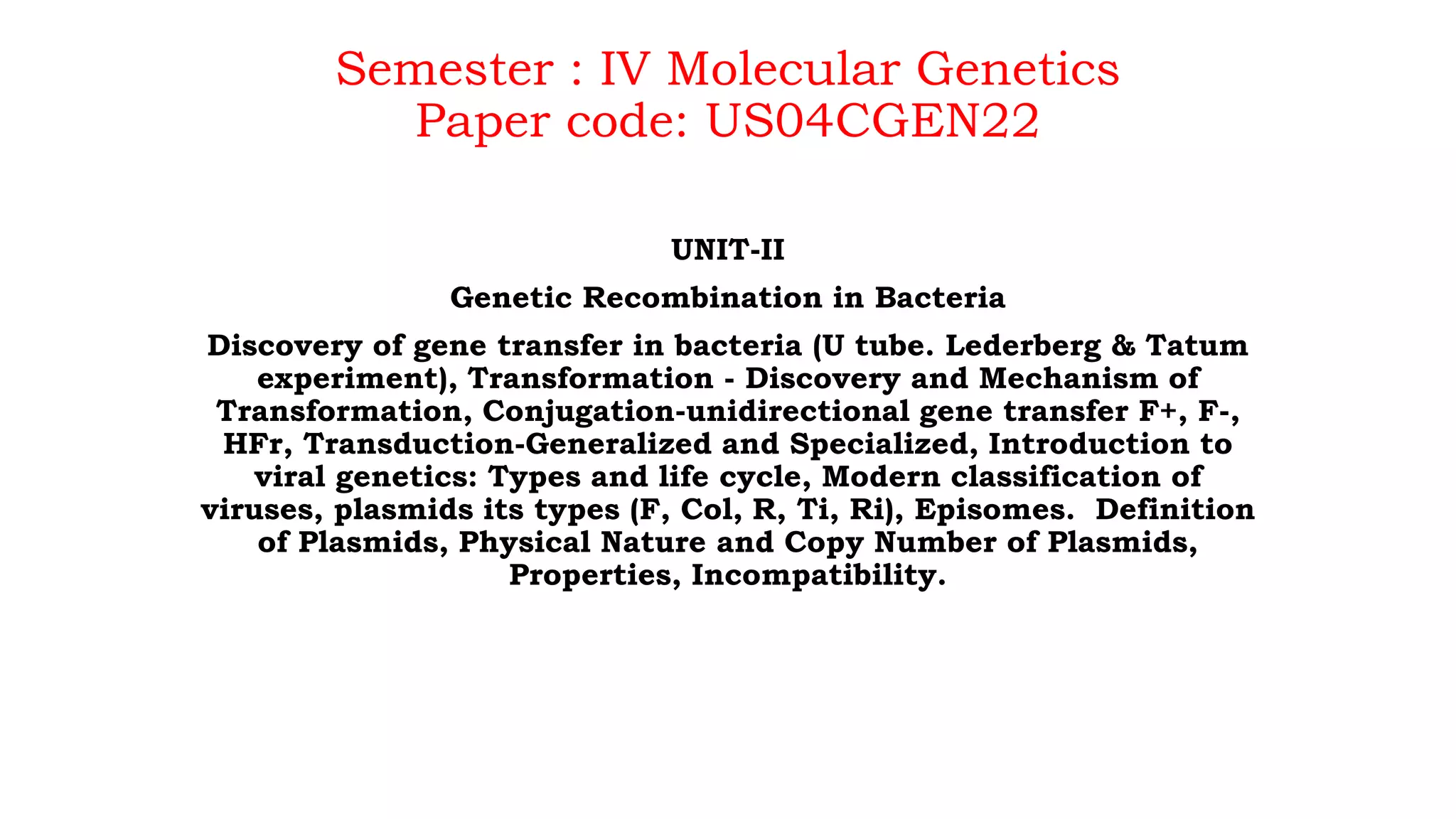
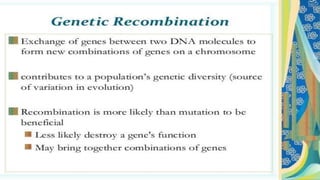
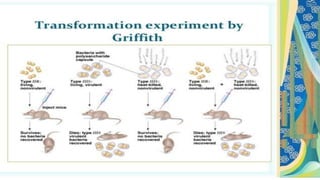
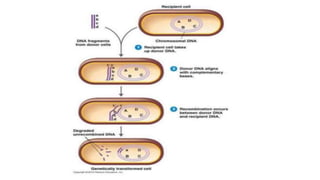
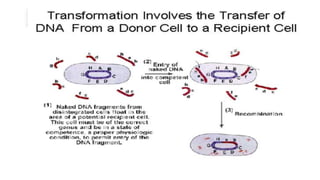
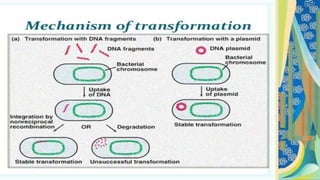
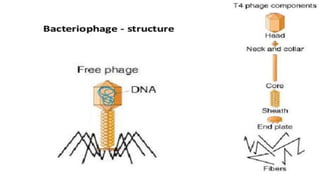
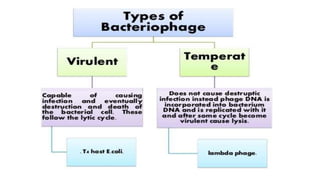
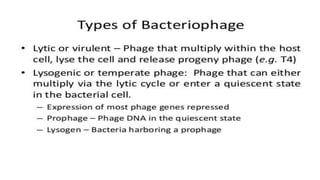
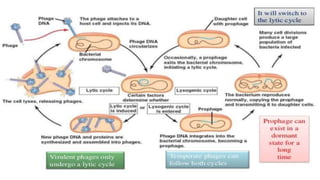
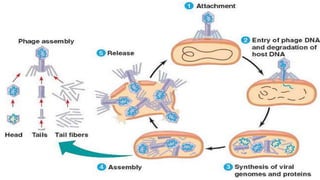
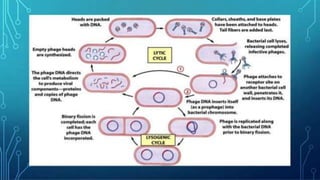
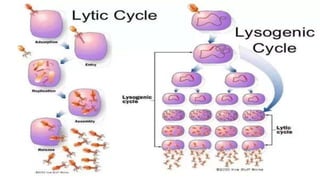
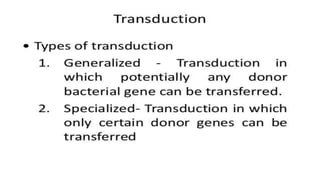
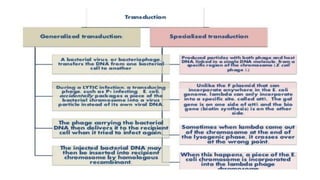
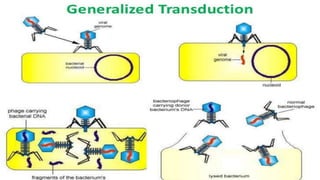
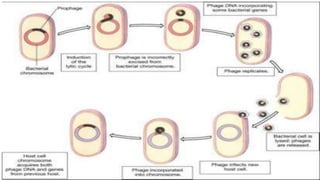
