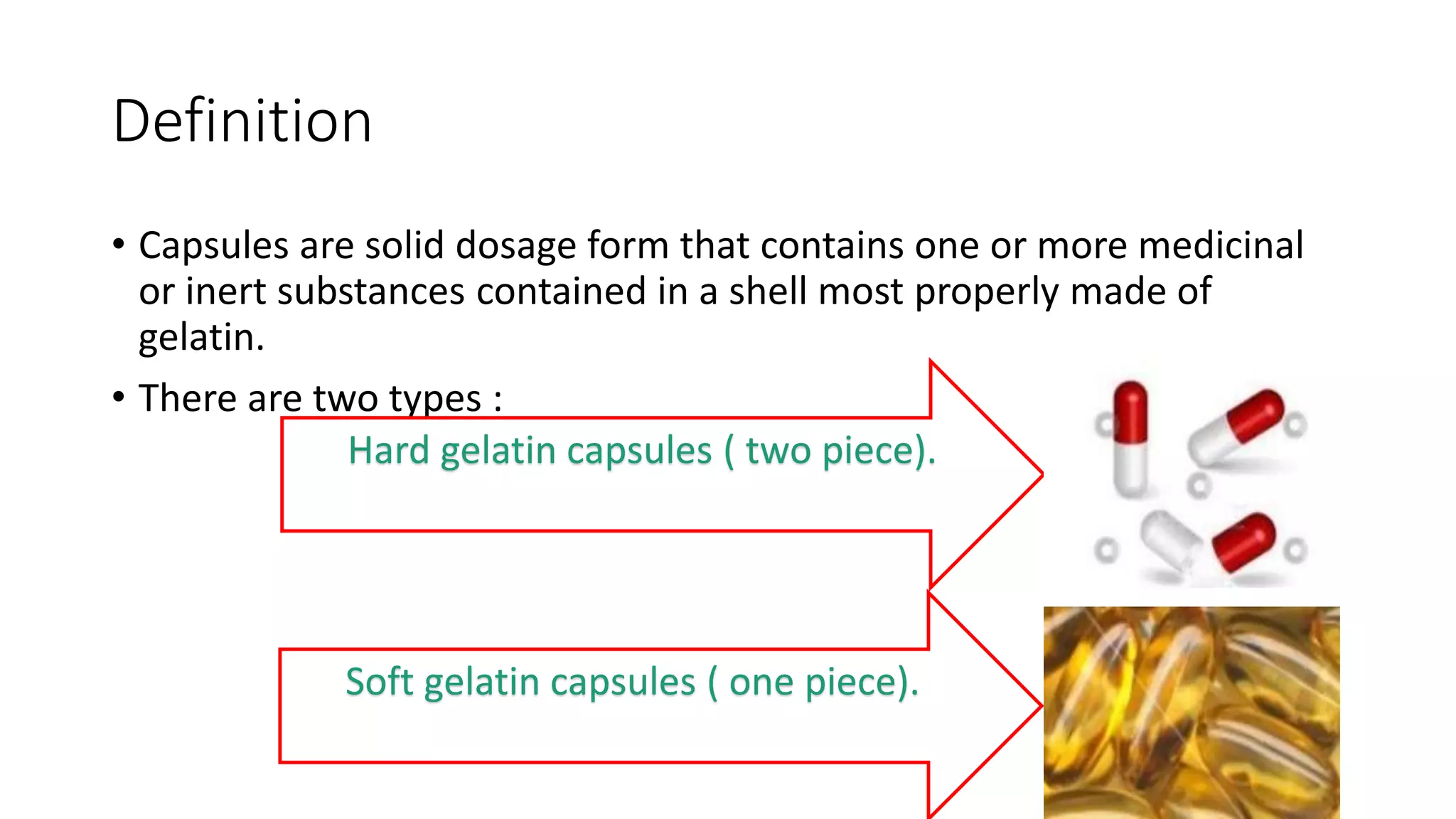
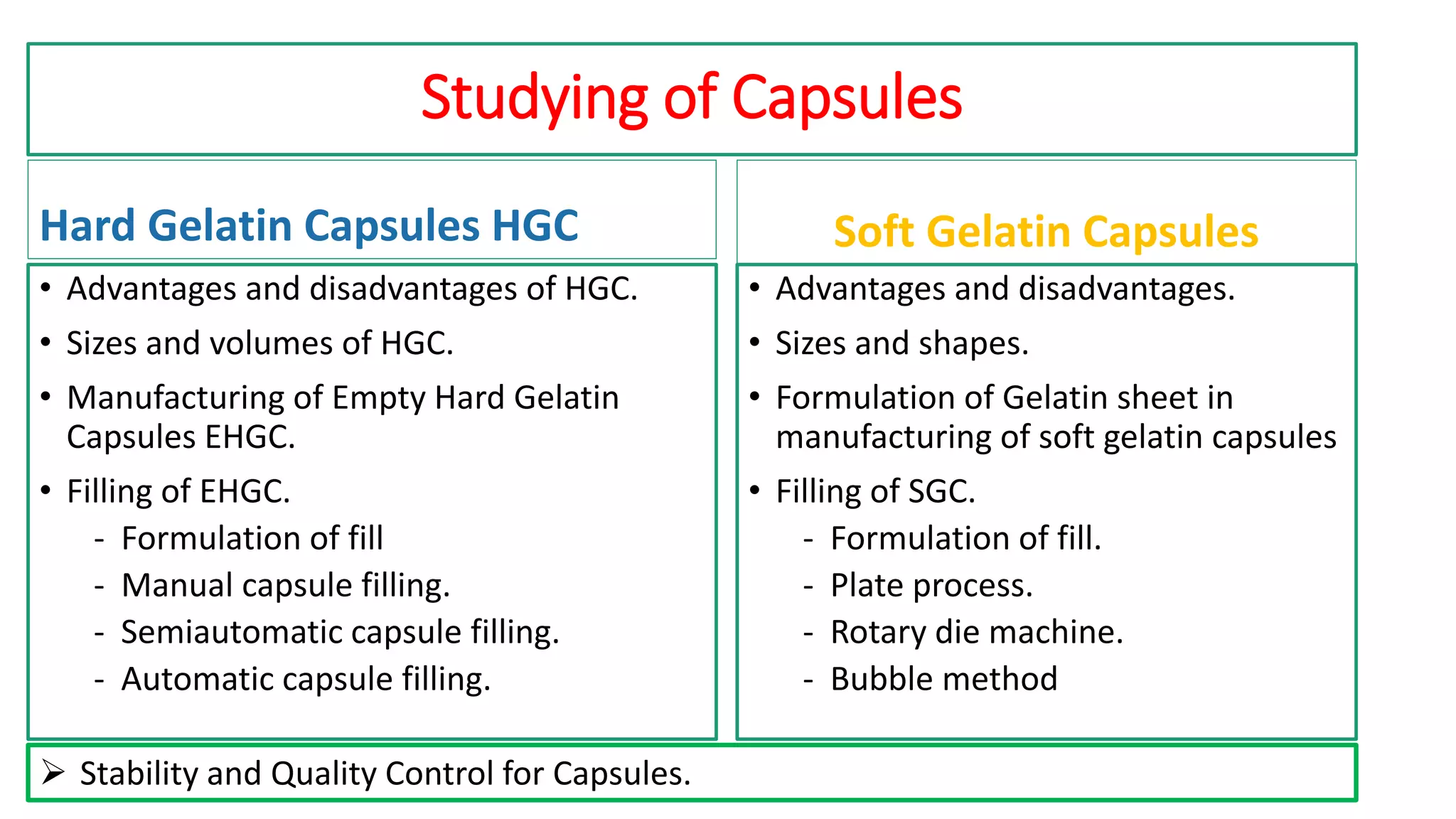
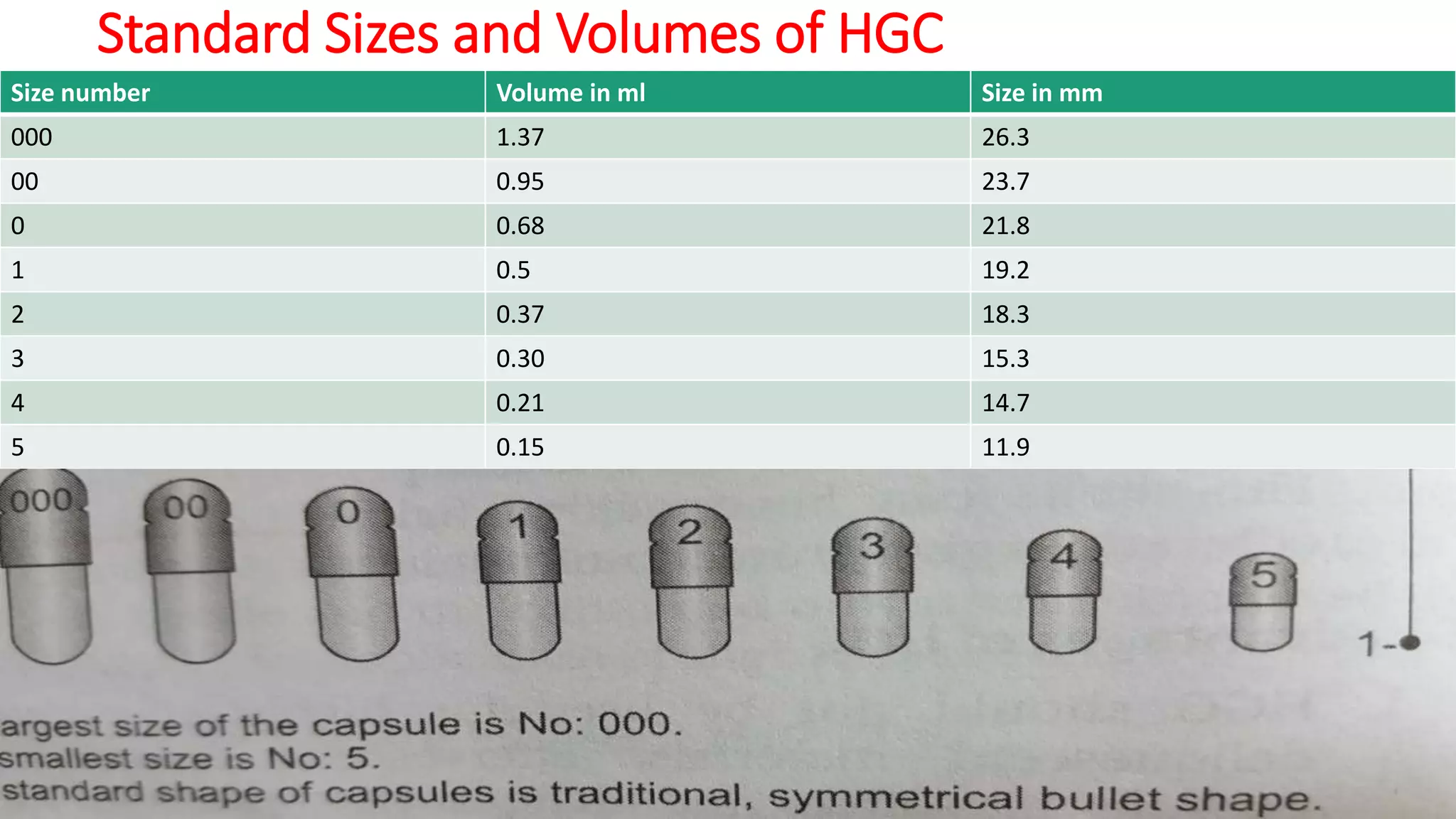
