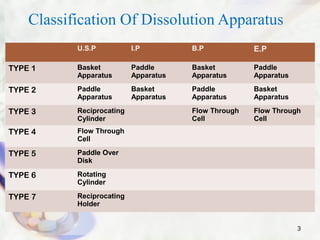
This presentation summarizes various dissolution testing apparatus. It describes 7 types of apparatus recognized by USP, IP, BP and EP. The first four apparatus are commonly used and include the rotating basket, paddle, reciprocating cylinder and flow through cell. The presentation provides details on the design, working, and typical uses of each apparatus type. It also discusses commonly used dissolution media and concludes that the goal of dissolution testing is to ensure pharmaceutical quality and understand biopharmaceutical properties like rate and extent of drug absorption.