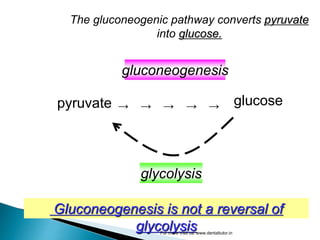
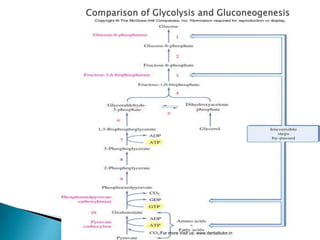
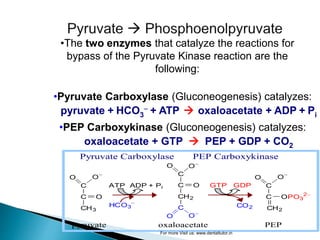
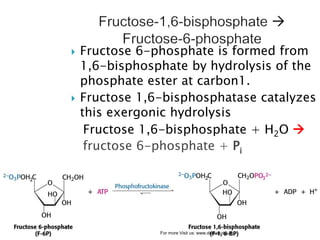
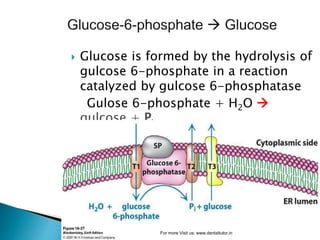
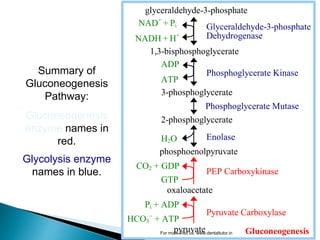
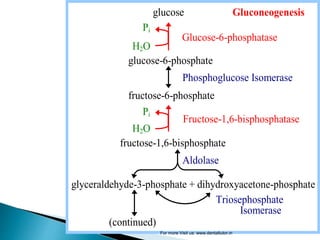
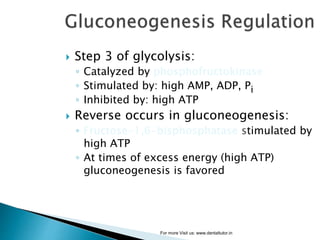
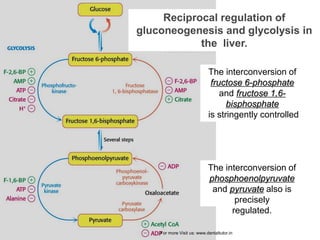
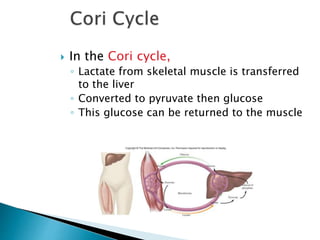
Gluconeogenesis is the process by which glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate precursors like lactate, glycerol, and certain amino acids. It occurs primarily in the liver and involves bypassing the three irreversible steps of glycolysis through different enzymes. Key enzymes in gluconeogenesis include pyruvate carboxylase and PEP carboxykinase which catalyze reactions to bypass pyruvate kinase. Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis share certain intermediate compounds but are not simple reversals of each other due to different enzymatic pathways. Regulation of these two processes helps determine whether glucose or glycogen will be synthesized or broken down depending on the body's energy needs.