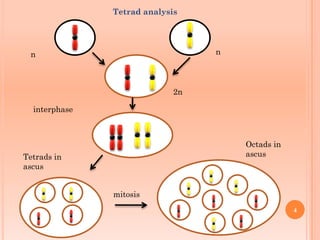
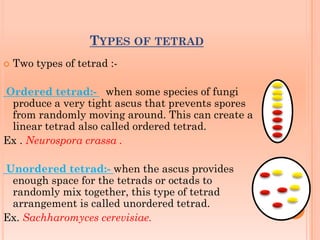
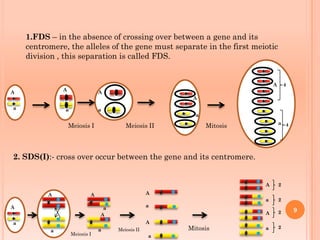
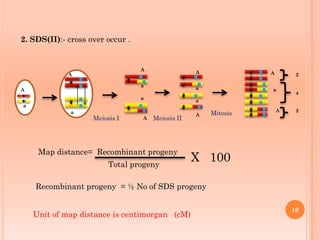
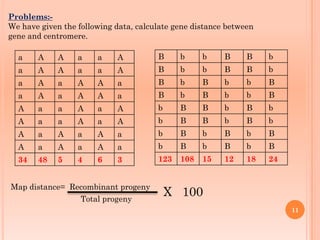
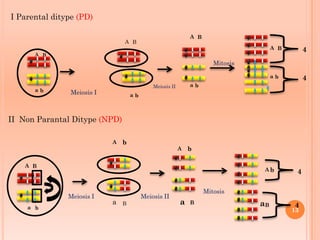
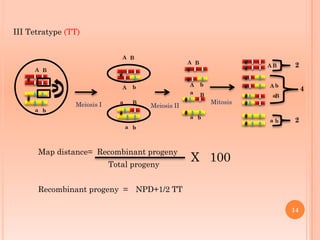
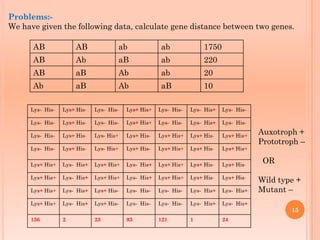
Tetrad analysis is a technique used to study genetic linkage in fungi and other lower eukaryotes. During meiosis in these organisms, four haploid spores, known as a tetrad, are produced. If spores remain in ordered linear formations, called ordered tetrads, the arrangement allows mapping of genes relative to centromeres. If spores are randomly mixed in unordered tetrads, patterns of allele segregation can determine if two genes are linked. Analysis of tetrad segregation patterns is used to calculate genetic distance between loci.