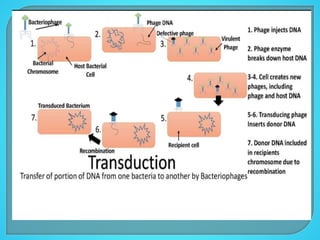
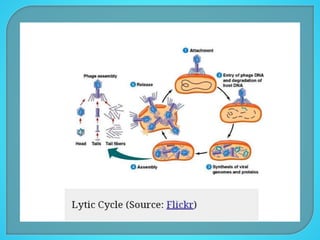
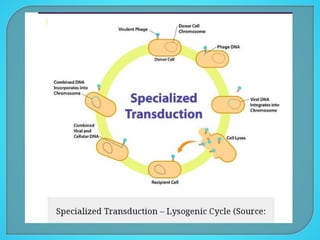
This document discusses bacterial transduction, which is a method of gene transfer between bacteria mediated by bacteriophages. There are two main types of transduction: generalized transduction, which occurs during the lytic cycle when viral genes are accidentally incorporated into the new host; and specialized transduction, which involves the specific insertion of viral DNA during lysogeny. Transduction contributes to genetic diversity and evolution in bacteria and can facilitate the spread of antibiotic resistance genes.