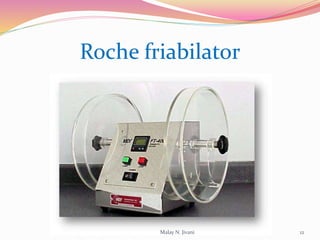
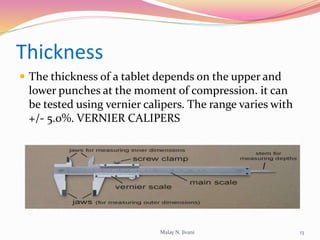
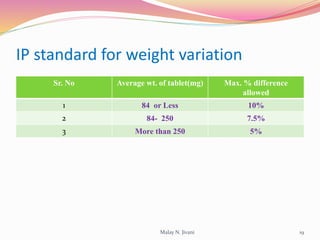
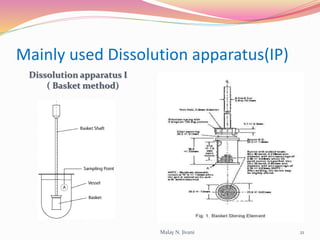
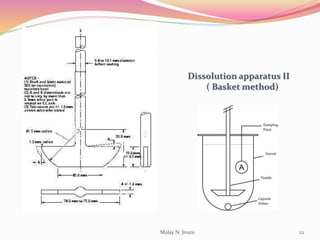
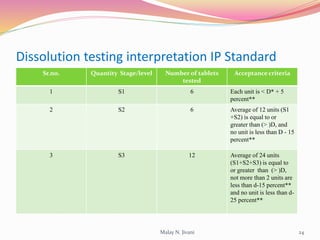
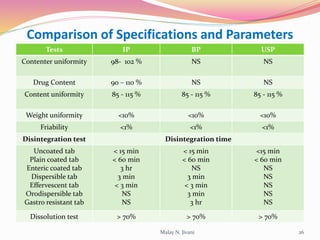
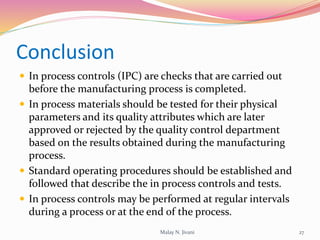
In-process quality control (IPQC) involves systematic procedures to ensure the quality of raw materials and finished dosage forms through various tests during manufacturing. It aims to minimize human errors, enforce established practices, and immediately detect abnormalities to maintain product integrity. Key tests include evaluating hardness, friability, thickness, disintegration, content uniformity, weight variation, and dissolution, which are pivotal in ensuring compliance with pharmaceutical standards.