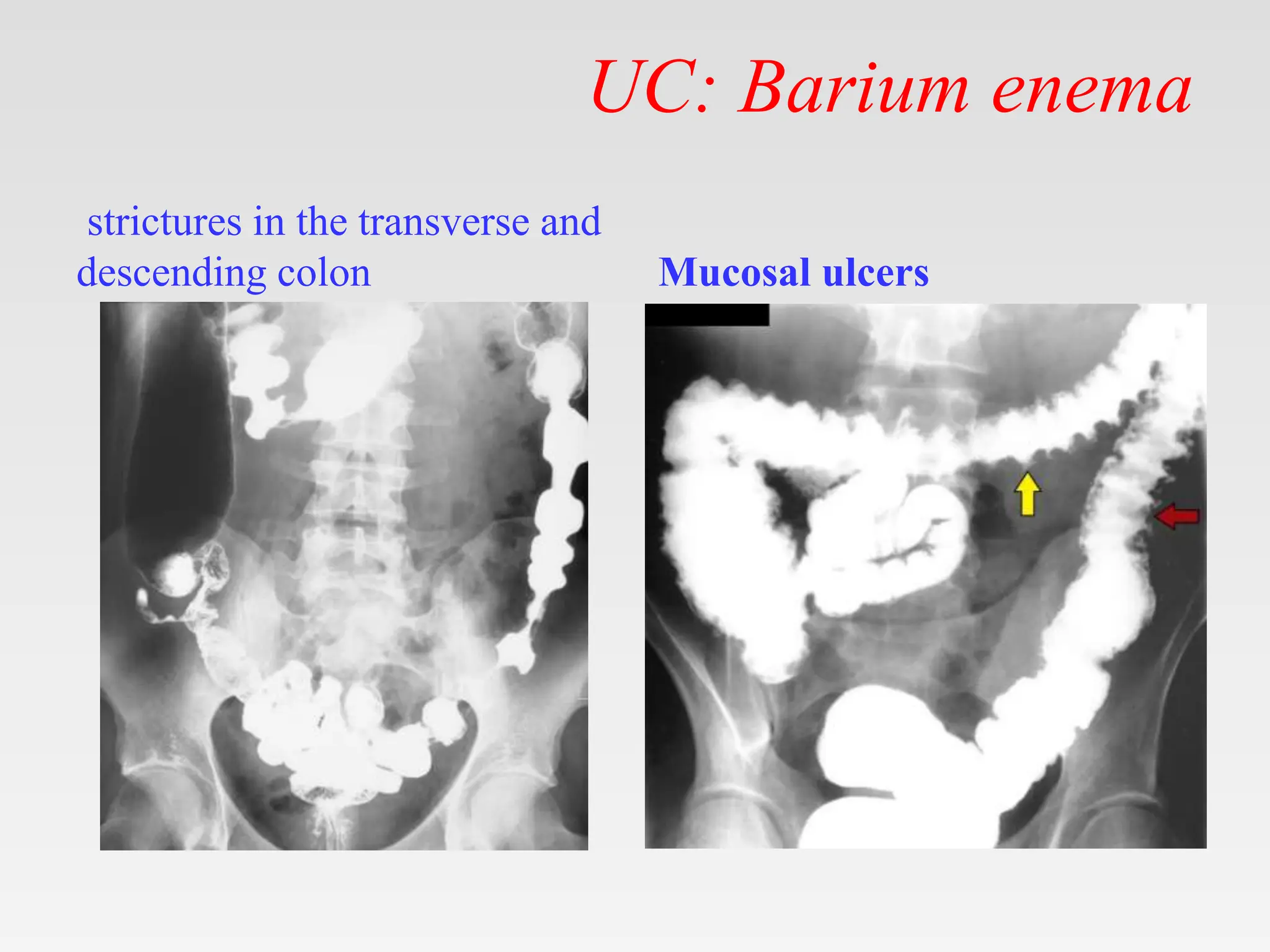
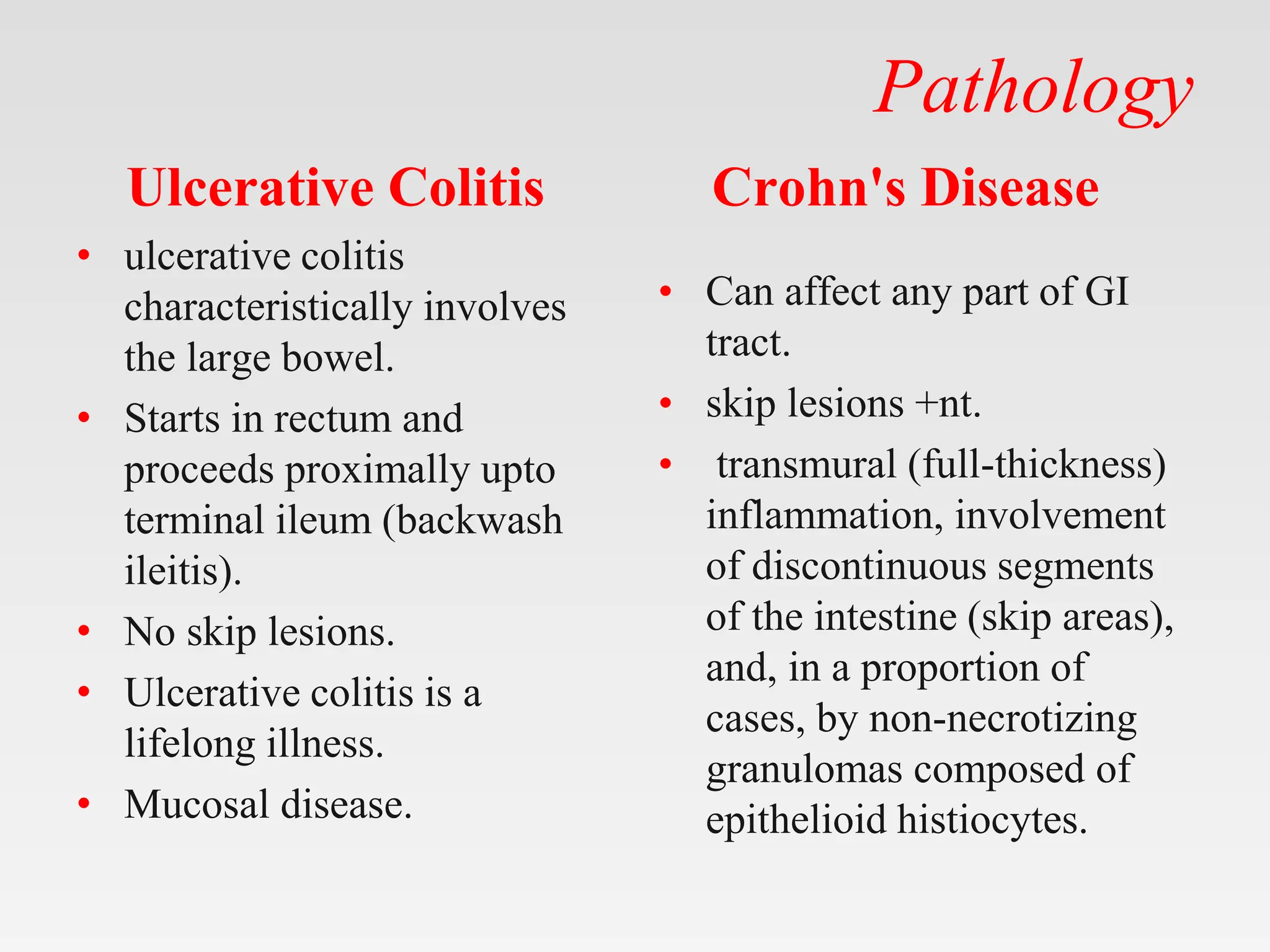
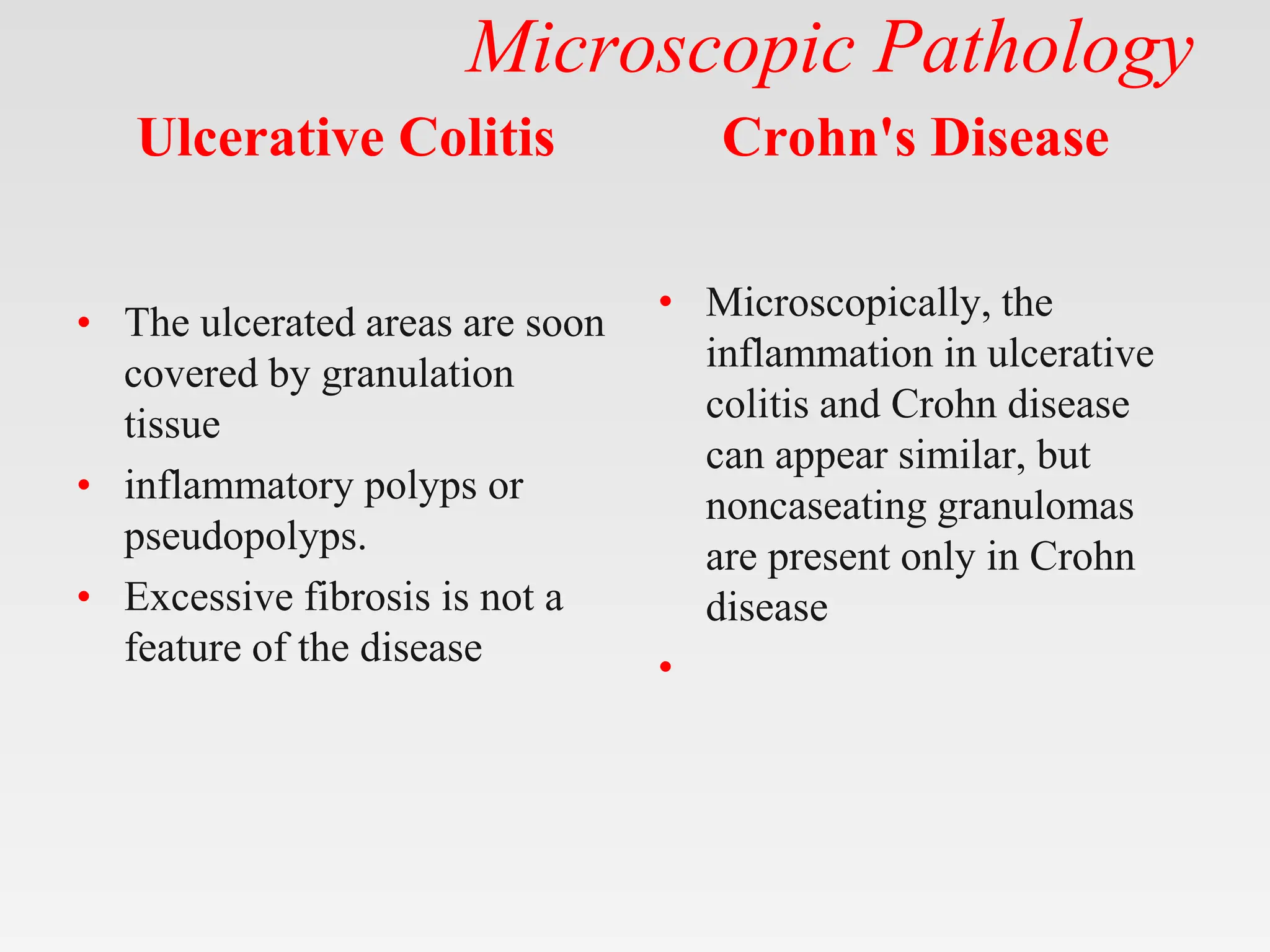
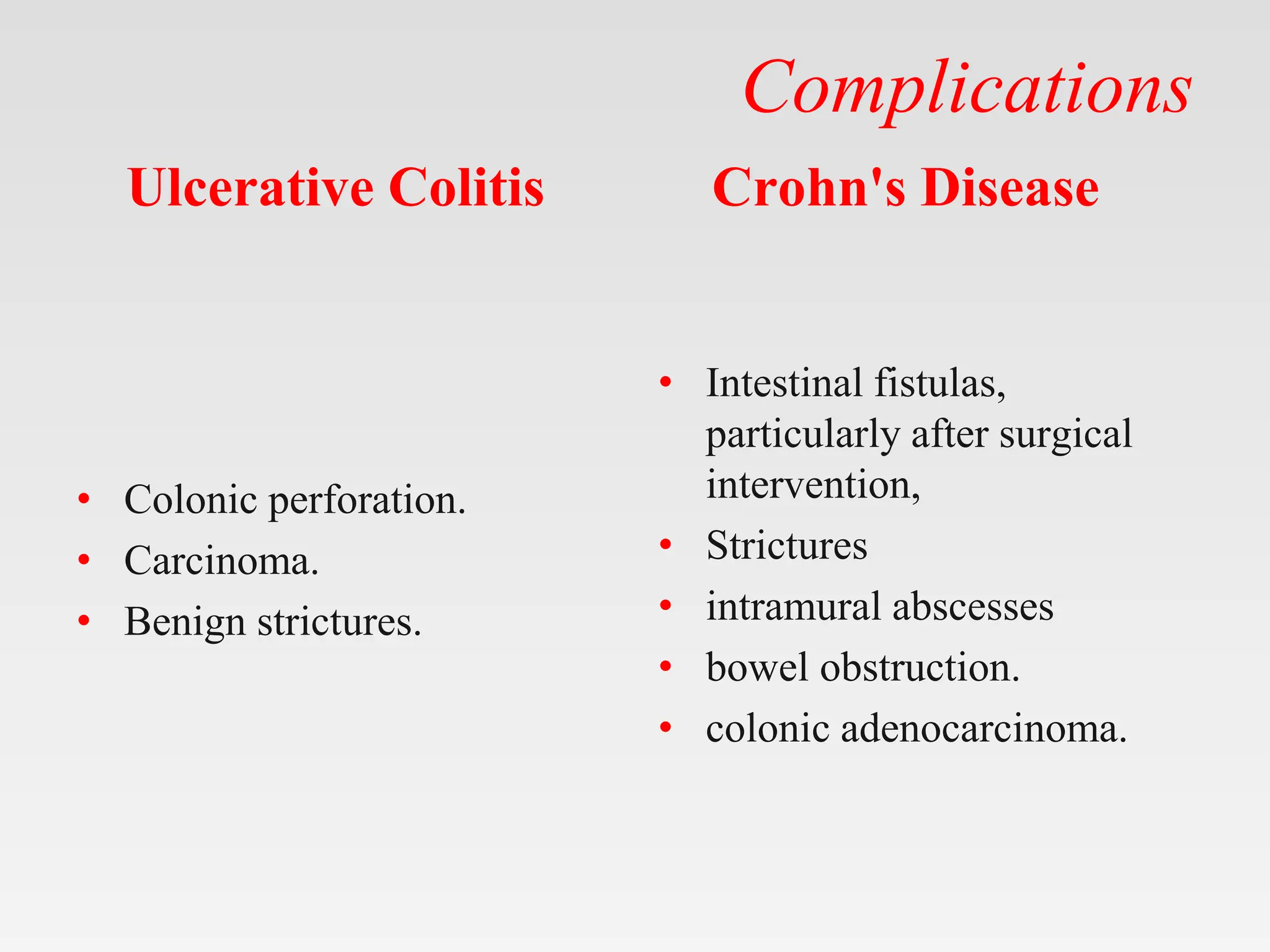
The document discusses inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), covering its two main forms: ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, including their pathology, etiology, demographics, symptoms, complications, and management strategies. Ulcerative colitis is characterized by inflammation confined to the mucosa of the large intestine, while Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract with transmural inflammation and skip lesions. Treatment options include aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biological therapies, with specific consideration for mild and moderate cases of both conditions.




























![Investigations
Ulcerative Colitis
• Serologic markers (eg,
antineutrophil cytoplasmic
antibodies [ANCA], anti–
Saccharomyces
cerevisiae antibodies [ASCA])
• Complete blood cell (CBC)
count
• Comprehensive metabolic
panel
• Inflammation markers (eg,
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
[ESR], C-reactive protein
[CRP])
• Stool assays
Crohn's Disease
• C-reactive protein (CRP)
and erythrocyte
sedimentation rate (ESR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflammatoryboweldiseaseclinicalrevised-240510164851-433585aa/75/Inflammatory-bowel-disease-clinical-revised-pptx-32-2048.jpg)