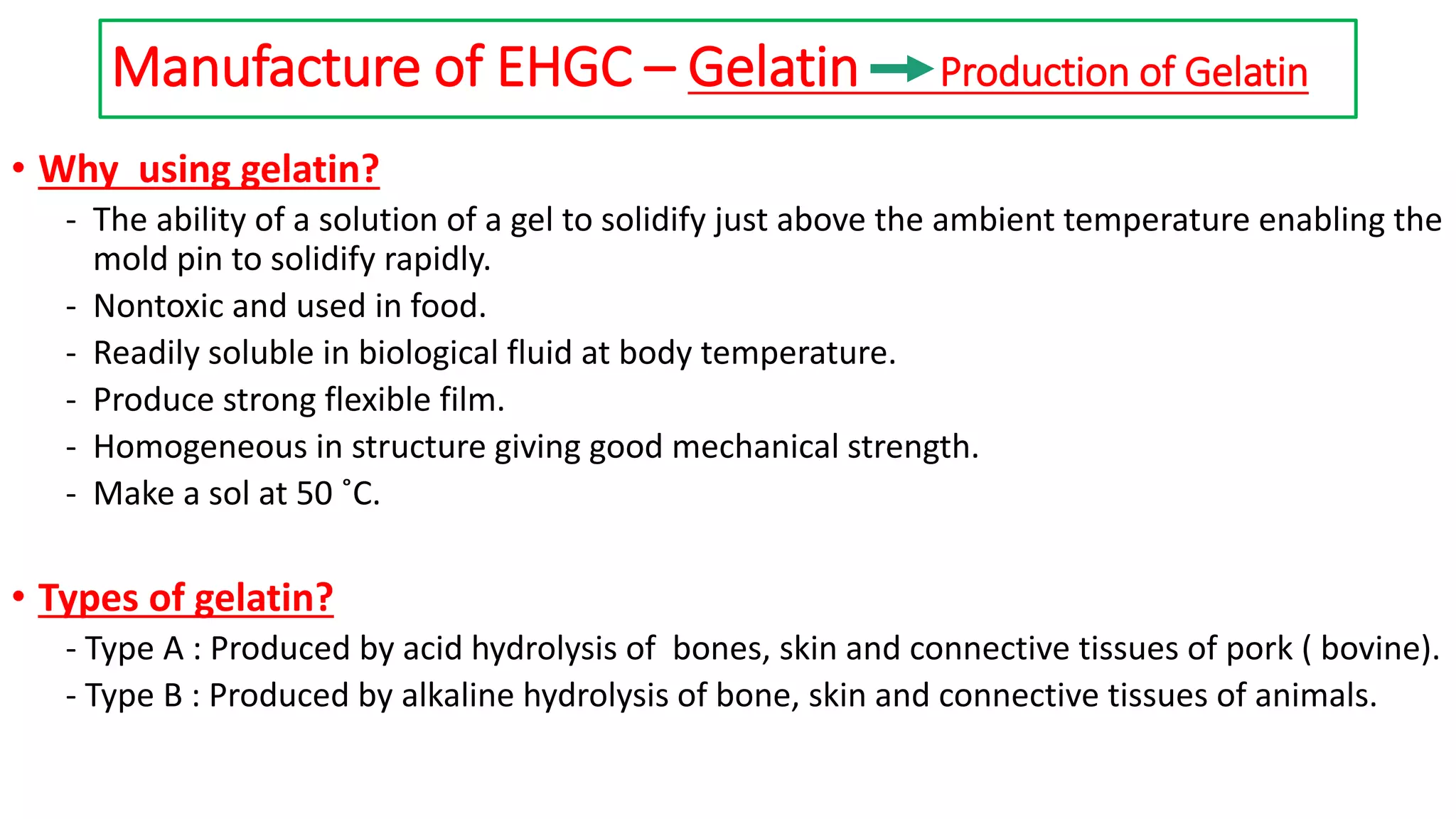
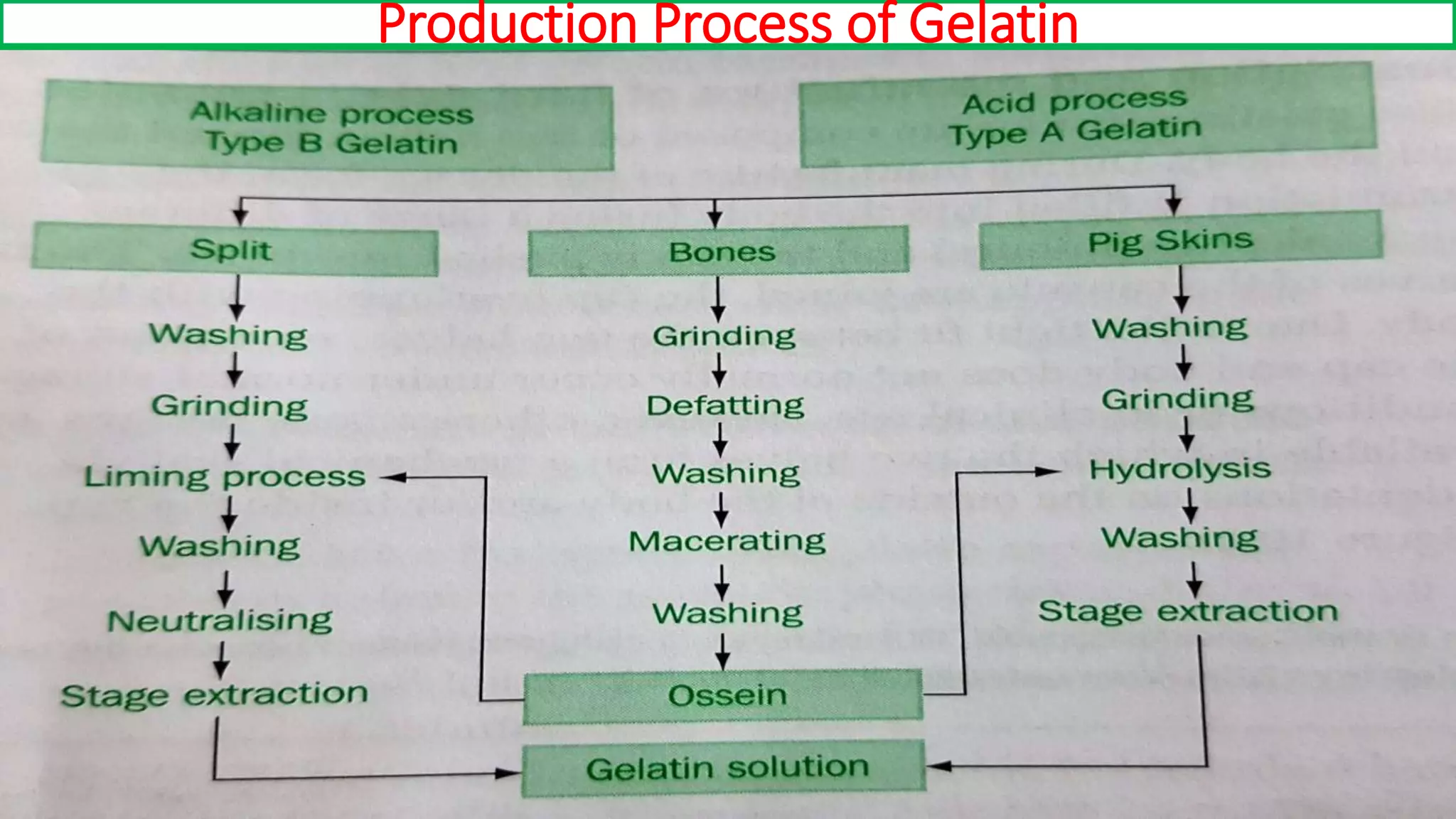
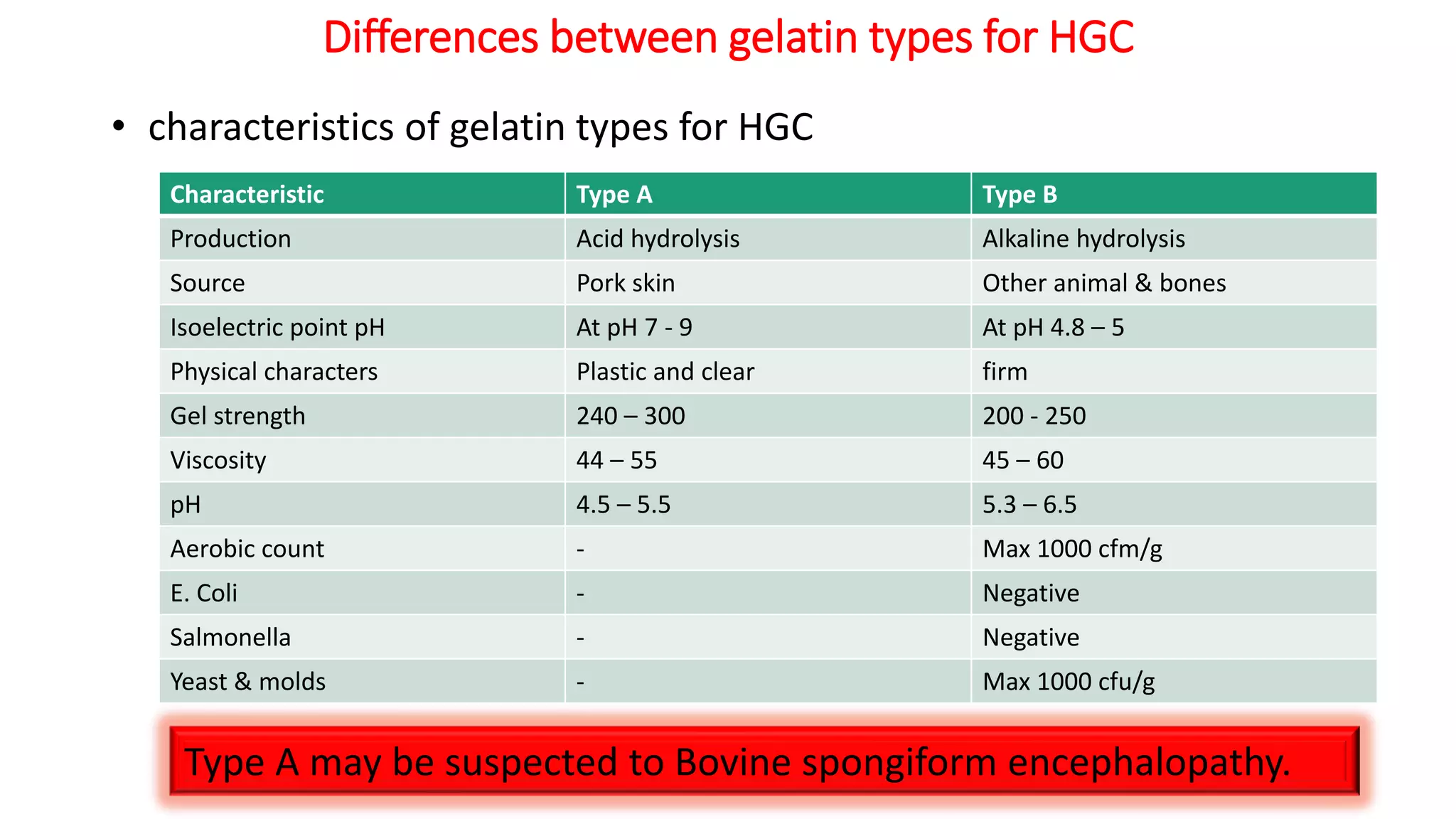
