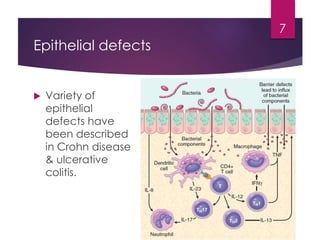
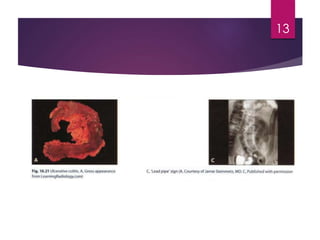
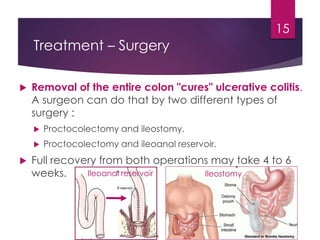
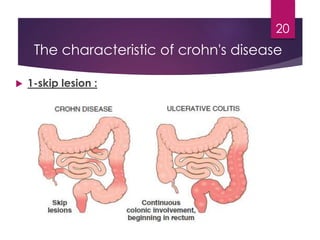
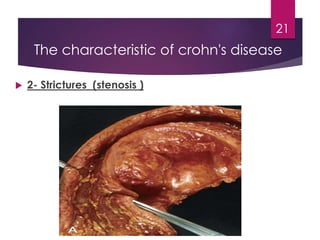
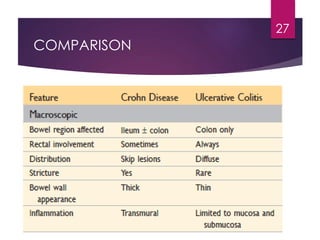
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes two major types: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and often involves the full thickness of the intestinal wall. Ulcerative colitis only involves the innermost layers of the colon and rectum. Both conditions result from an interaction between genetic, immune, environmental, and bacterial factors. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Treatment focuses on inducing remission through medications like aminosalicylates or surgery to remove the colon. Crohn's disease is characterized by "skip lesions" and strictures while ulcerative colitis causes inflammation and ulcers confined to the colon.