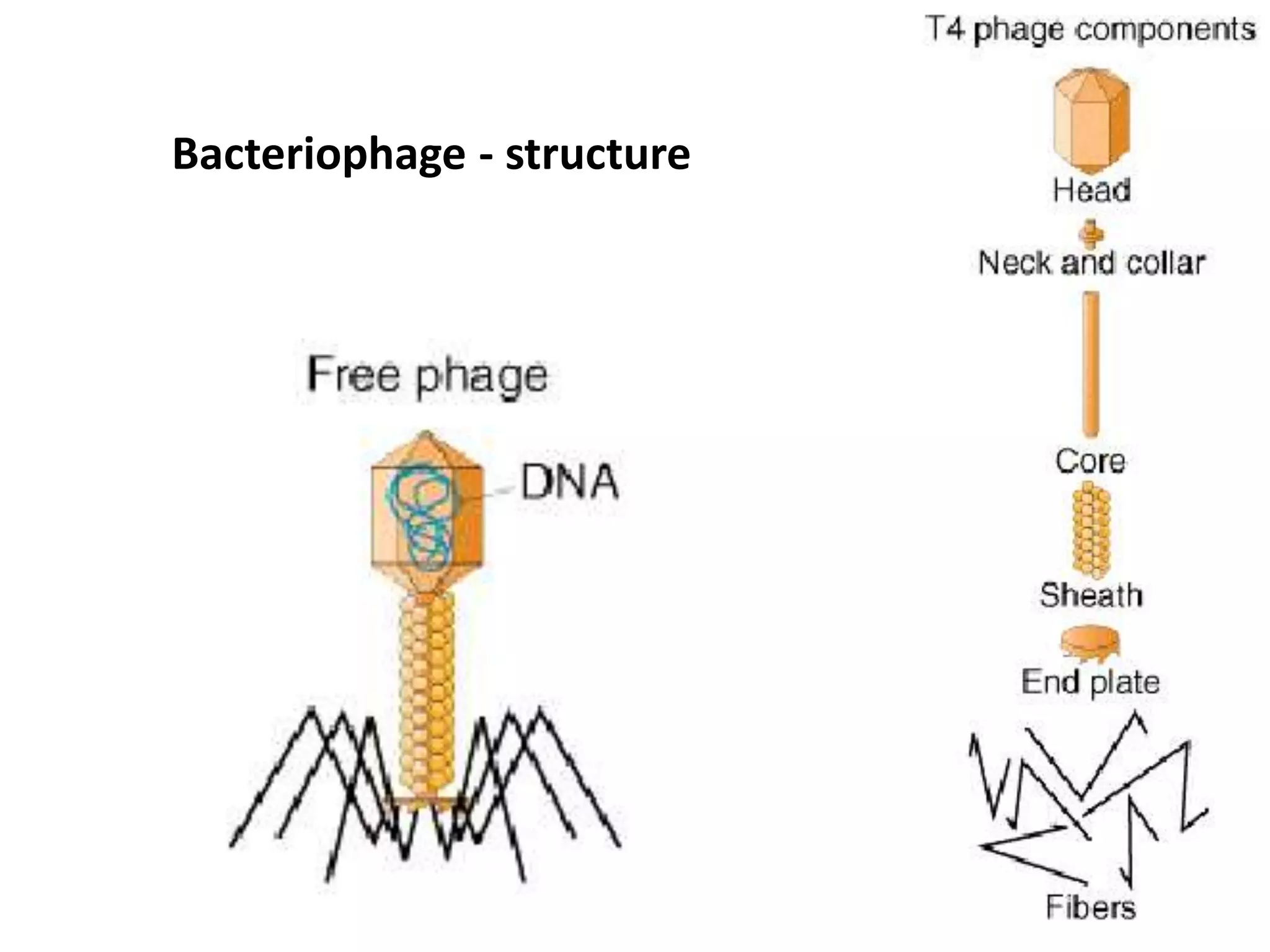
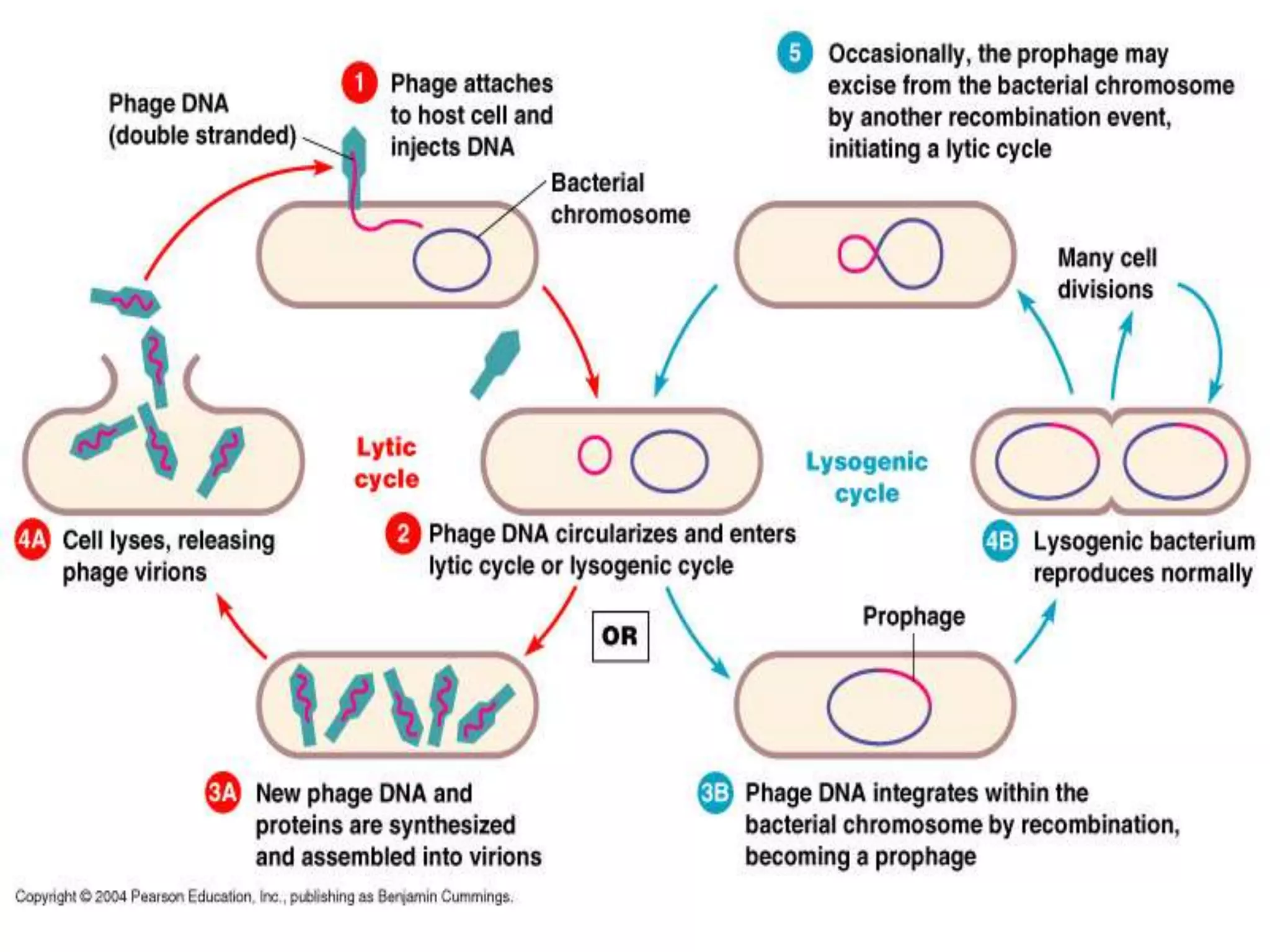
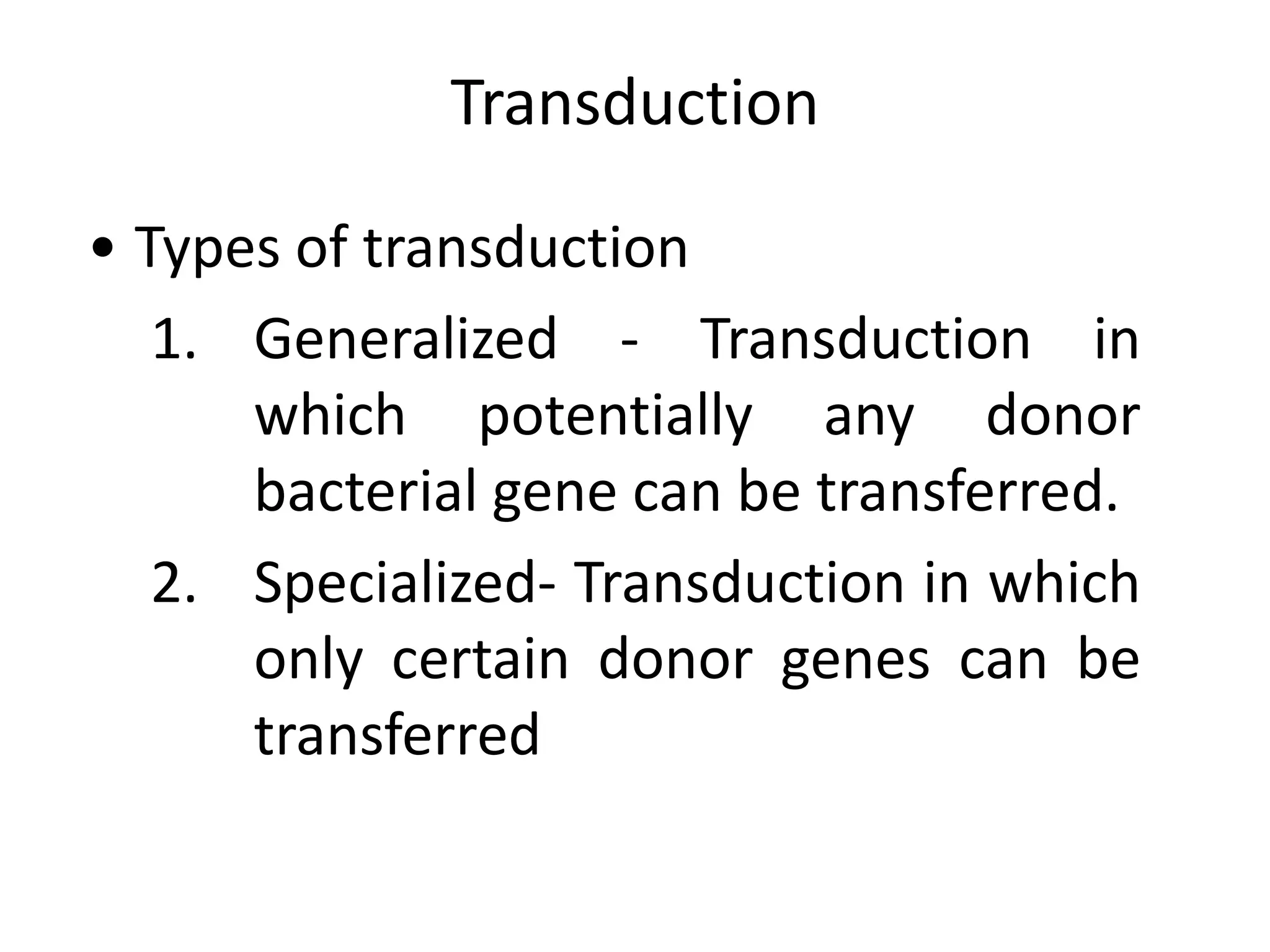
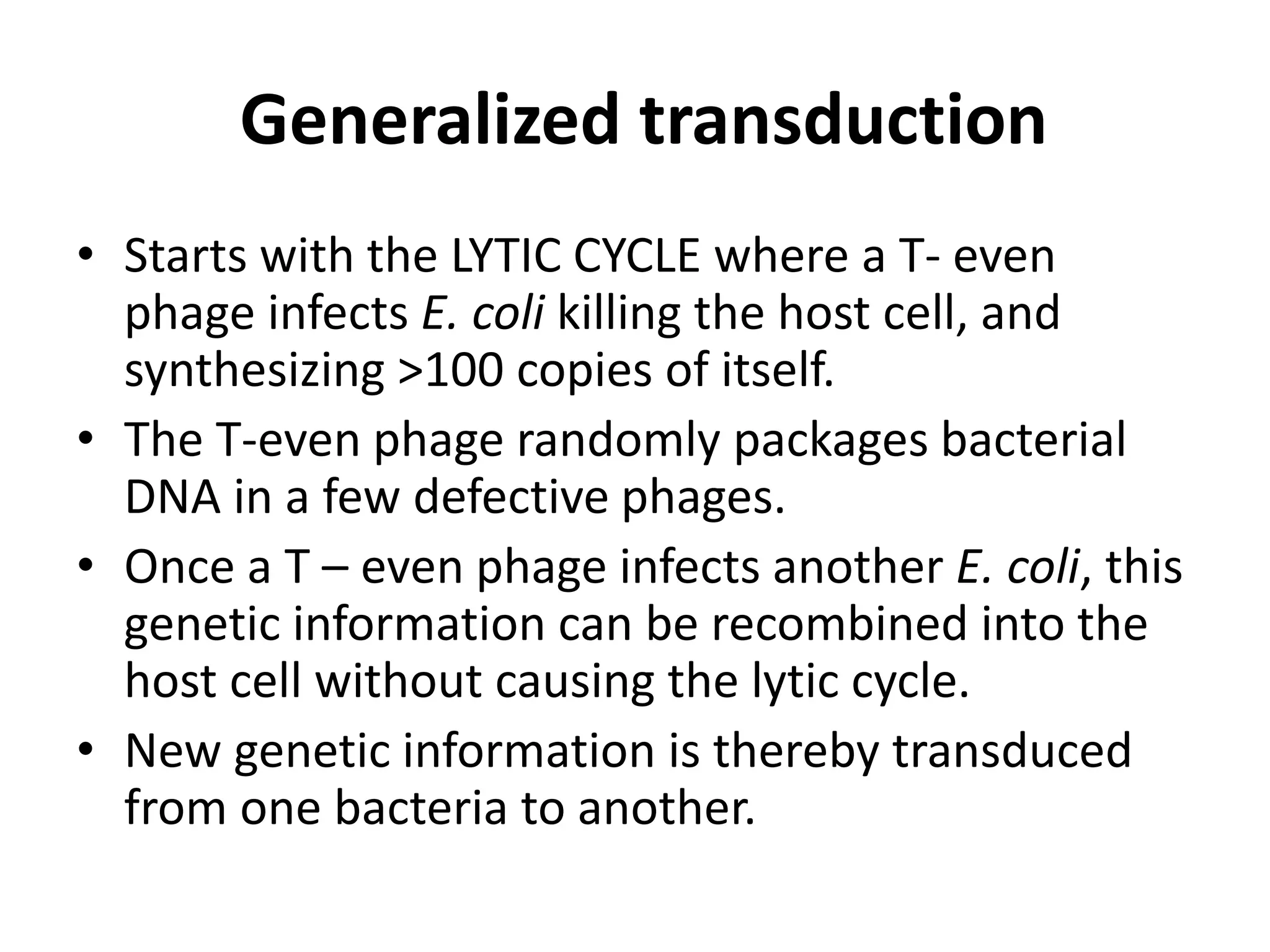