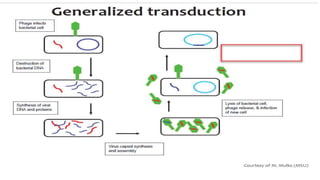
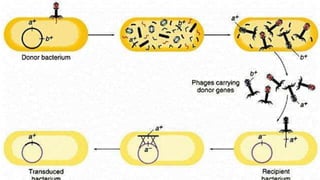
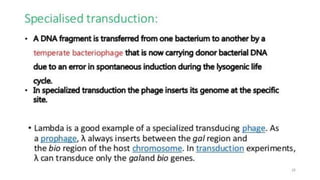
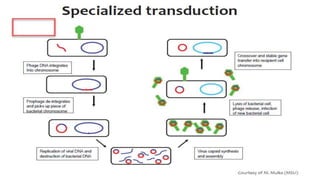
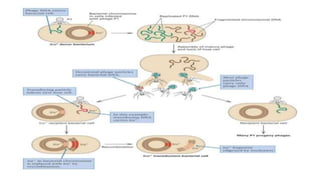
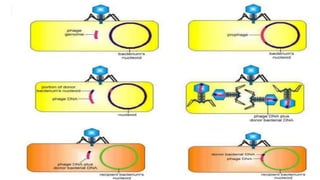
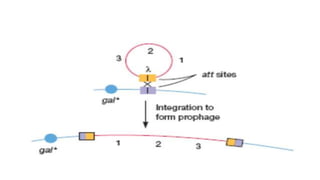
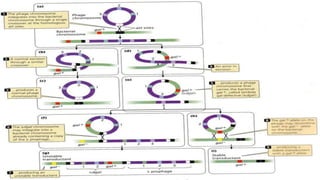
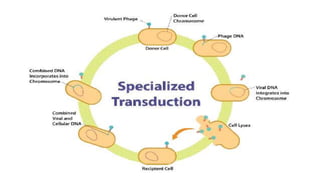
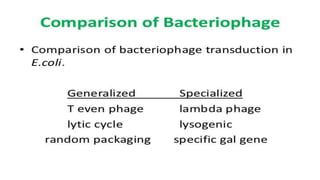
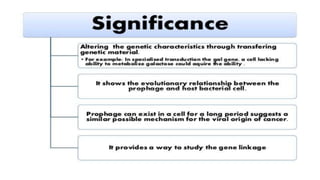
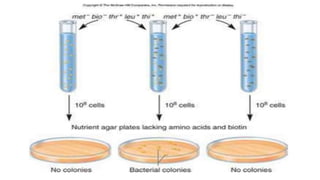
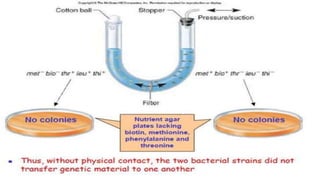
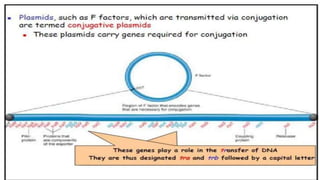
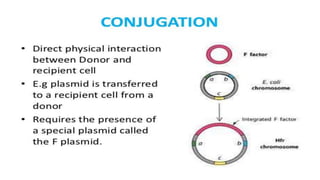
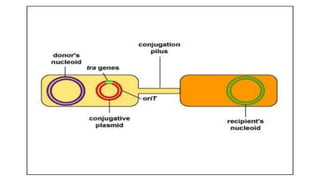
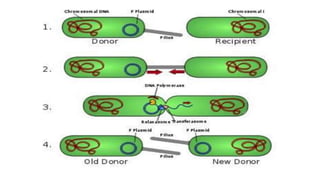