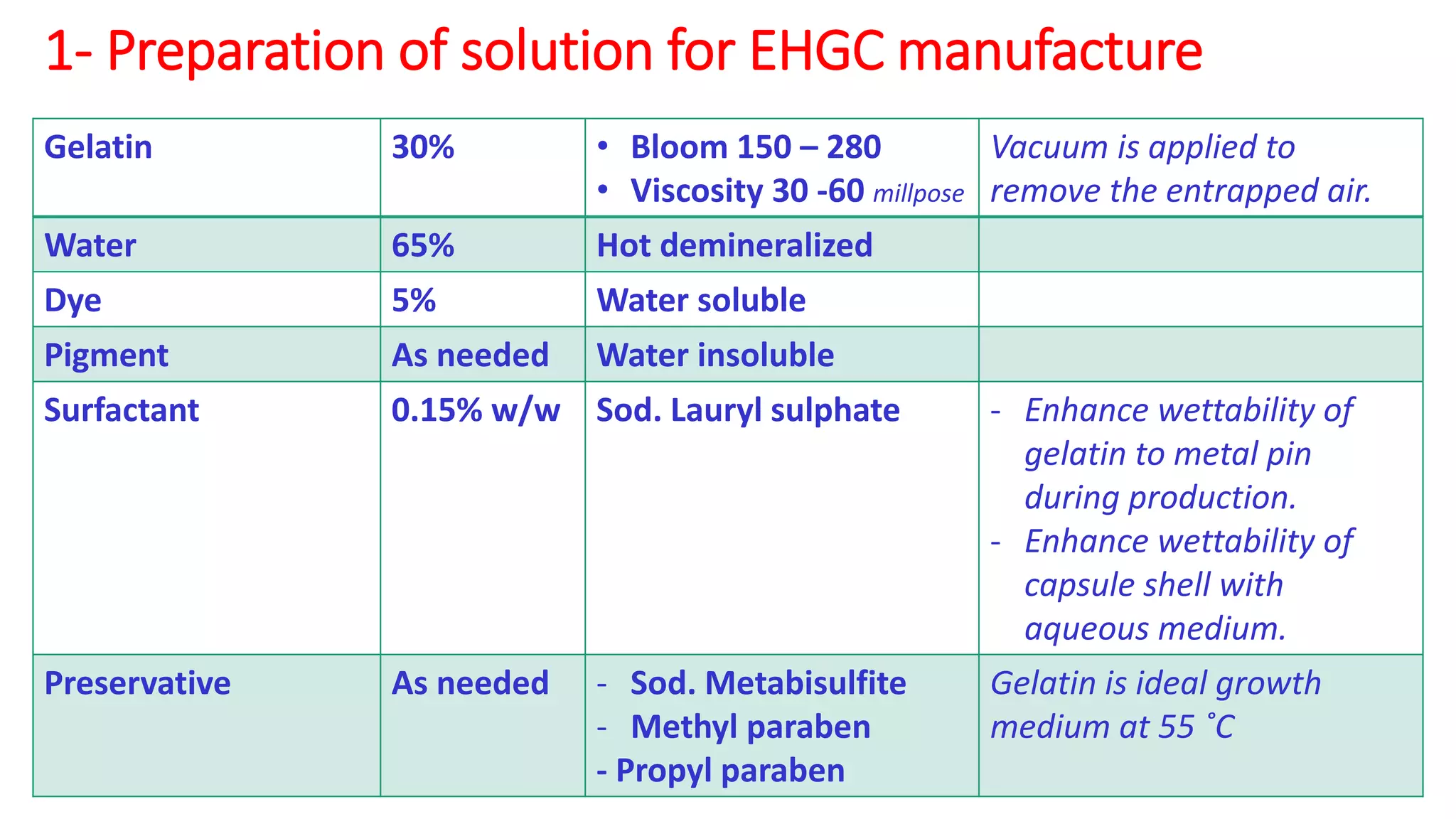
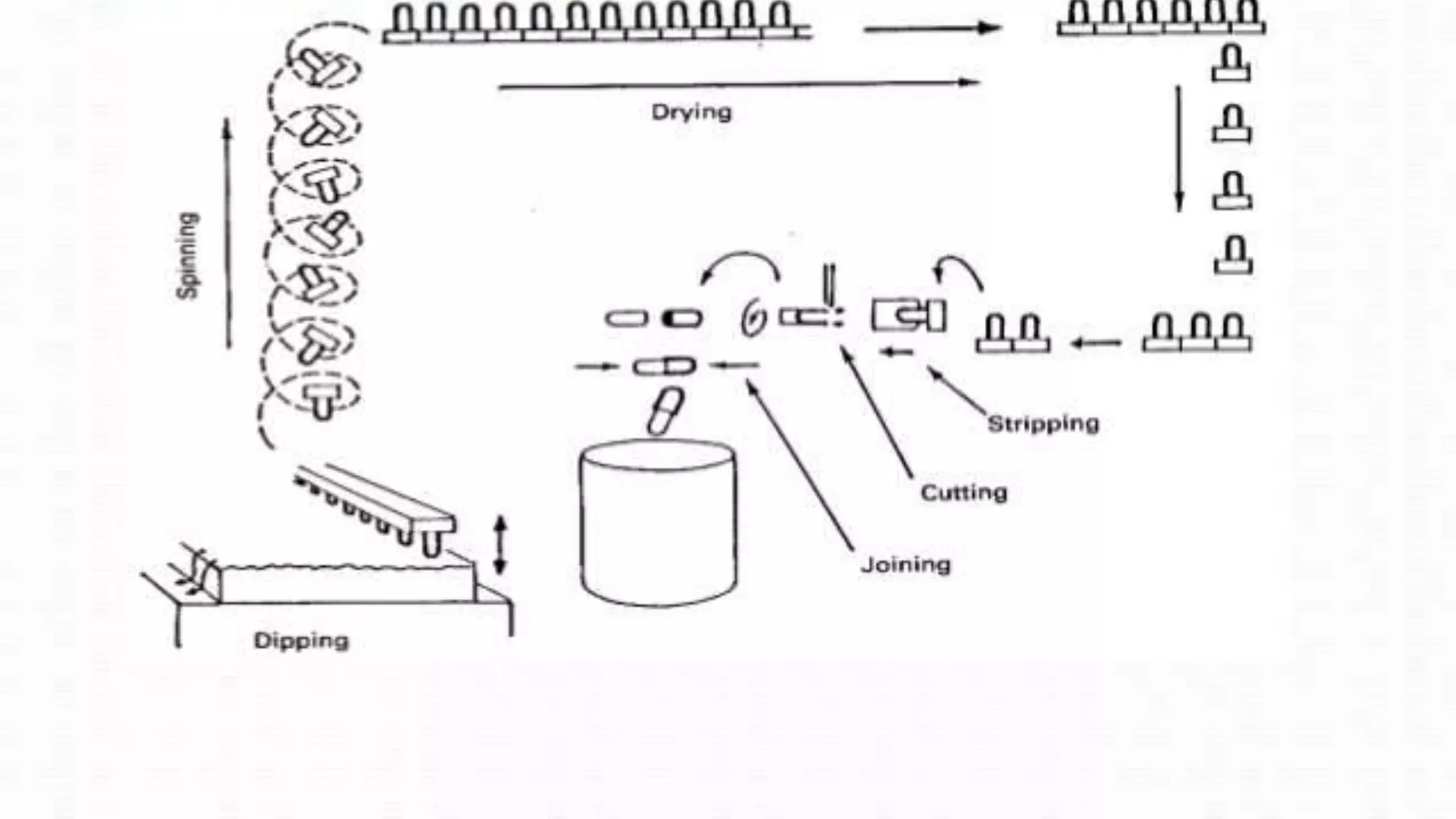
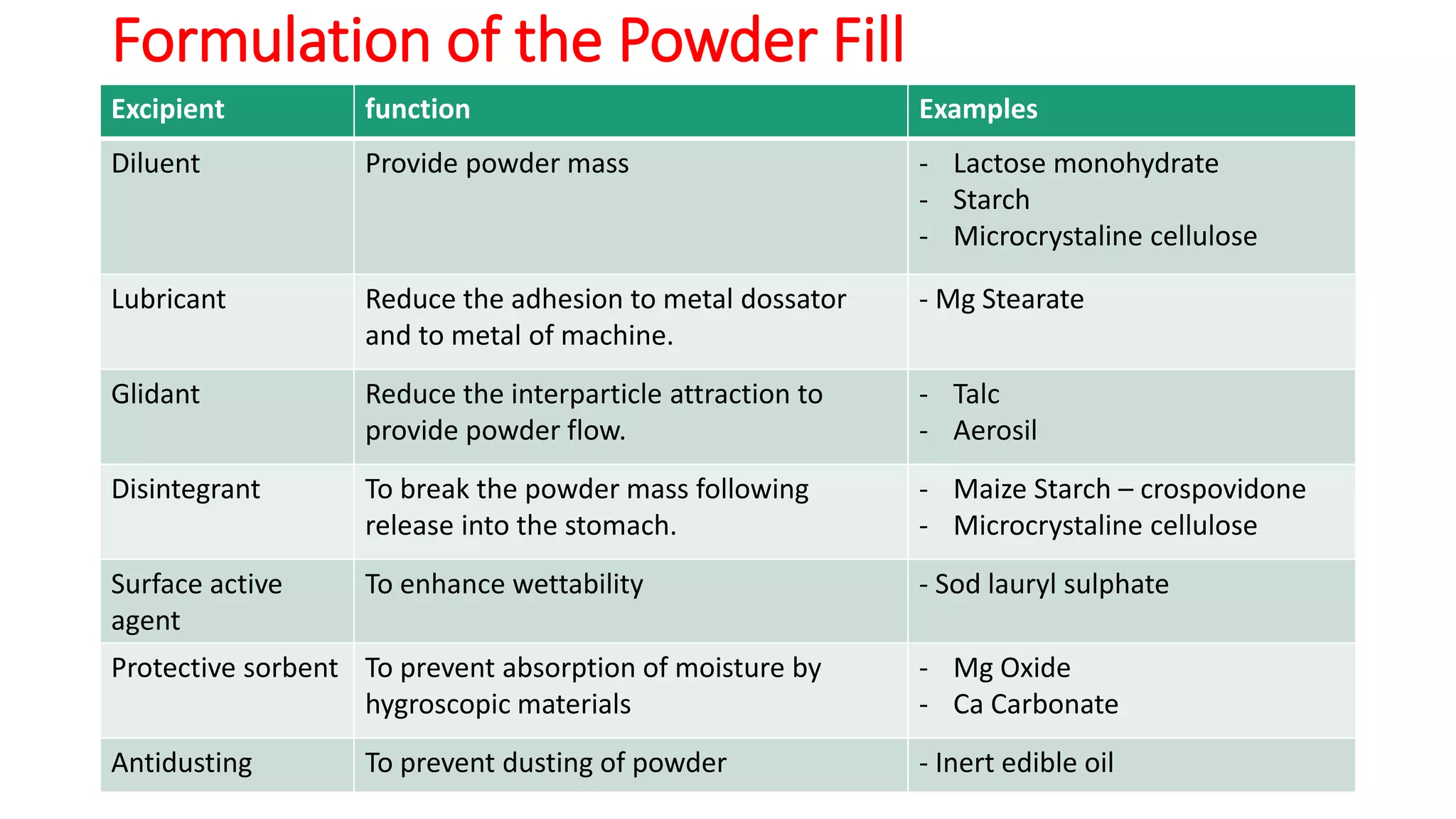
