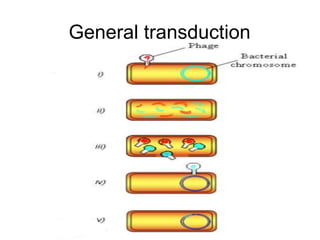
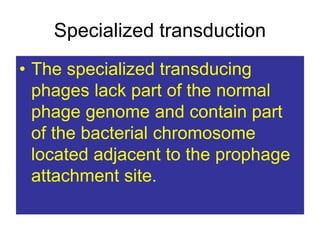
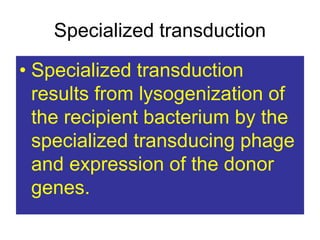
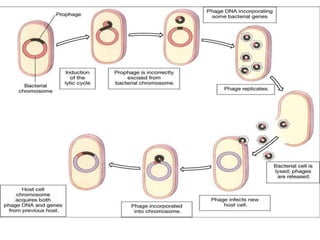
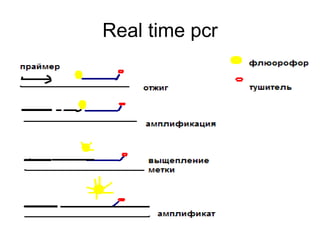
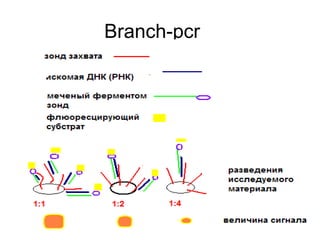
This document summarizes key information about bacterial genomes and genetic elements:
- Bacterial genomes vary in size and can contain one or more replicons like chromosomes and plasmids. Most bacteria have a single circular chromosome but some have linear or multiple chromosomes.
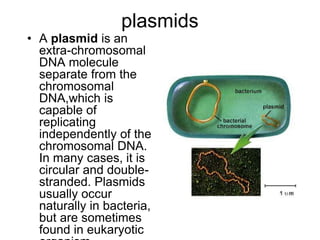
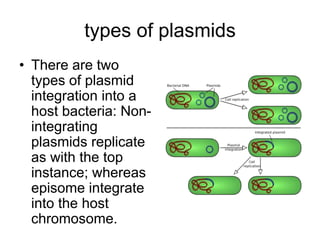
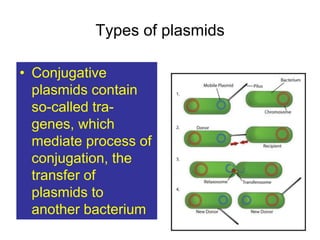
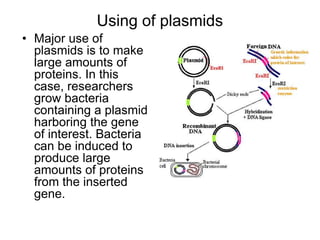
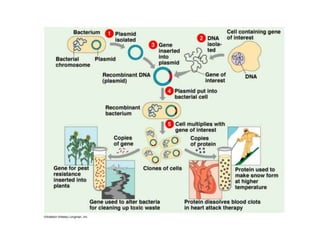
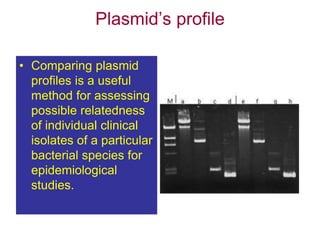
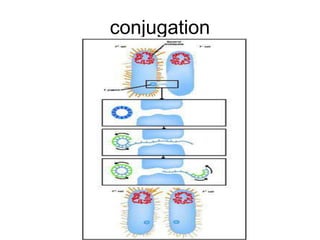
- Plasmids are extra-chromosomal DNA that can replicate independently. They often contain genes for functions like antibiotic resistance and virulence. Conjugative plasmids can transfer between bacteria.
