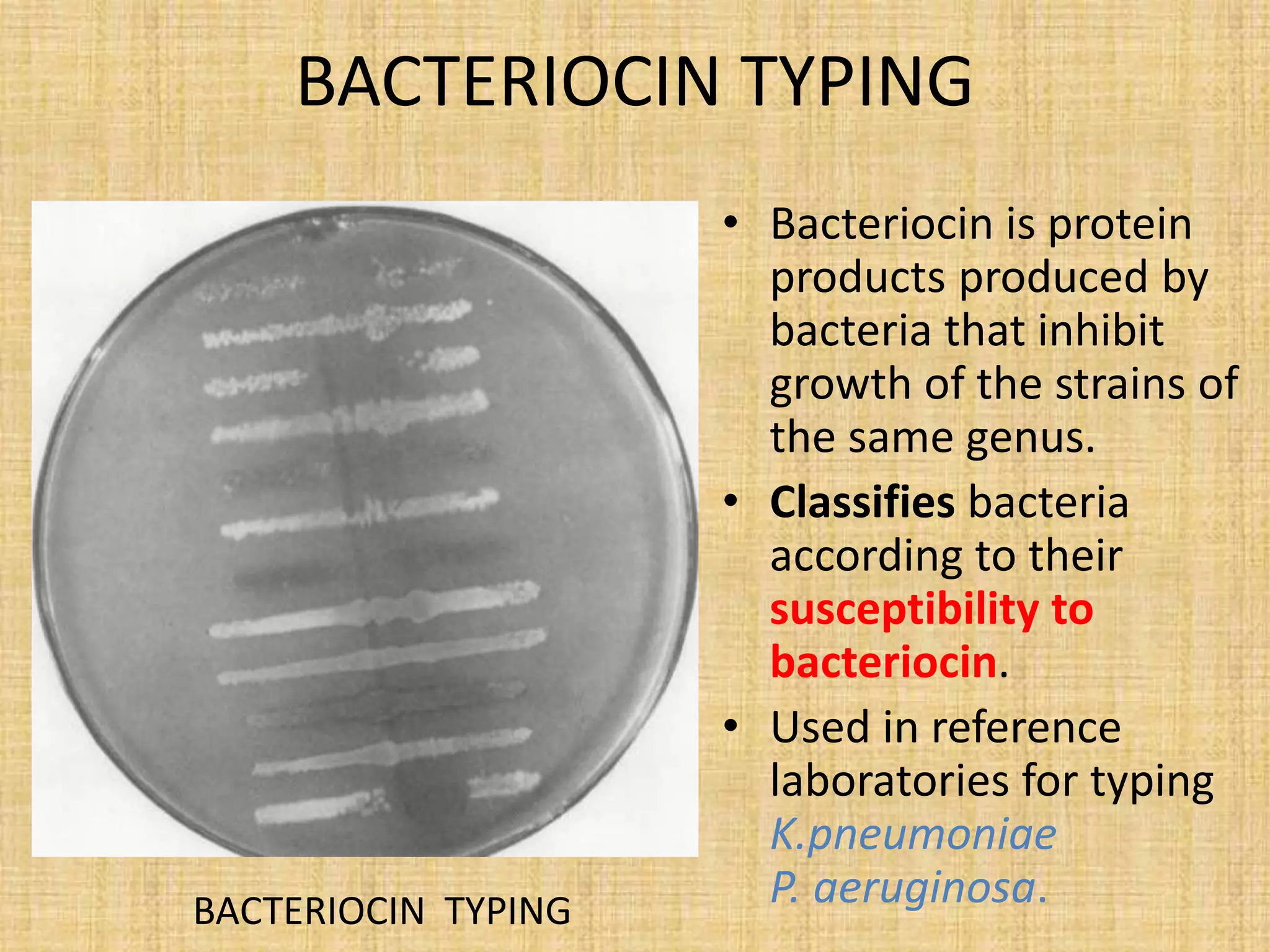
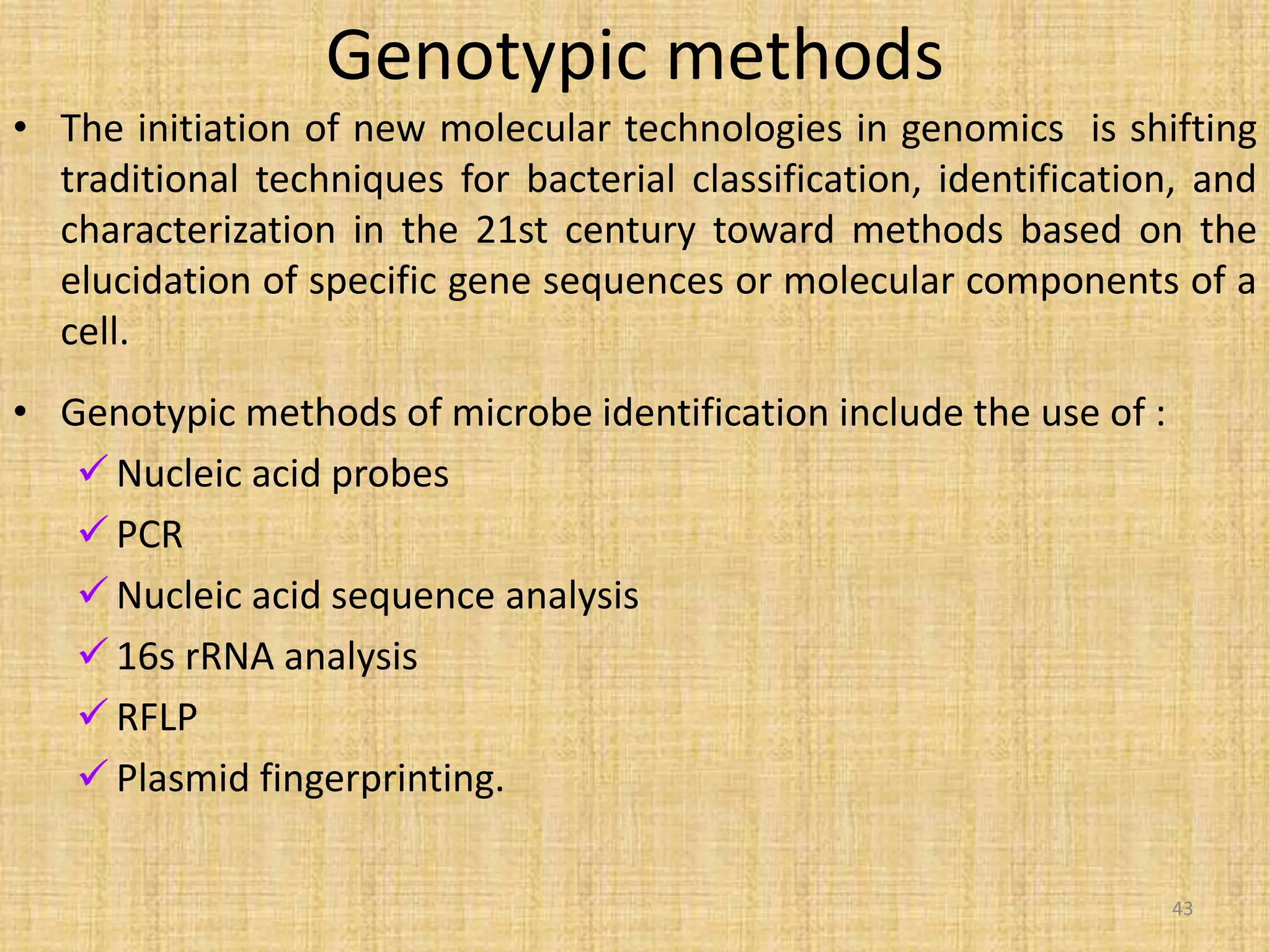
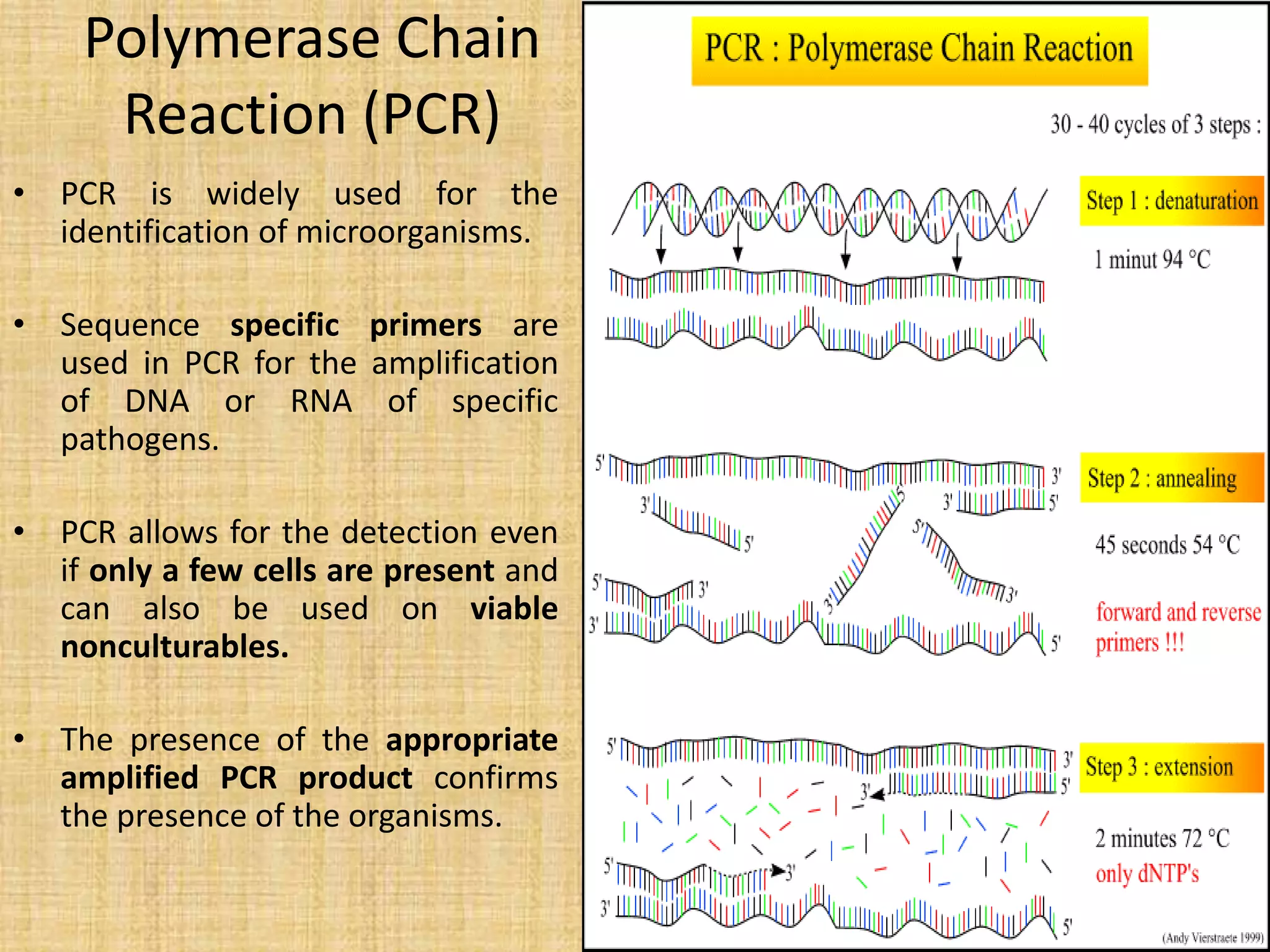
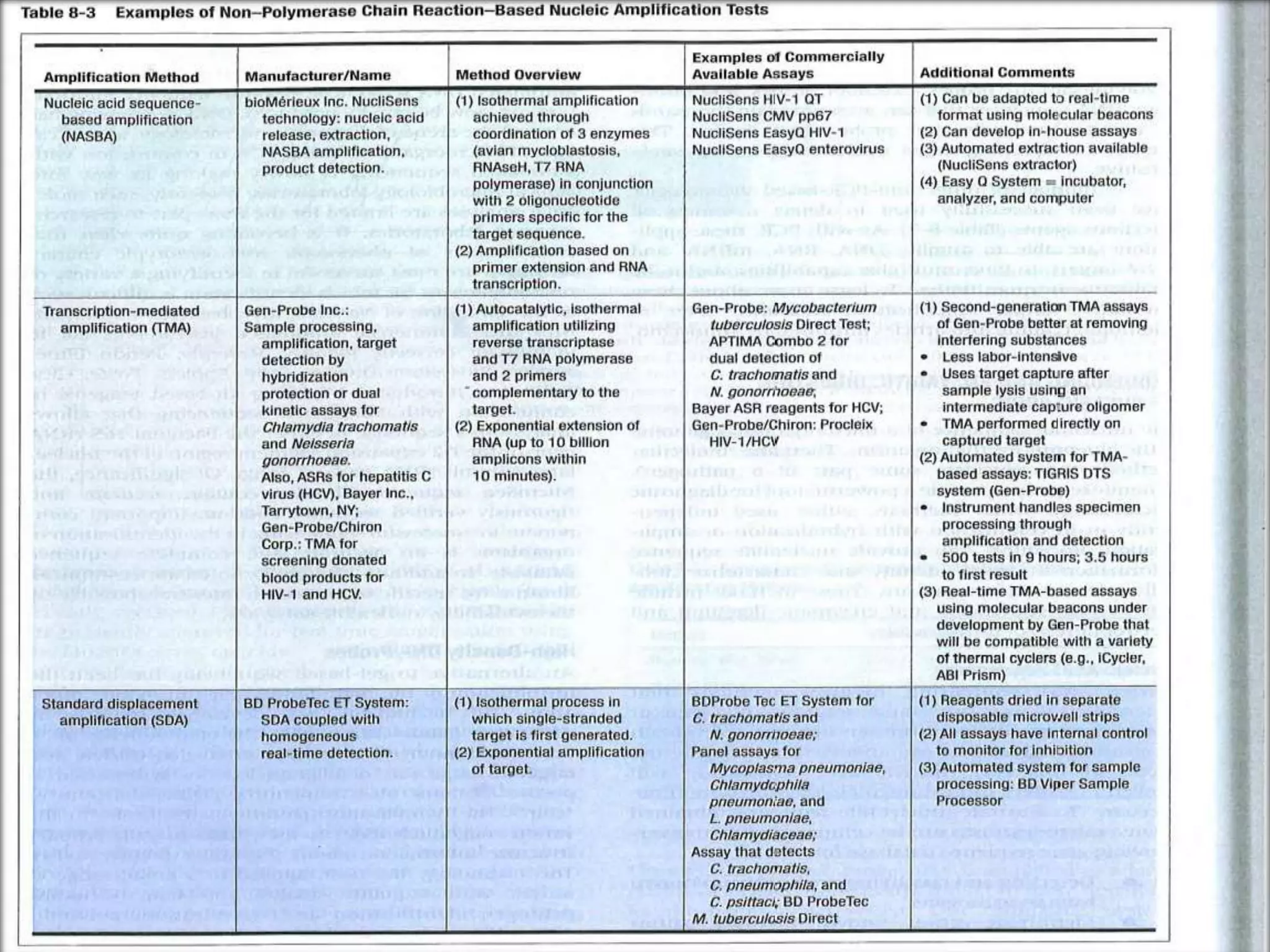
This document discusses various methods for identifying bacteria, including traditional phenotypic methods, immunochemical methods, and genotypic molecular methods. Phenotypic methods involve examining bacterial morphology, staining characteristics, growth requirements, and biochemical reactions. Immunochemical methods like immunofluorescence and ELISA use antigen-antibody reactions for identification. Molecular identification methods analyze bacterial DNA sequences. Correct specimen collection, handling, and transport are essential for accurate identification. Identification determines clinical significance and appropriate treatment.
![Identification scheme of
bacteria
Dr. Sayantan Mondal
[pgt]
Dept. of Microbiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptbysanti-140609022731-phpapp01/75/identification-of-bacteria-1-2048.jpg)