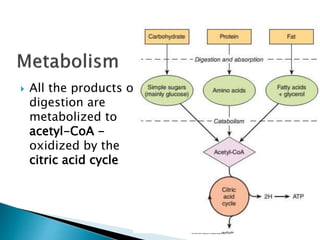
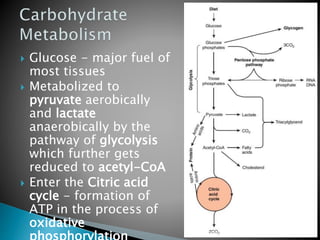
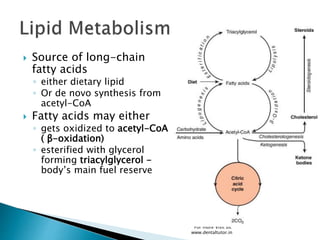
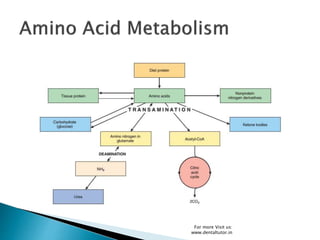
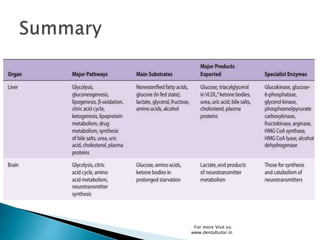
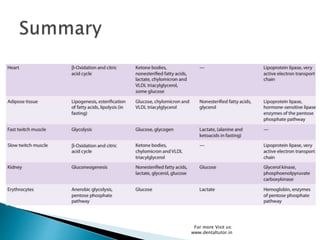
Metabolism involves the breakdown and synthesis of compounds in the body through various pathways. It falls into three main categories: catabolism, which breaks down molecules; anabolism, which builds molecules; and amphibolic pathways, which link the two. The document then discusses the metabolic pathways for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and other compounds, explaining how they are broken down to acetyl-CoA and enter the citric acid cycle to produce energy or are used to synthesize other molecules through various intermediates. Energy reserves such as glycogen and triglycerides are also formed and utilized depending on energy intake and expenditure.