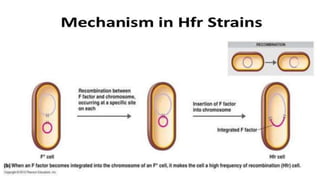
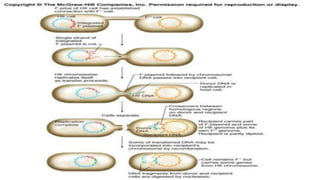
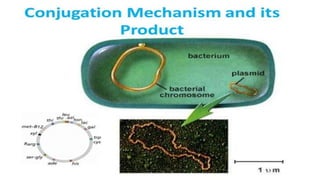
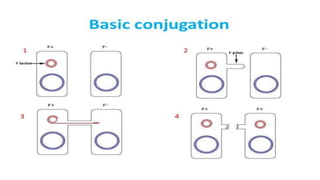
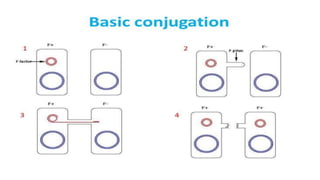
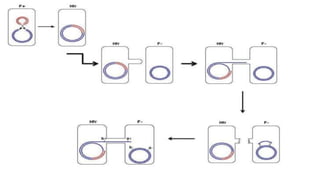
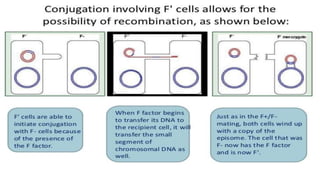
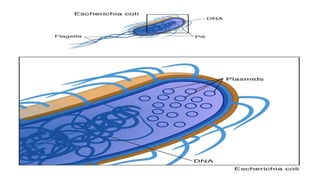
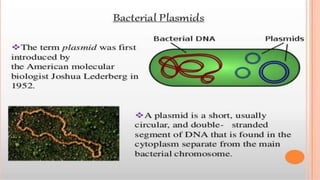
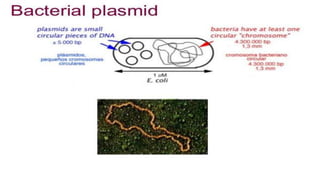
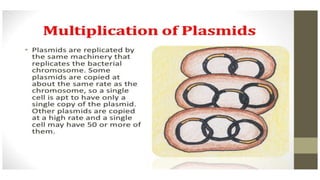
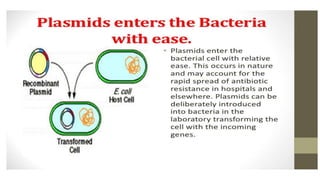
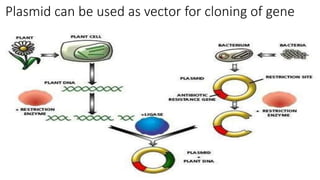
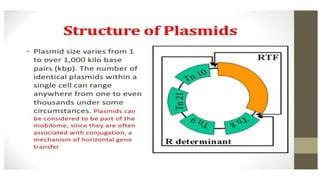
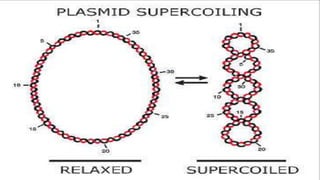
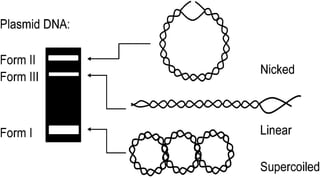
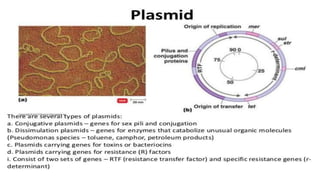
