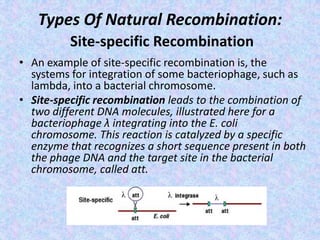
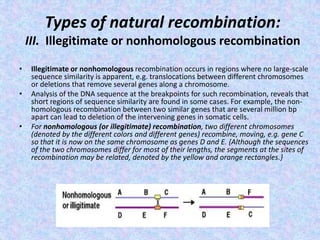
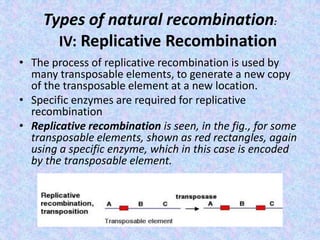
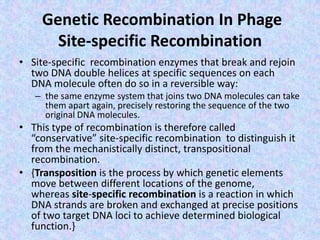
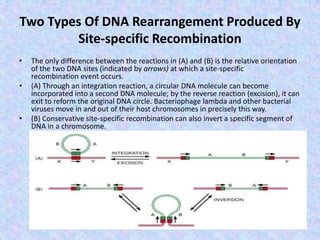
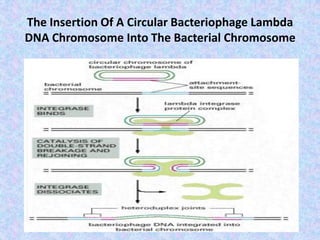
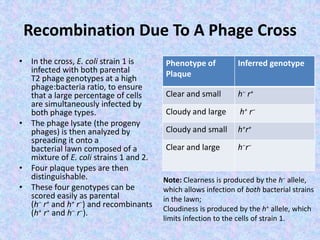
The document discusses genetic recombination mechanisms, particularly in phages, and categorizes them into four main types: general or homologous recombination, site-specific recombination, illegitimate or nonhomologous recombination, and replicative recombination. Each type has distinct processes and biological implications, such as the integration of bacteriophage genomes into bacterial chromosomes or the exchange of genetic material during mixed infections. The importance of these recombination events in genetic diversity and various biological systems is highlighted throughout the presentation.