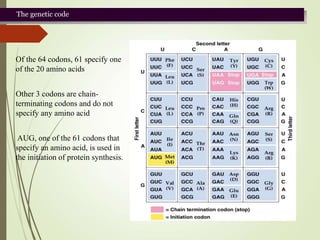
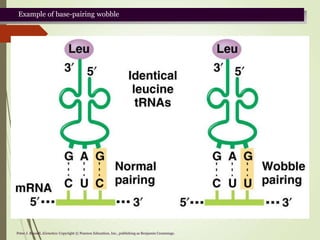
The genetic code is a triplet code where each group of three nucleotides (codon) in mRNA specifies a single amino acid in the resulting polypeptide. The genetic code is almost universal across organisms, with 61 codons specifying 20 standard amino acids and 3 codons acting as termination signals. It exhibits several key properties including being comma-free, non-overlapping, degenerate, and containing start and stop signals. Wobble can occur in the third position of the codon-anticodon pairing to allow some redundancy.