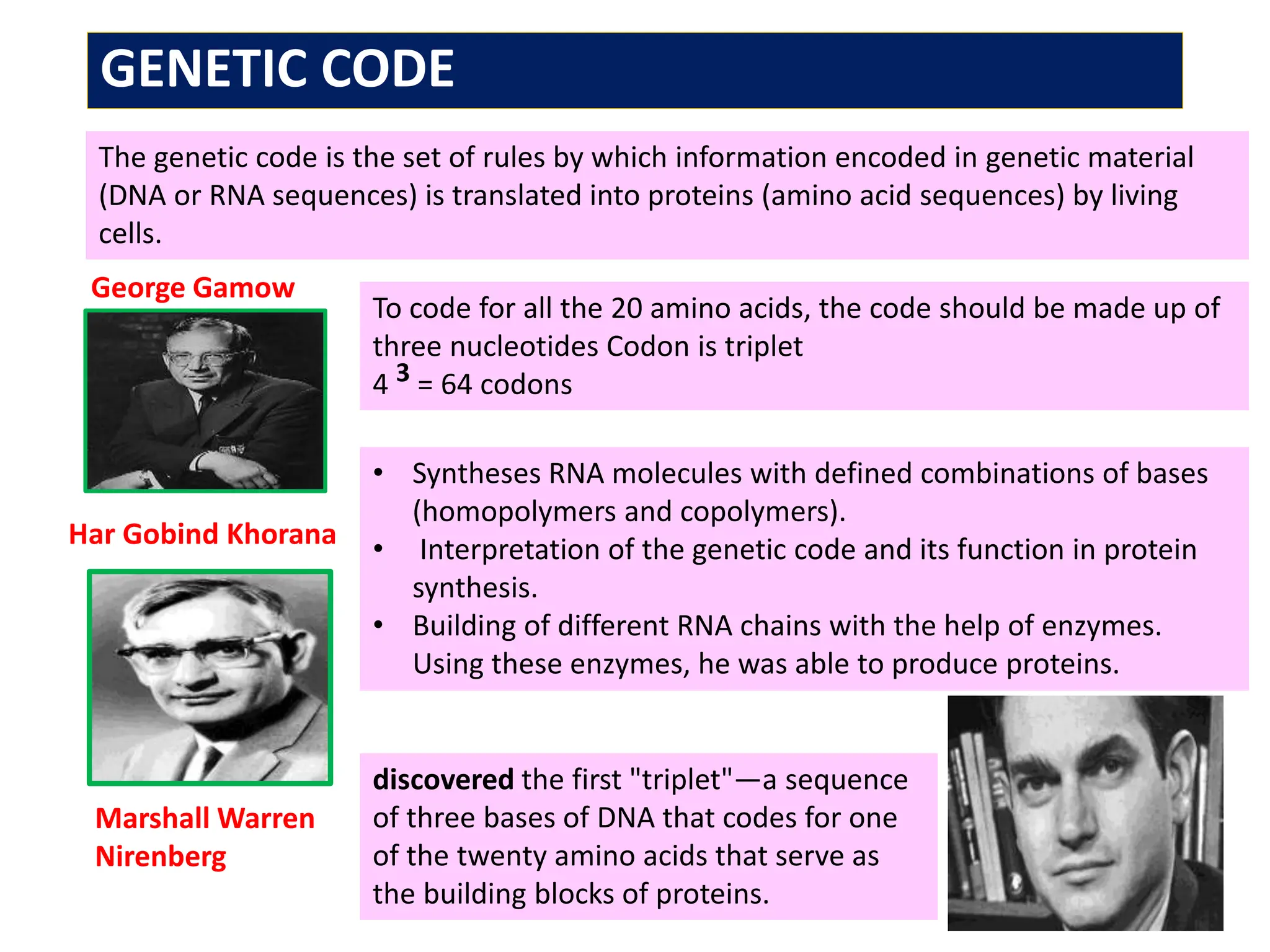