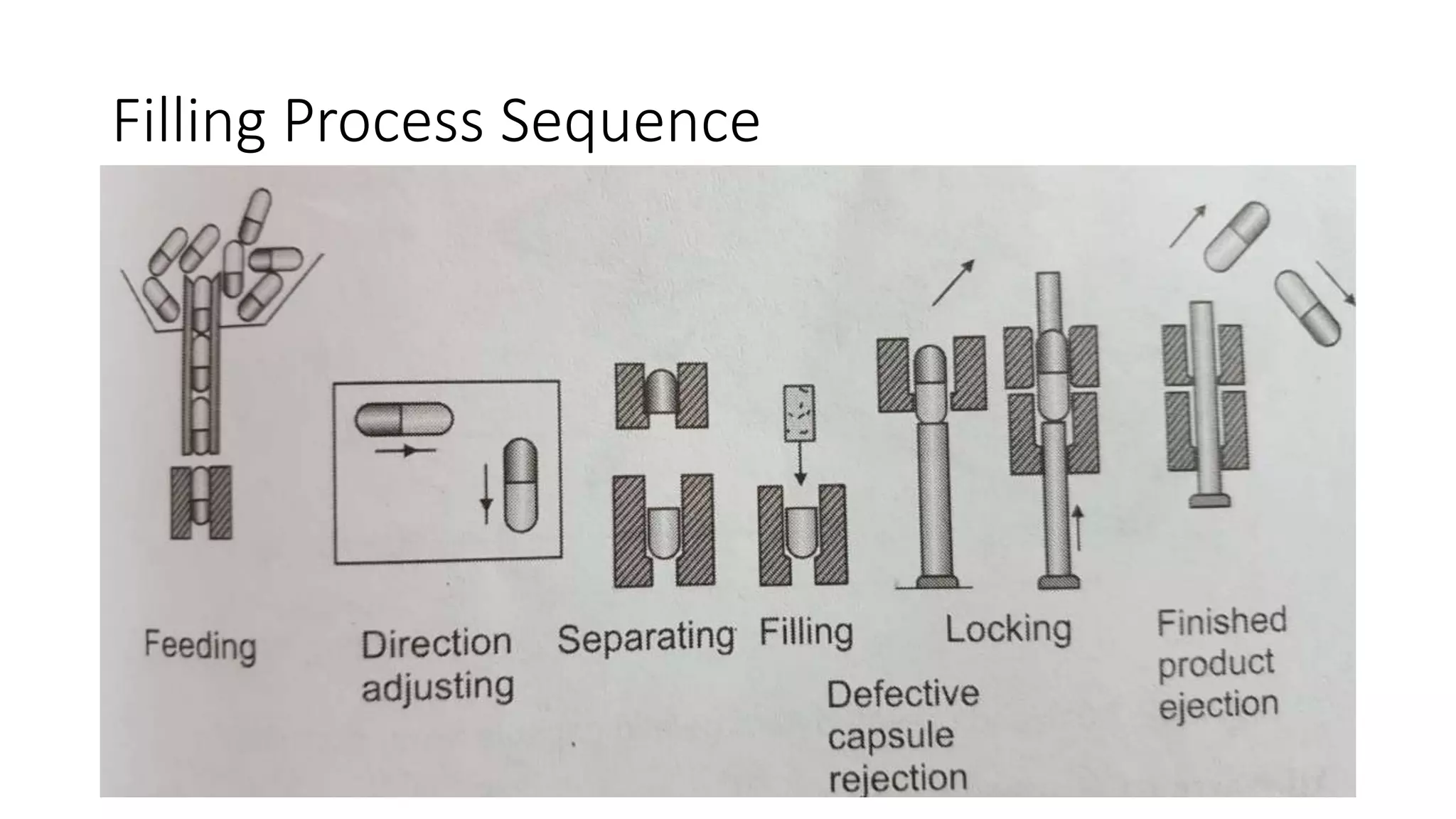
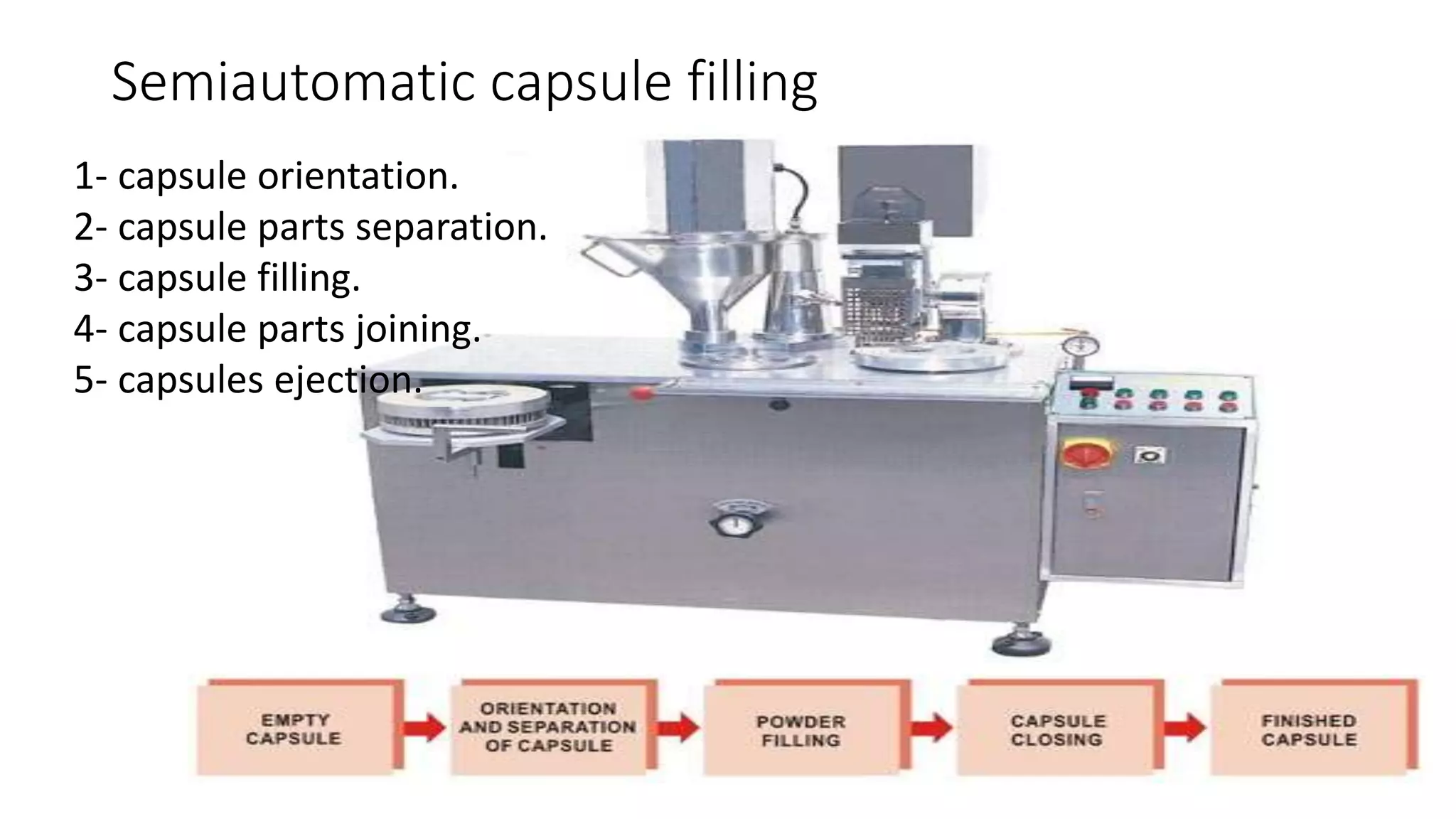