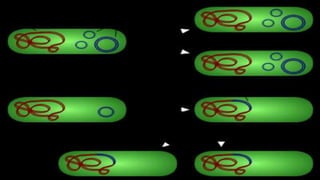
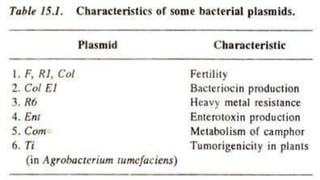
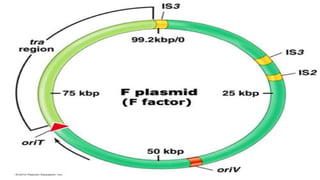
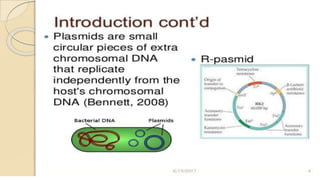
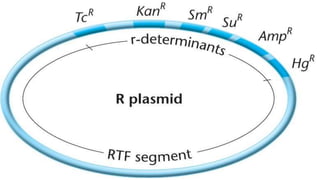
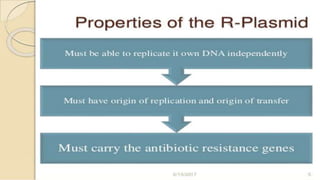
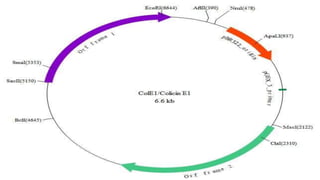
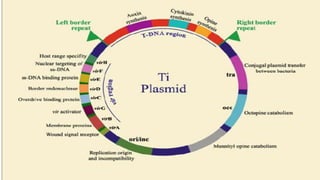
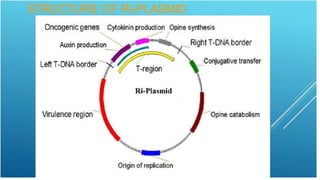
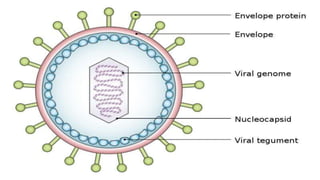
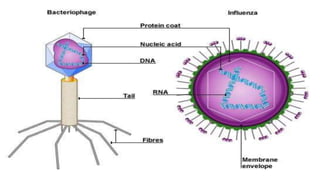
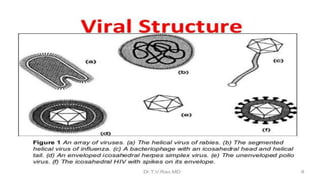
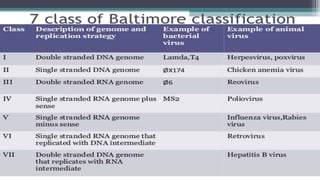
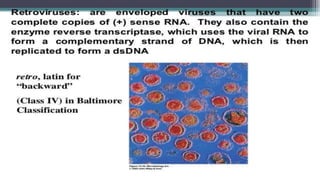
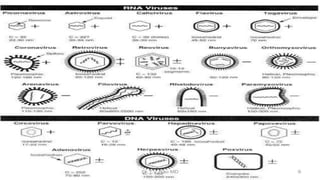
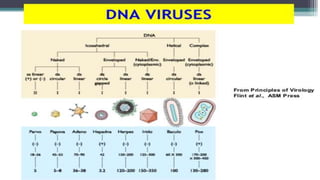
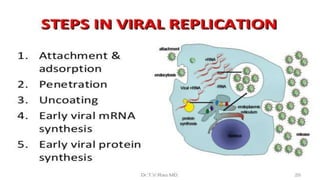
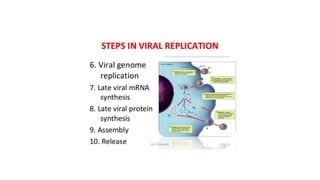
This document discusses genetic recombination in bacteria, including the discovery of gene transfer between bacteria through experiments by Lederberg and Tatum. It describes three main mechanisms of genetic recombination in bacteria: transformation, transduction, and conjugation. Transformation involves the uptake of extracellular DNA by bacteria. Transduction involves the transfer of bacterial DNA by bacteriophages. Conjugation involves the direct transfer of DNA between bacteria through cell-to-cell contact. The document also discusses plasmids, their types and properties, and introduces viral genetics and the classification of viruses.