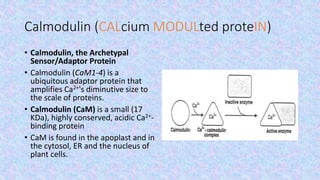
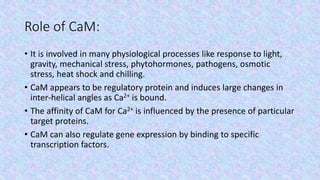
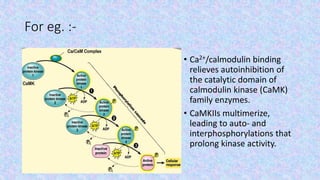
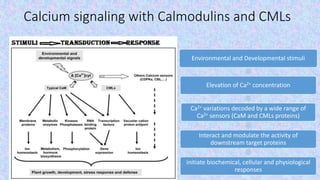
The document discusses the role of calcium-binding proteins, specifically calmodulin and its related proteins, in signal transduction processes within plant cells. It highlights how these proteins sense and respond to transient increases in cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels, their structural features, and their involvement in various physiological and stress-related responses. Calmodulin acts as a pivotal regulator in calcium signaling pathways, influencing processes like gene expression and stress responses by binding to specific target proteins.

![Calcium Binding Proteins
• Transient increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ in response to signals is
sensed by an array of Ca2+ sensors.
• Ca2+ sensors are small proteins that bind Ca2+ and change their
conformation in a Ca2+ dependent manner.
• Specificity in the signaling pathway is provided by
• the uniqueness in calcium signatures and
• by plethora of Ca2+ sensors, which can sense the deviation in
Ca2+ concentration, quite precisely.
• Once Ca2+ sensors decode the elevated [Ca2+]cyt, Ca2+efflux into the
cell exterior and/or the sequestration into cellular organelles such as
vacuoles, ER and mitochondria restores its levels to resting state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signaltransductioncalmodulin-210801154427/85/Calmodulin-2-320.jpg)