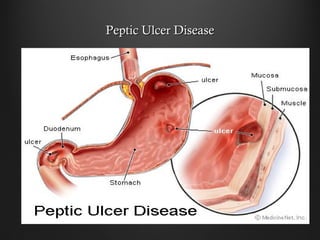
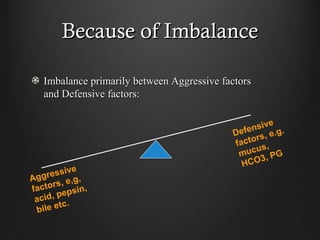
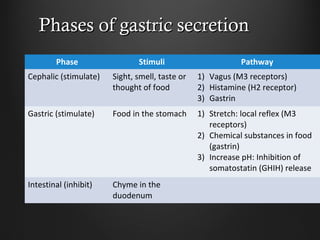
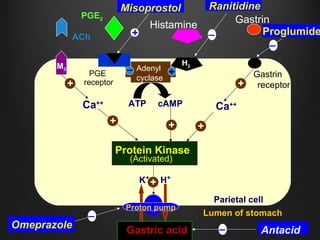
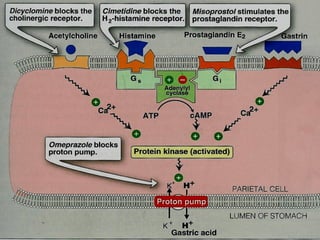
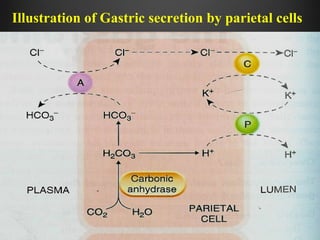
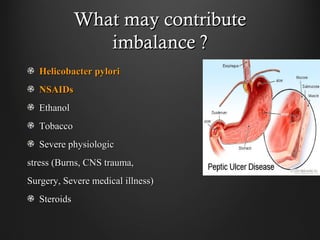
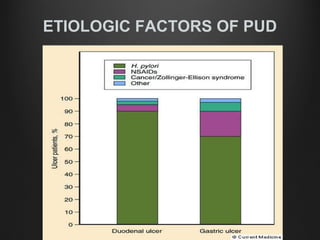
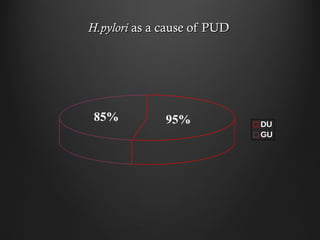
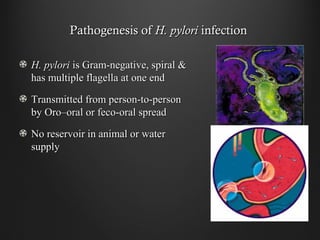
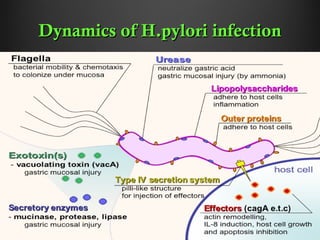
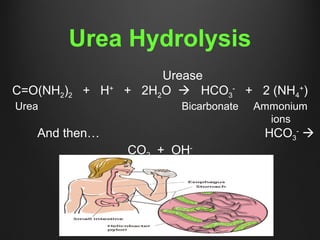
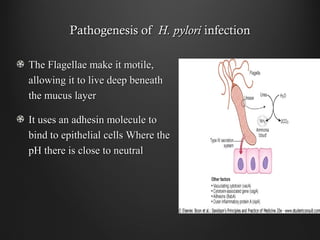
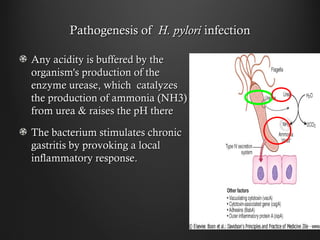
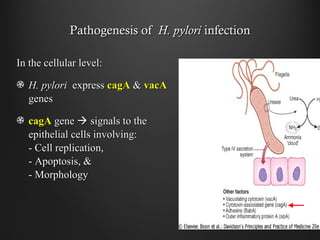
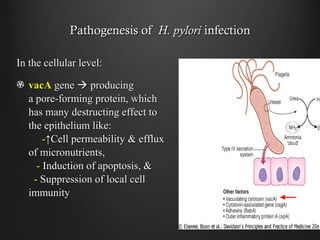
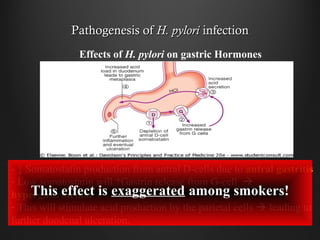
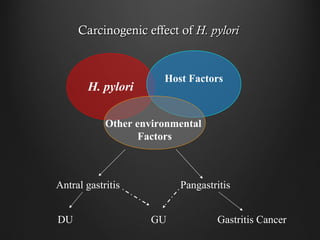
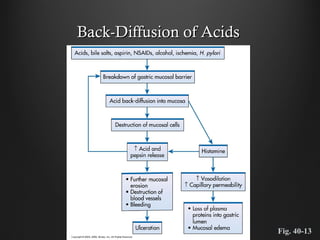
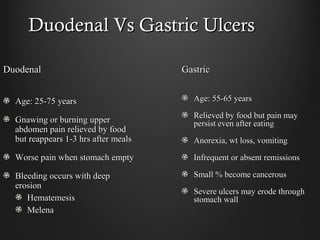
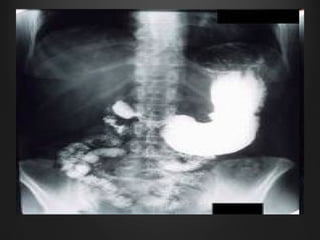
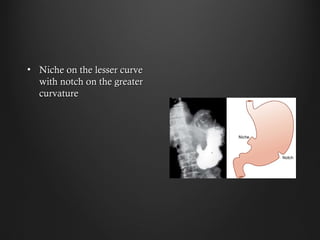
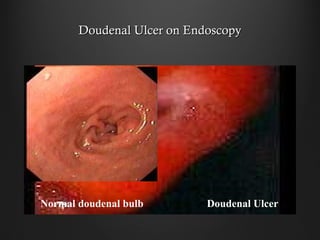