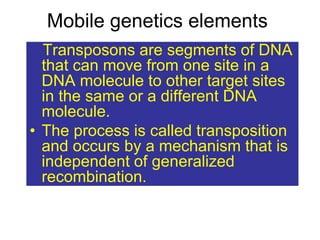
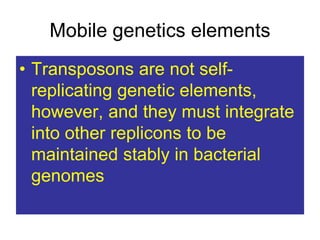
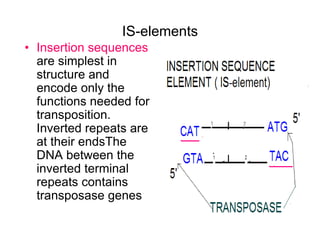
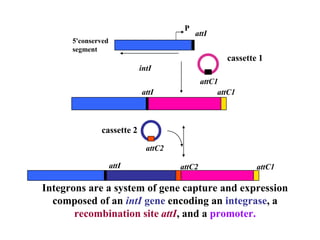
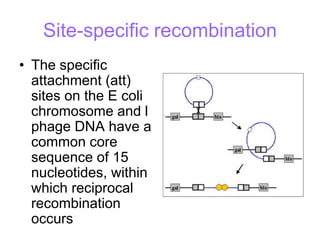
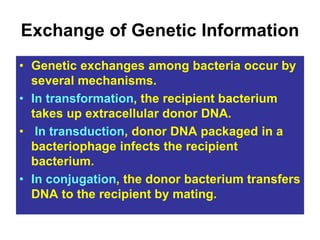
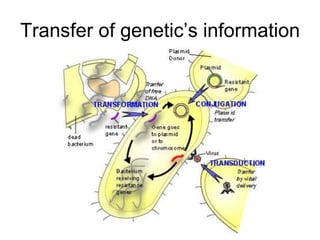
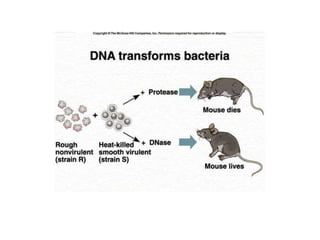
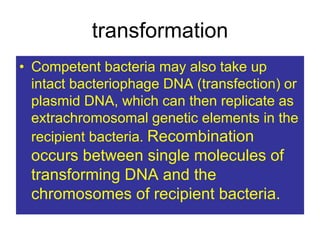
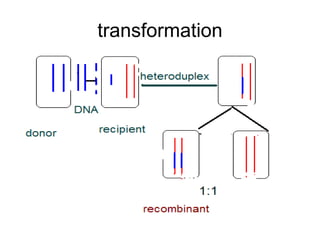
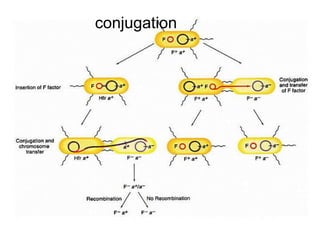
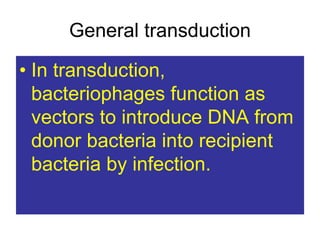
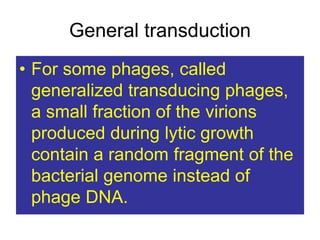
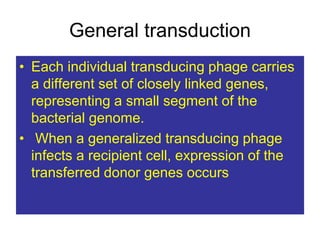
- Other mobile genetic elements like transposons and integrons can move resistance genes between replicons. Site-specific recombination and horizontal gene transfer through transformation, transduction, and conjugation allow for genetic exchange between bacteria.