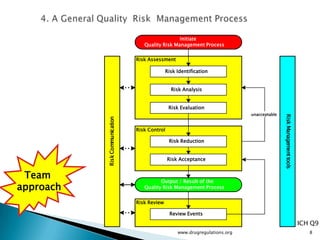
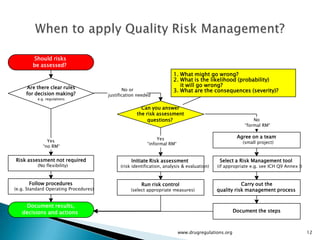
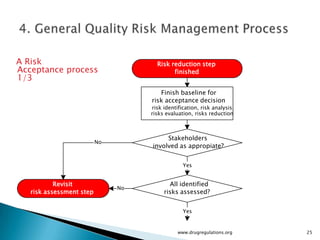
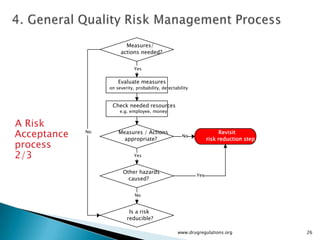
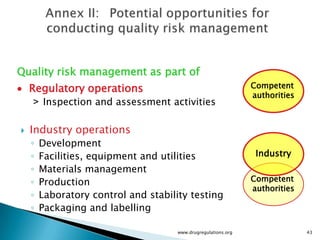
The document outlines guidelines on quality risk management (QRM) within the pharmaceutical industry, developed by a non-profit organization using information from regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA. It emphasizes a systematic approach to risk assessment and communication to ensure patient safety throughout the drug lifecycle, detailing methodologies, principles, and tools applicable to various processes including development, manufacturing, and regulatory compliance. The document also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary teamwork and transparency in managing quality risks.