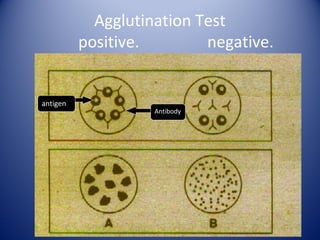
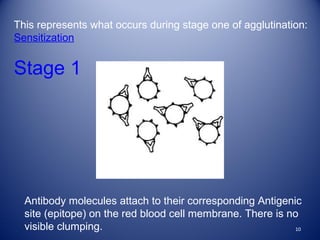
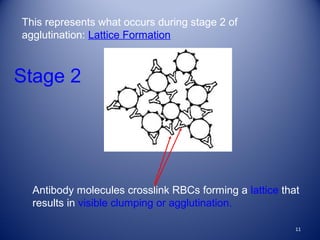
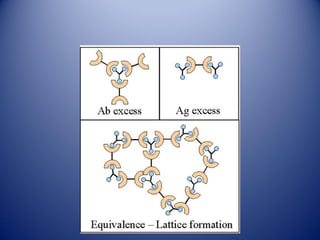
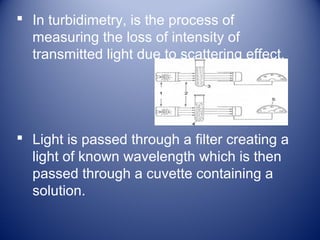
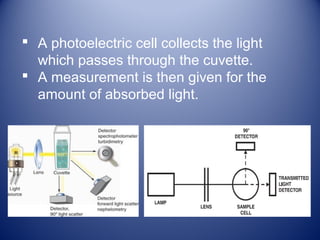
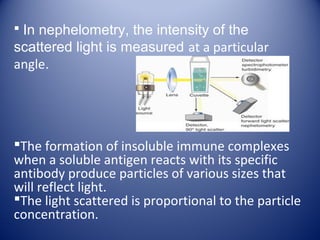
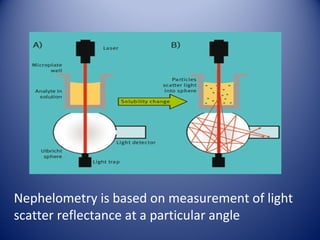
1) Agglutination tests detect antigens or antibodies by exploiting the ability of antibodies to cross-link antigen-coated particles, forming visible clumps or lattices.
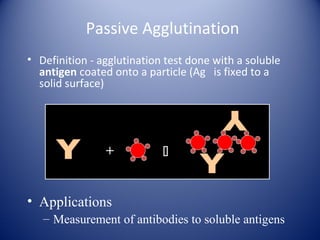
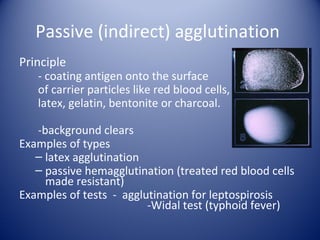
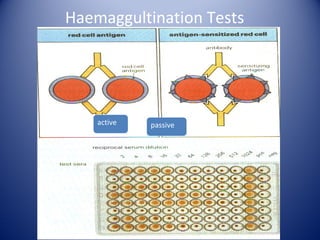
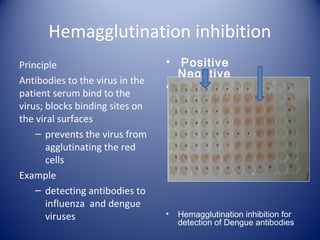
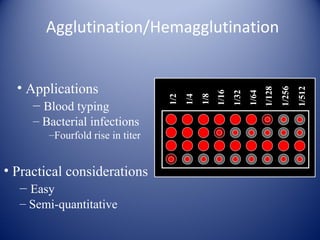
2) There are several types of agglutination tests including direct, passive, and reverse passive agglutination as well as hemagglutination and hemagglutination inhibition.
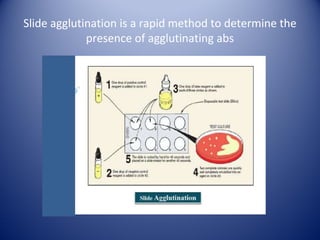
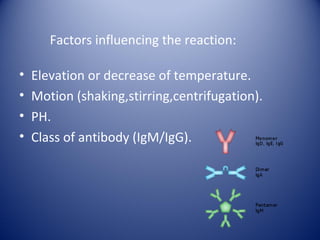
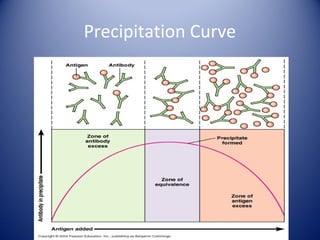
3) Agglutination tests are useful, rapid techniques for detecting various infectious diseases and other analytes but can be limited by prozone effects at high antibody concentrations.