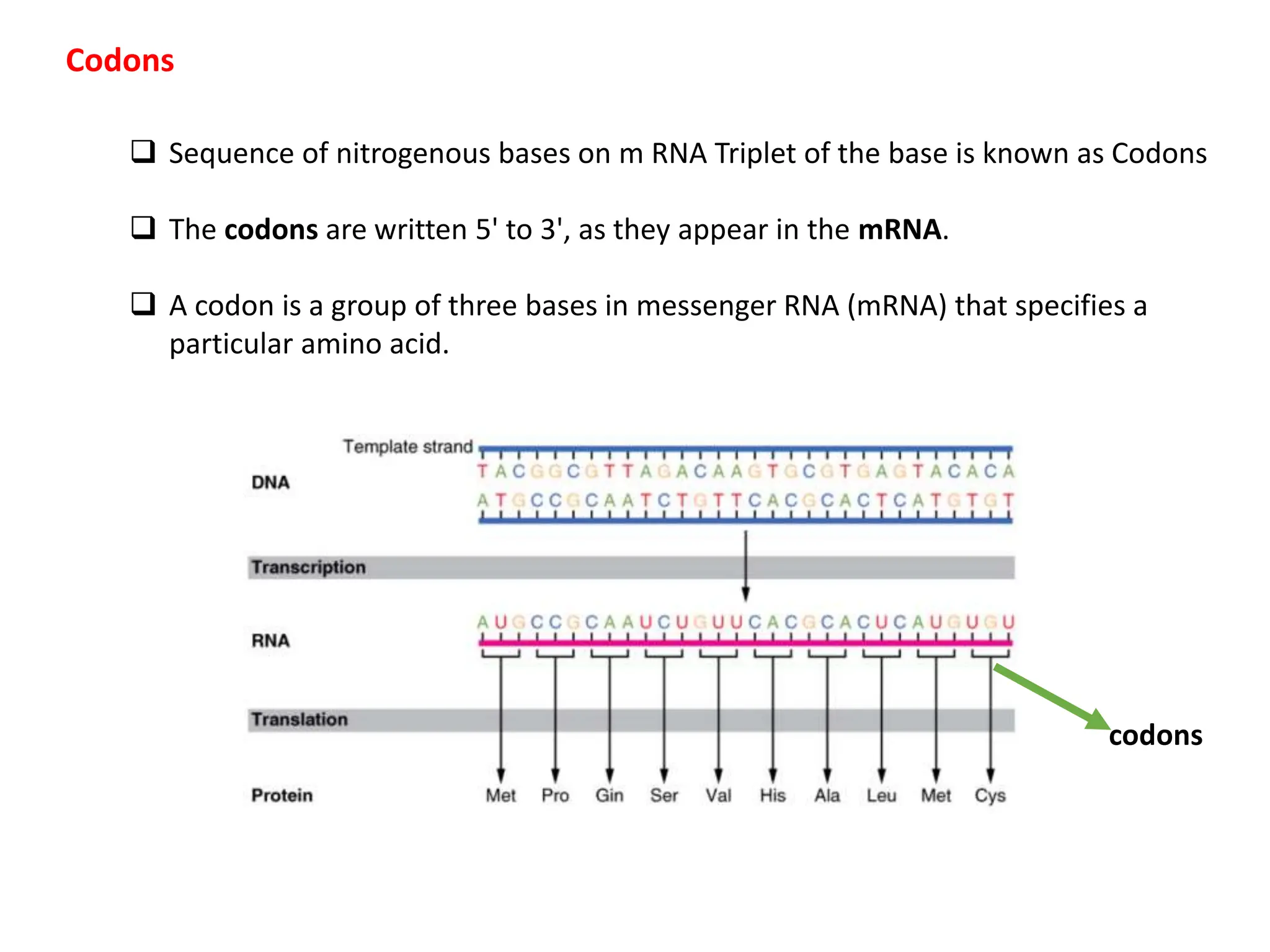