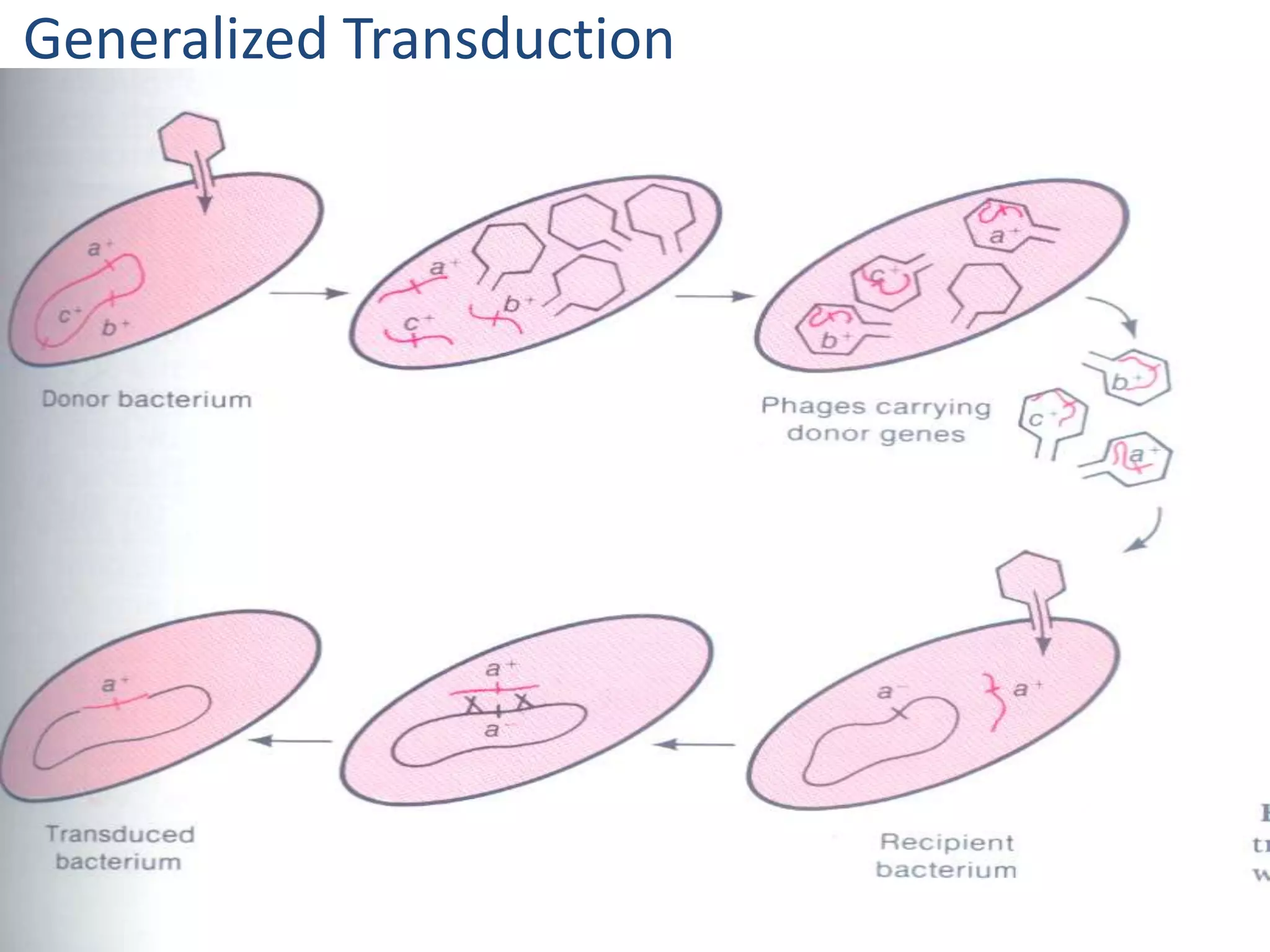
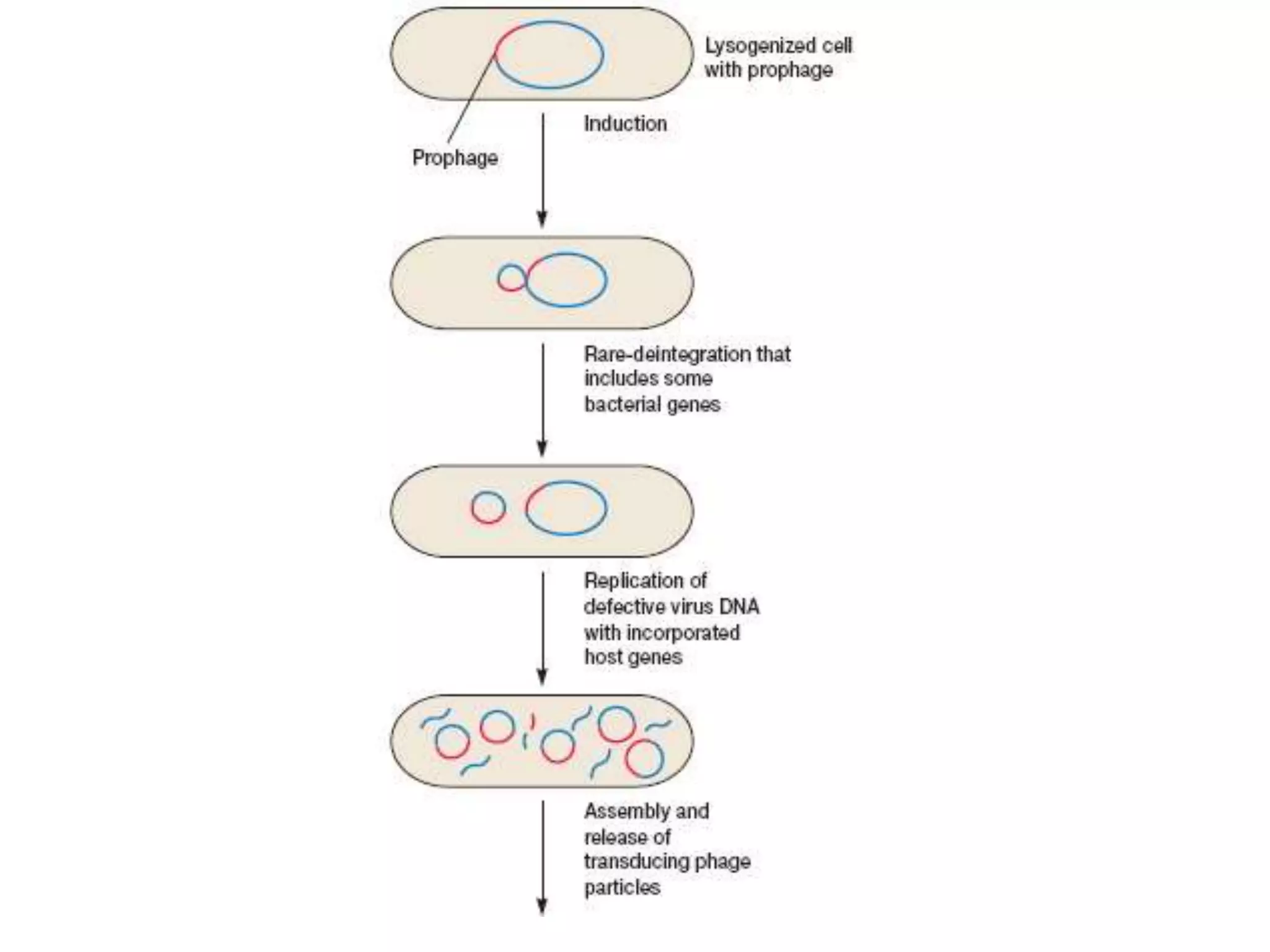
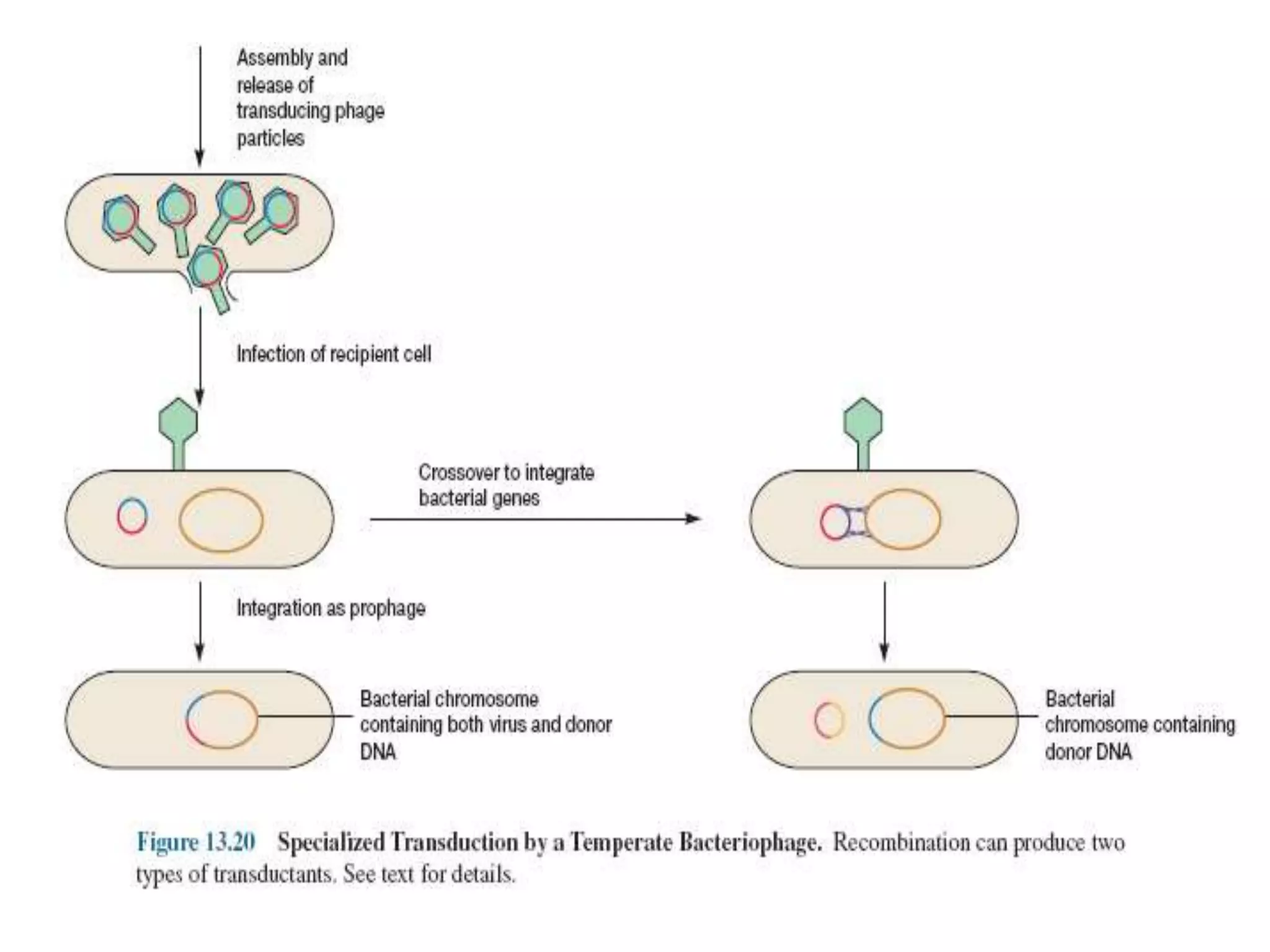