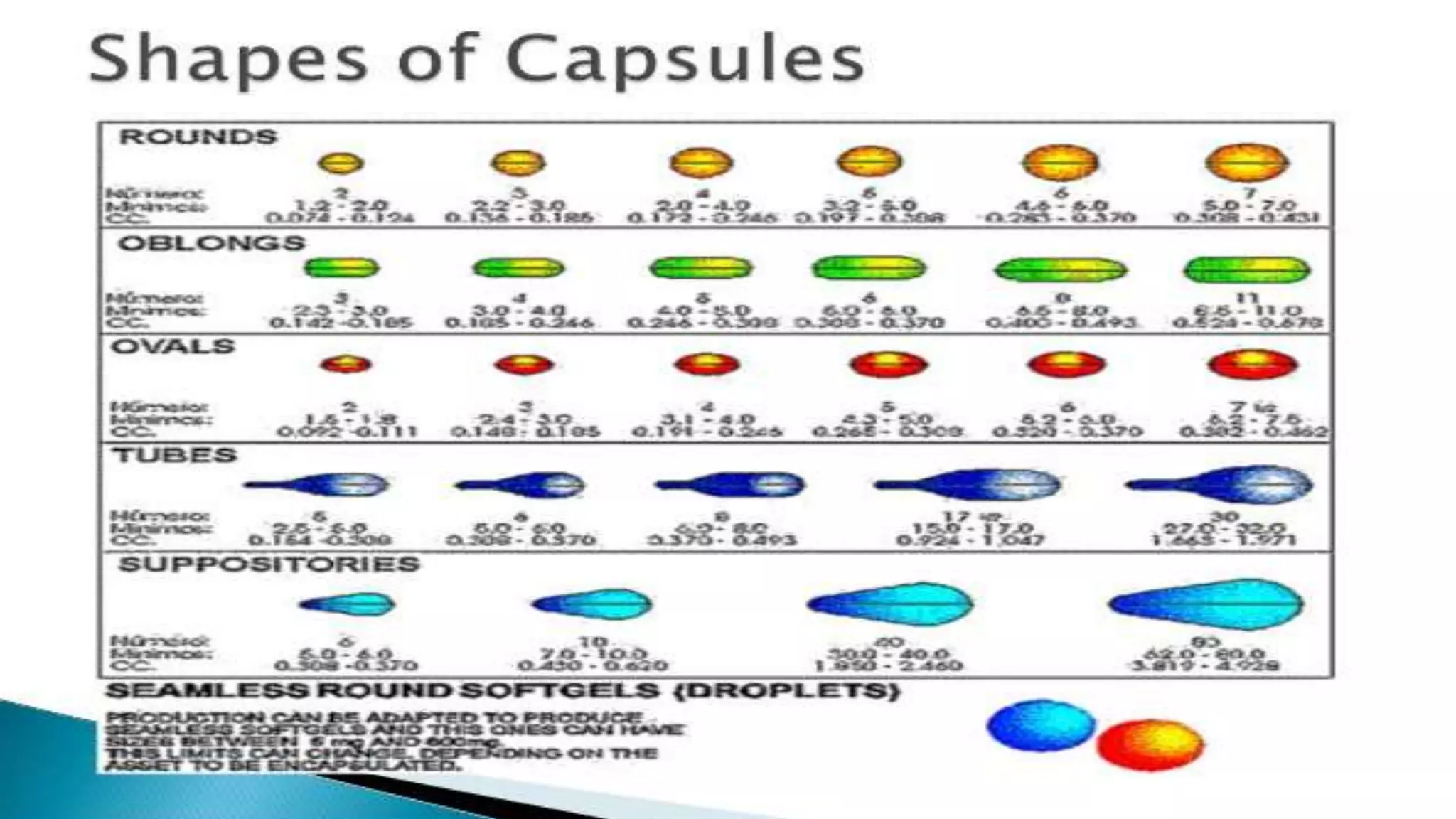
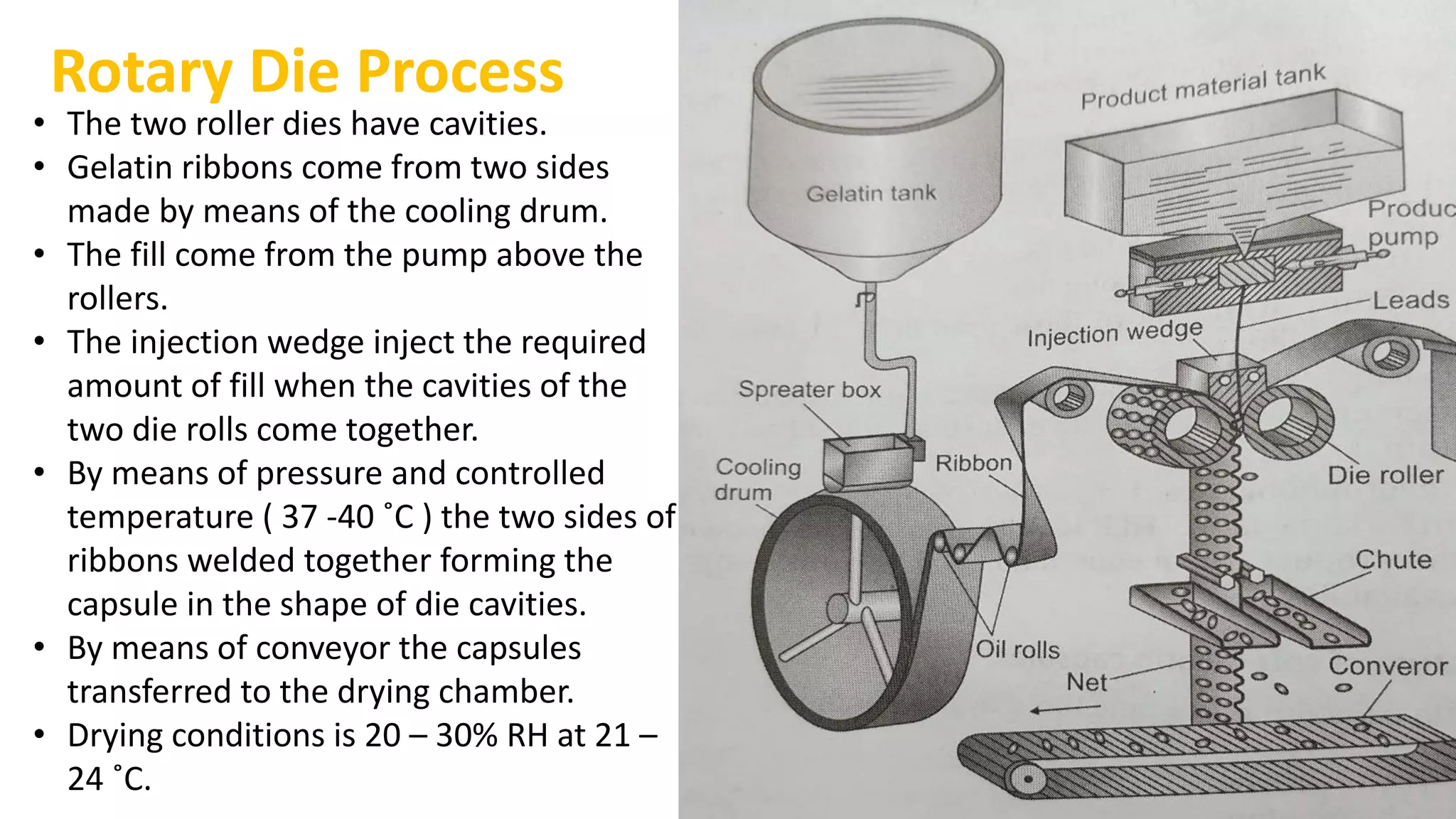
The document provides an overview of hard and soft gelatin capsules, detailing their definitions, manufacturing processes, advantages, and disadvantages. It discusses the stability, quality control measures, and specific formulation methods for both types of capsules. Additionally, it covers the types of gelatin used, filling processes, and the properties required for effective capsule production and use.