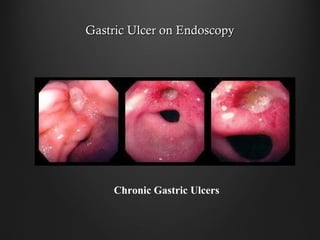
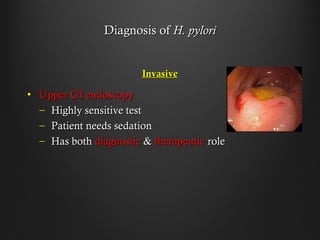
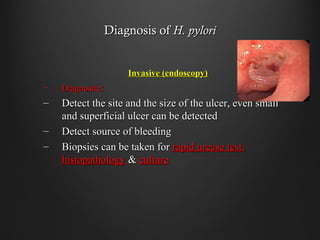
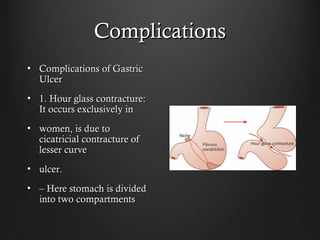
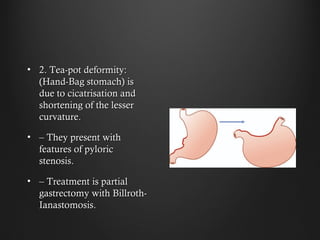
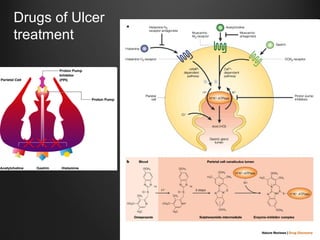
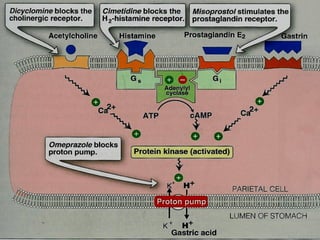
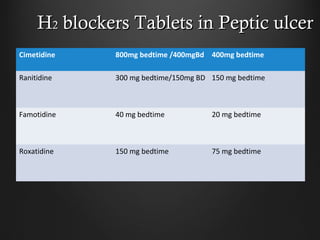
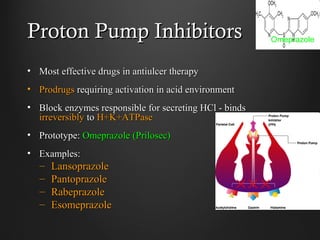
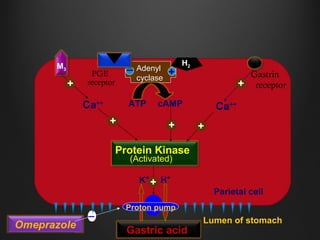
Helicobacter pylori infection and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the two most common causes of peptic ulcer disease (PUD). H. pylori infection, found in 70-80% of PUD cases, causes chronic gastritis and impairs the stomach's defenses, allowing acid to damage the lining. NSAIDs also impair defenses and can cause ulcers even in the absence of H. pylori. Together these factors disrupt the stomach's balance between aggressive acid and pepsin secretions and protective mucosal defenses, leading to ulcer formation.