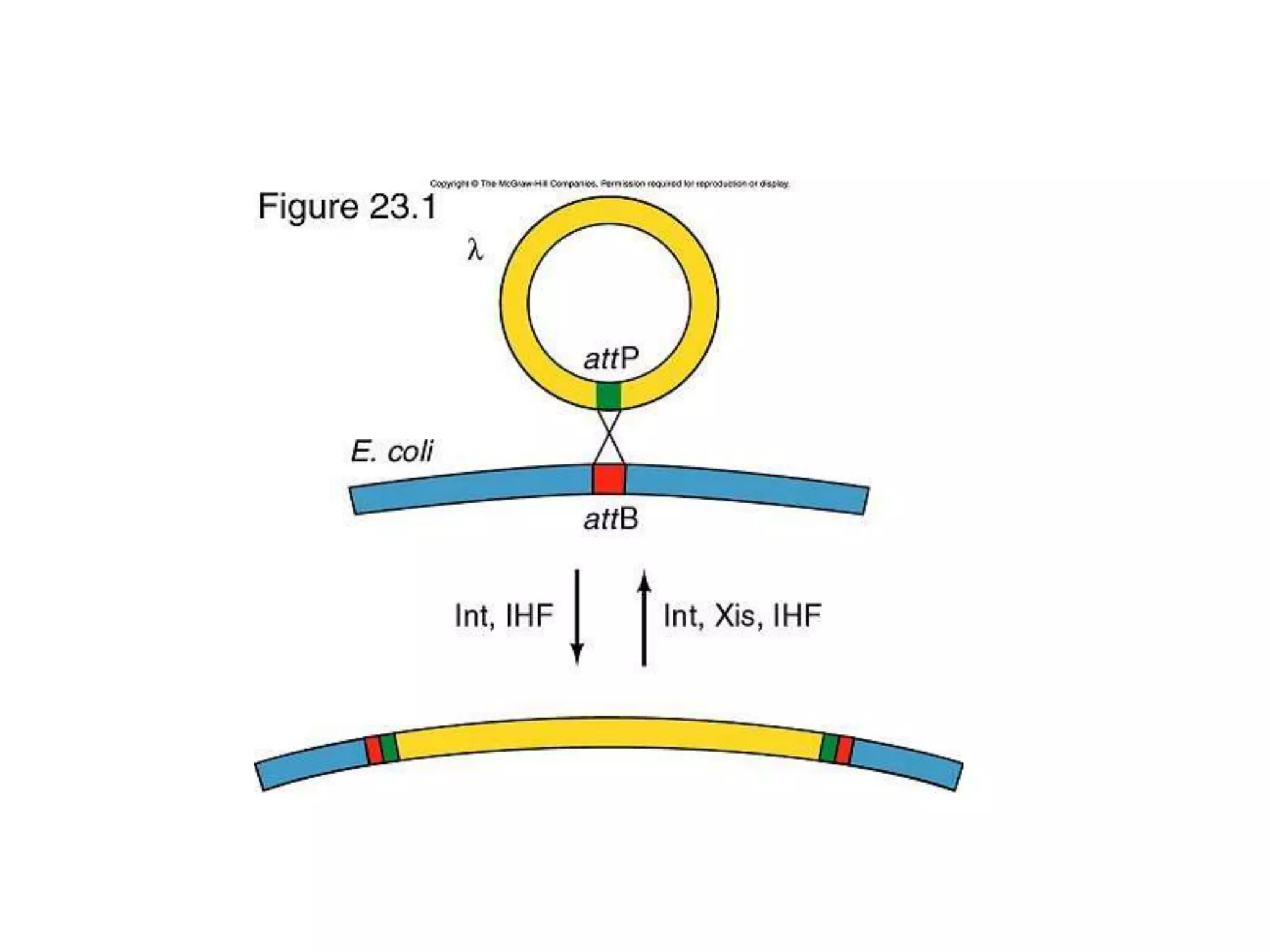
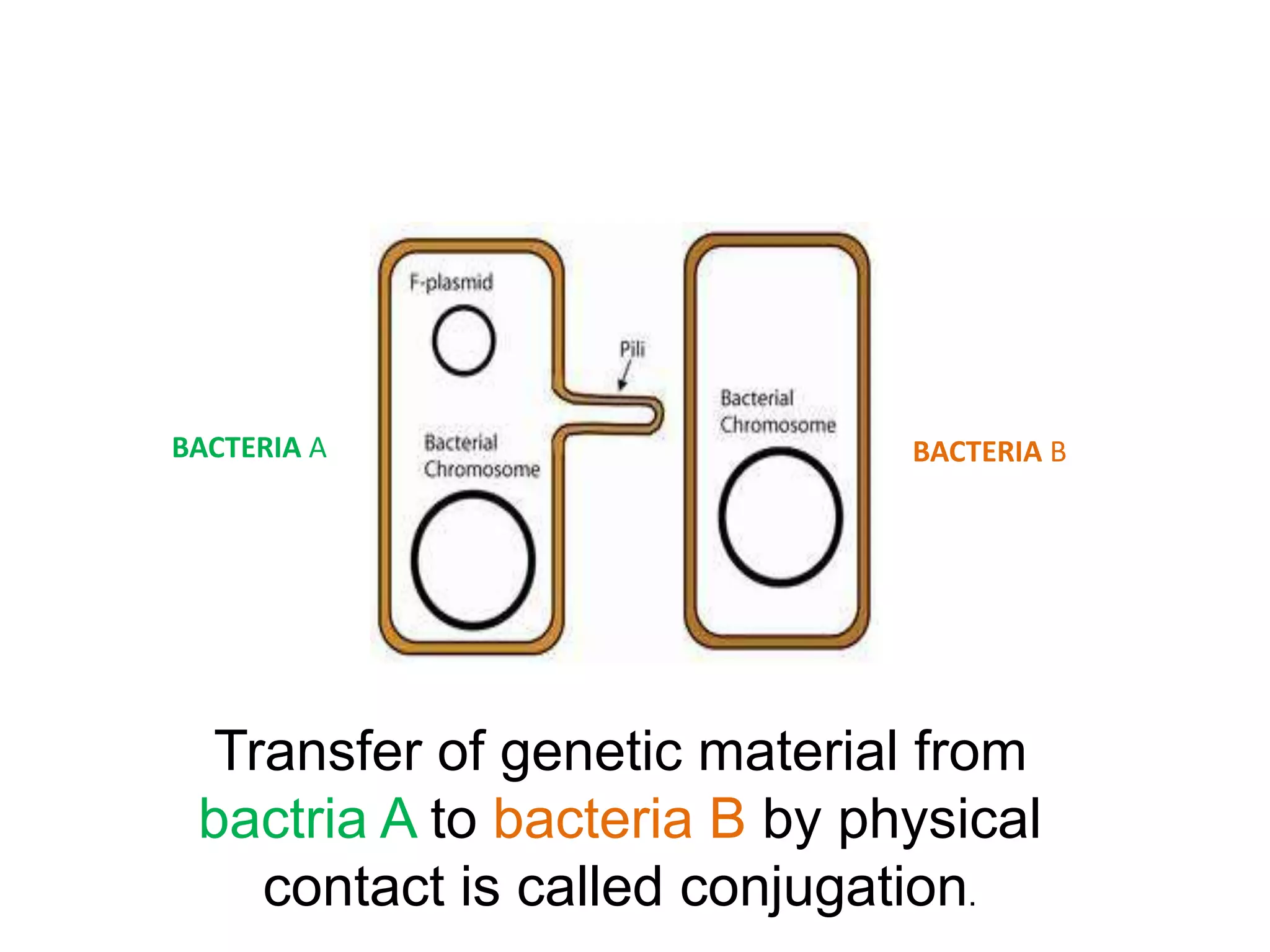
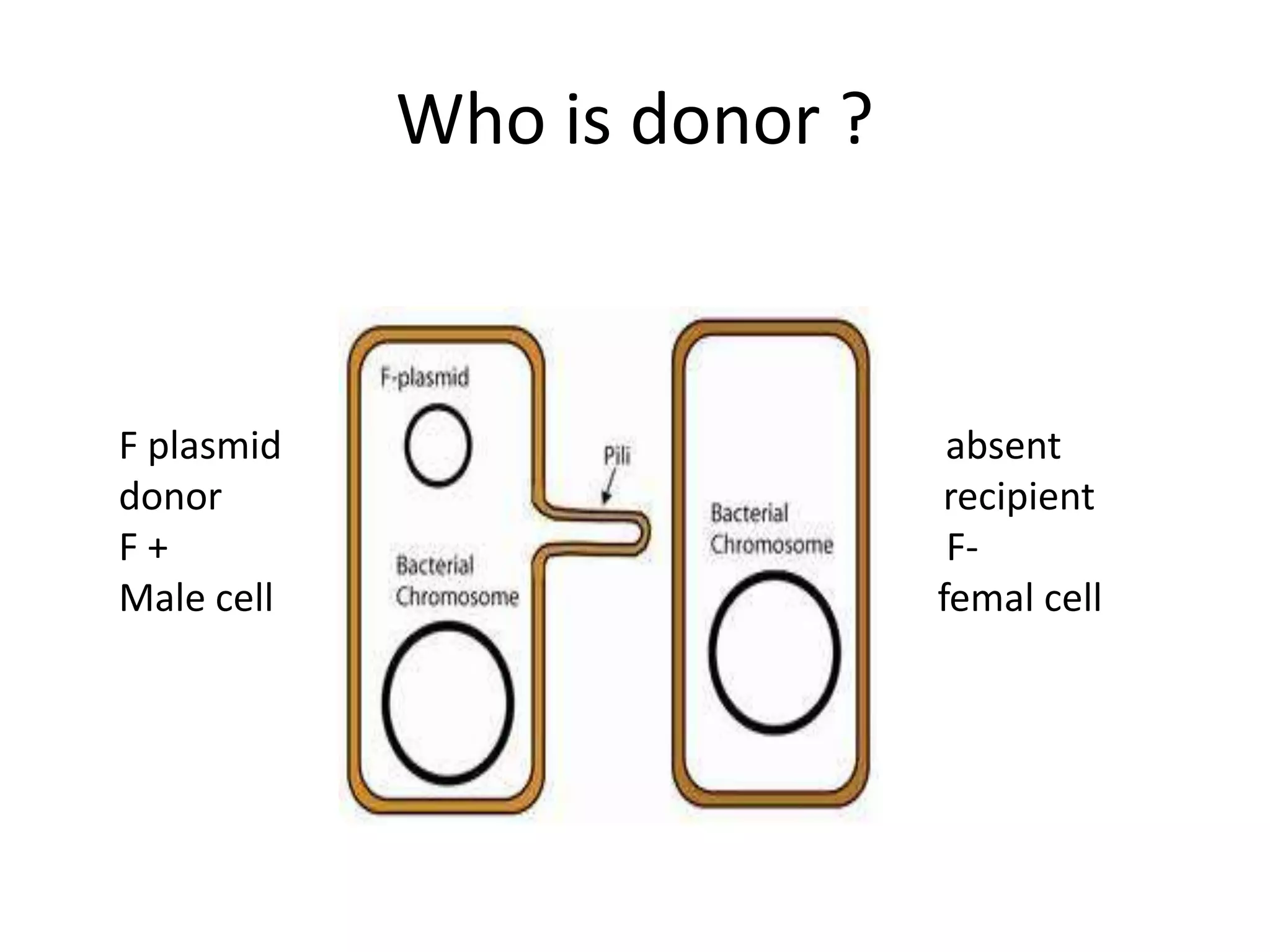
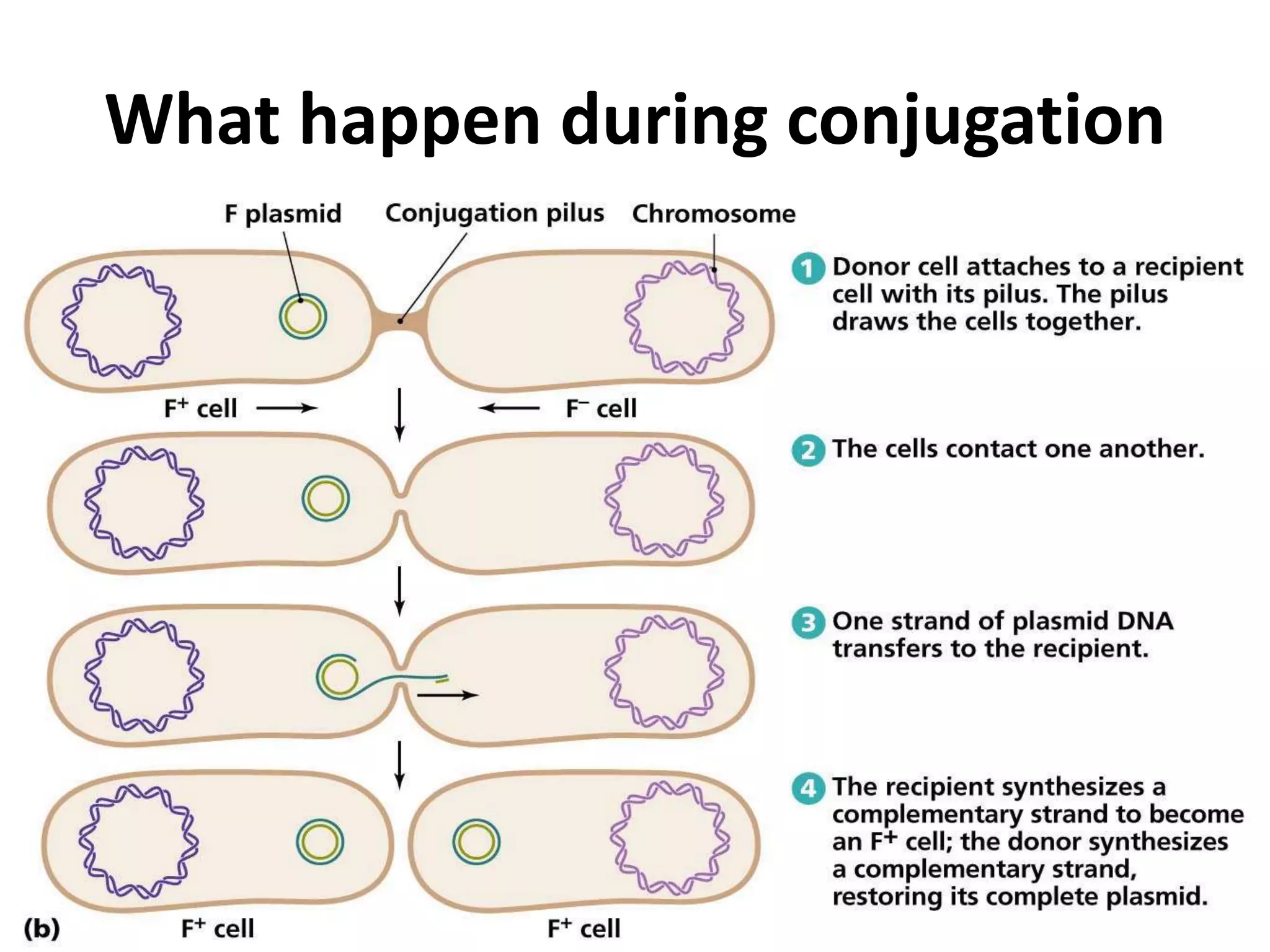
