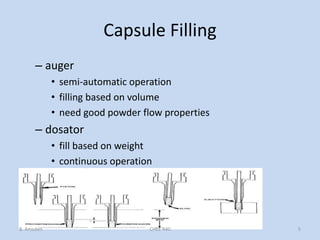
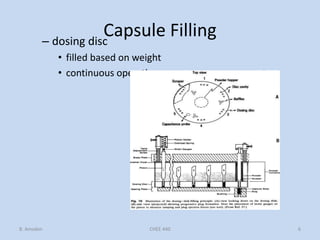
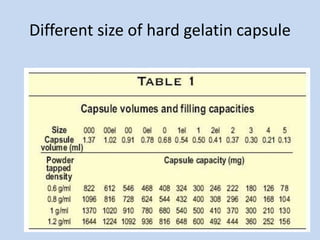
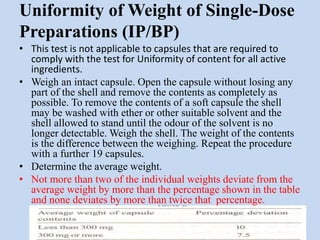
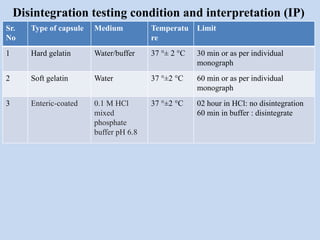
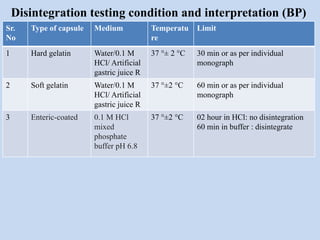
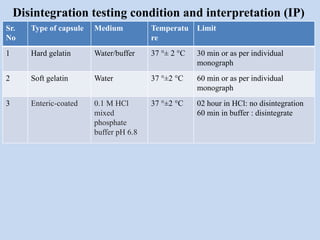
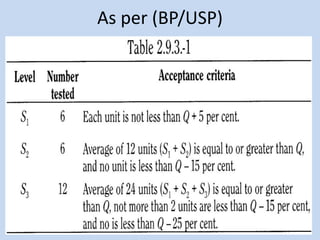
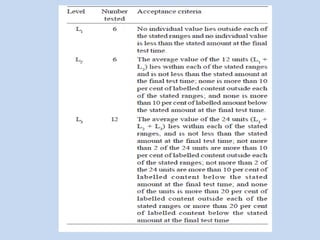
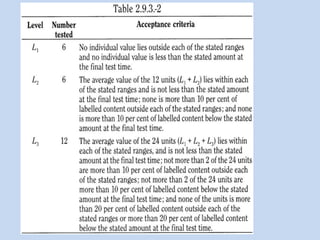
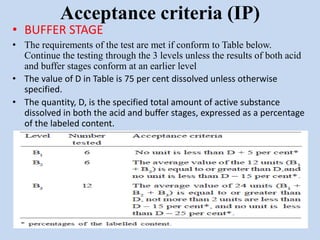
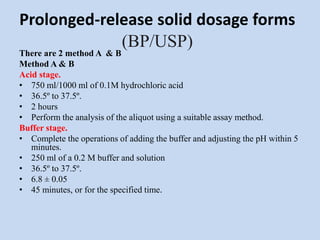
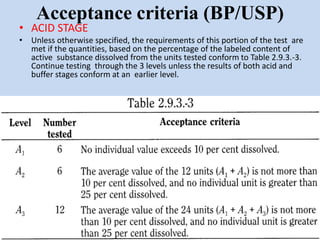
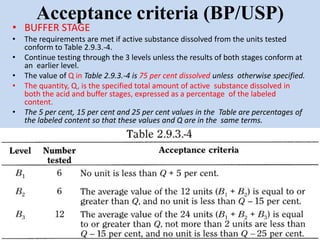
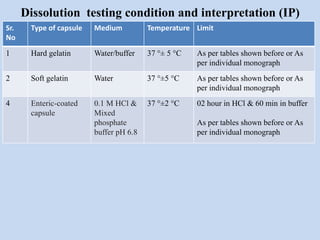
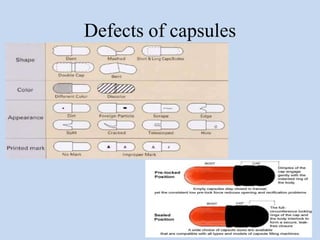
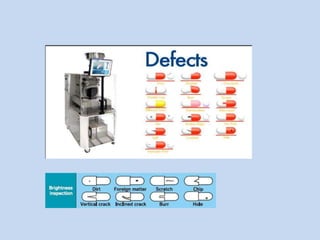
Capsules are solid dosage forms that contain a drug or mixture of drugs enclosed within a shell. The shell is typically made of gelatin but can also be other materials. Capsules are intended for oral administration and provide rapid release of contents unless they are modified or enteric release capsules. Capsules can be filled using various methods like auger, dosator, or dosing disc systems. Tests are conducted to ensure uniformity of contents, weight, and dissolution based on pharmacopeial standards.