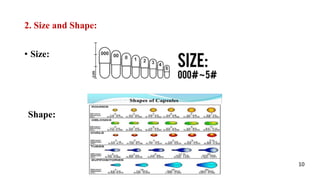
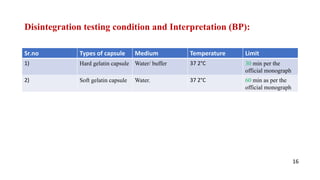
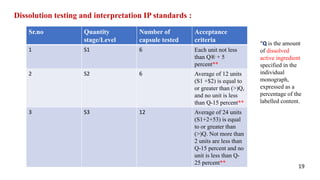
The document presents a seminar on in-process quality control (IPQC) tests for capsules at Mahatma Gandhi Vidhyamandir's Pharmacy College, detailing the importance of IPQC in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure product safety and quality. It includes an introduction to capsules, their advantages and disadvantages, and outlines various IPQC testing methods such as appearance, weight variation, disintegration, dissolution, content uniformity, and moisture permeation. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity of adhering to pharmacopoeial specifications and regulatory requirements to maintain the highest quality of pharmaceuticals.