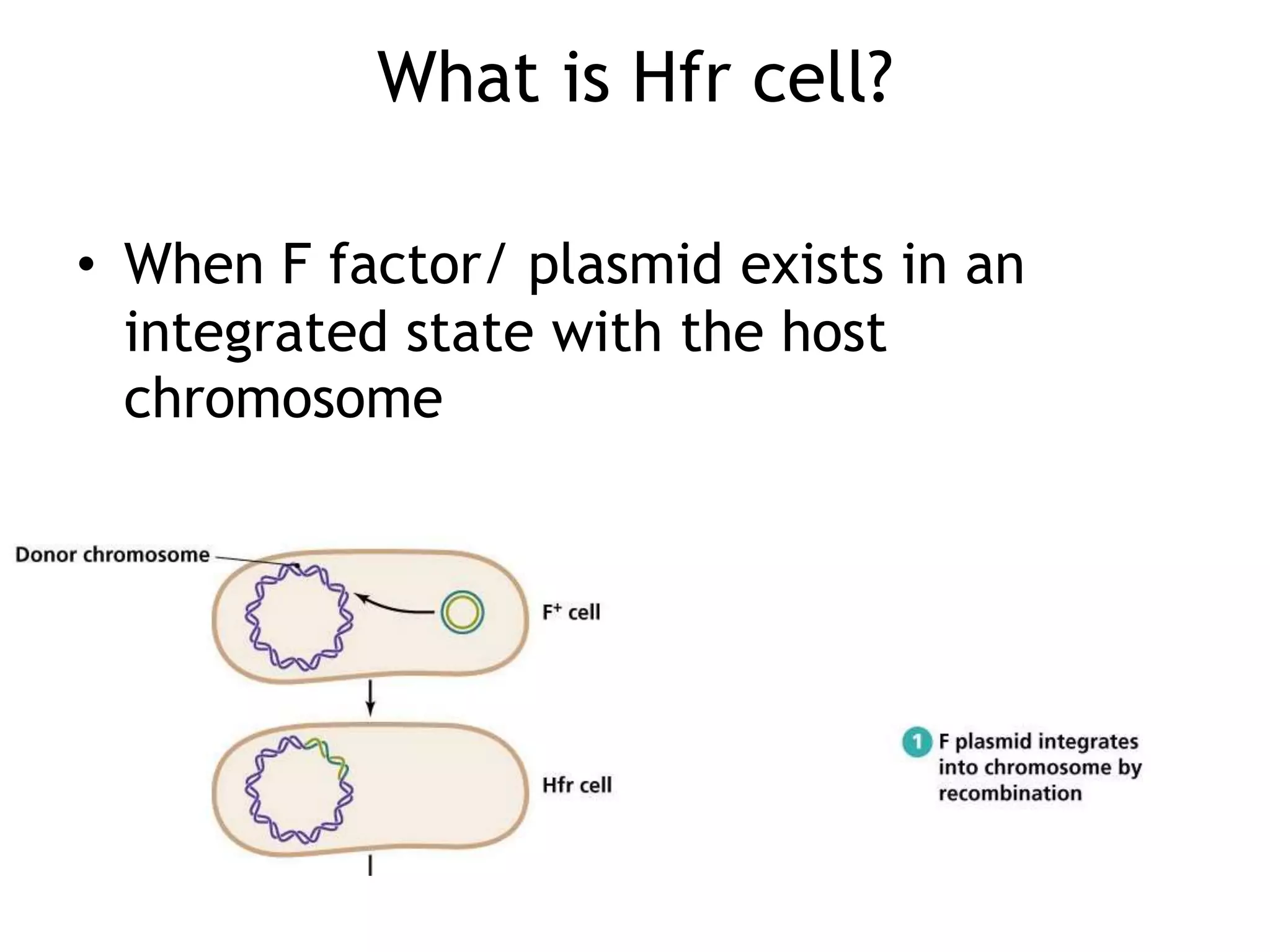
This document discusses three types of genetic transfer in bacteria: transduction, conjugation, and transformation. It focuses on transduction, describing how bacteriophages can transfer genetic material from one bacteria to another. There are two types of transduction - generalized, where any bacterial gene can be transferred randomly, and specialized, where only certain genes are transferred. The document provides details on the lytic and lysogenic cycles of bacteriophages and how this relates to generalized and specialized transduction. It also briefly discusses conjugation, the transfer of genetic material between bacteria via direct contact through plasmids.