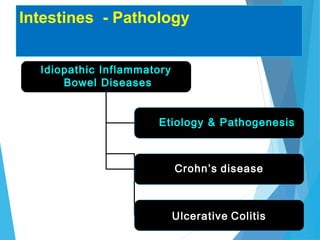
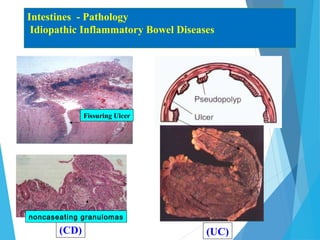
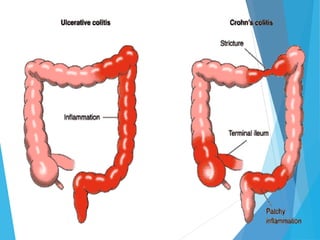
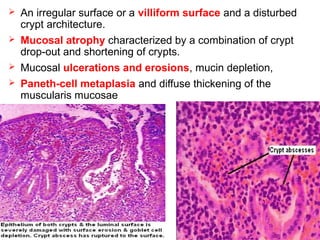
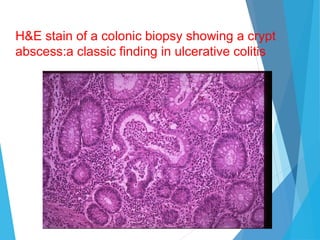
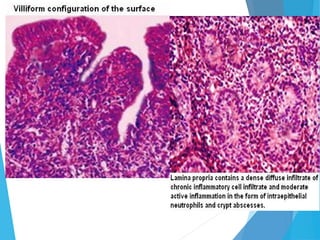
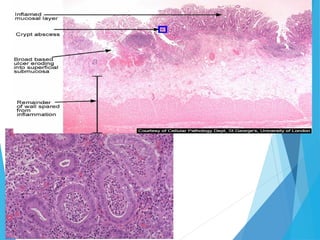
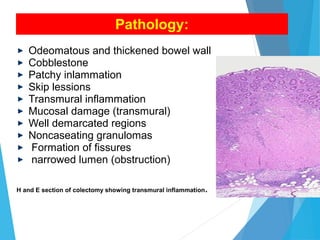
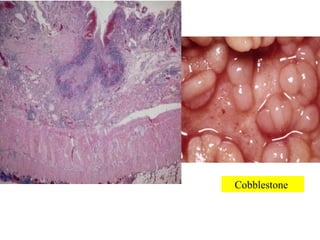
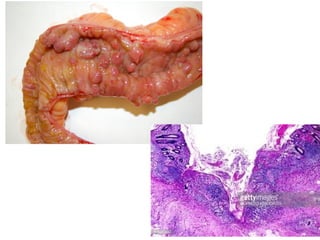
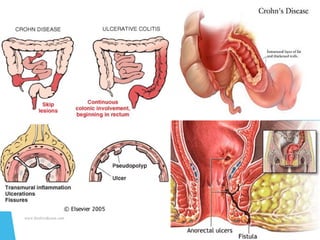
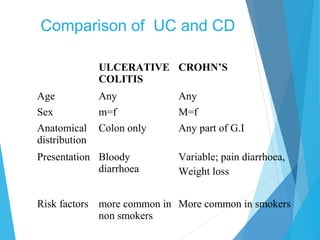
This document discusses inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. IBD is characterized by chronic, relapsing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract of unknown etiology. Ulcerative colitis only affects the large intestine, while Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and causes transmural inflammation. Both involve periods of disease activity and remission. Common symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea. Treatment involves dietary changes, medications like aminosalicylates and immunosuppressants, and sometimes surgery.








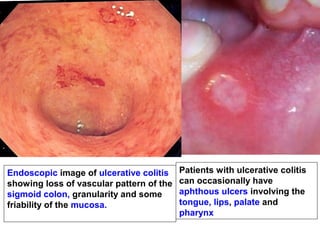
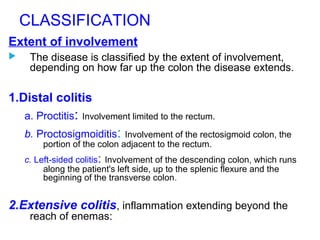



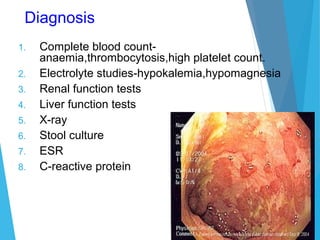



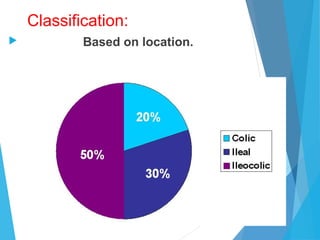












![Clinical Manifestation
Usually affects individuals younger than 45.
Decreased incidence in older individuals
Women are 2-3 times more likely to have IBS.
[80% patients are women]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect-7-ibd-151207031627-lva1-app6892/85/inflammatory-bowel-disease-48-320.jpg)