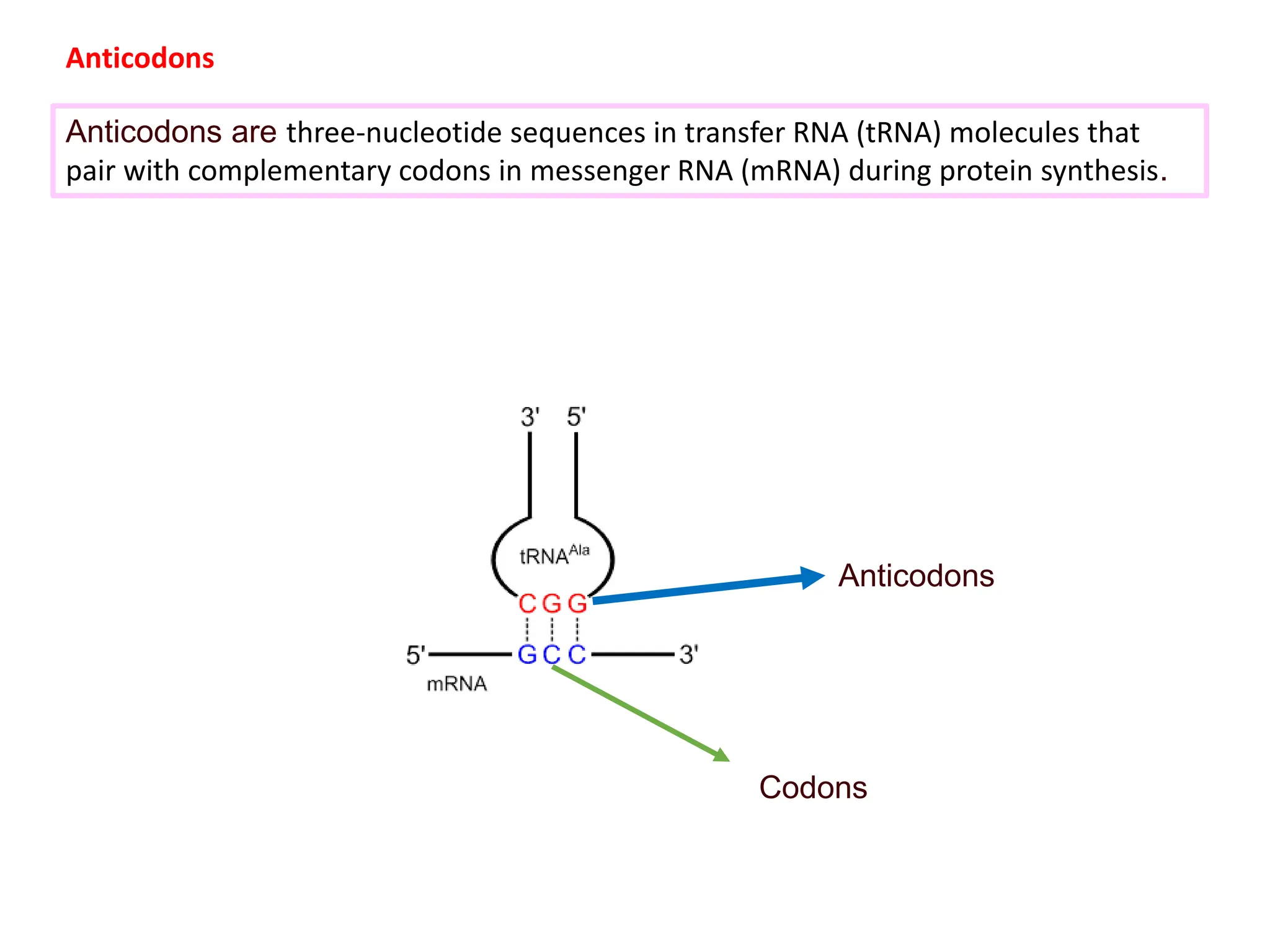
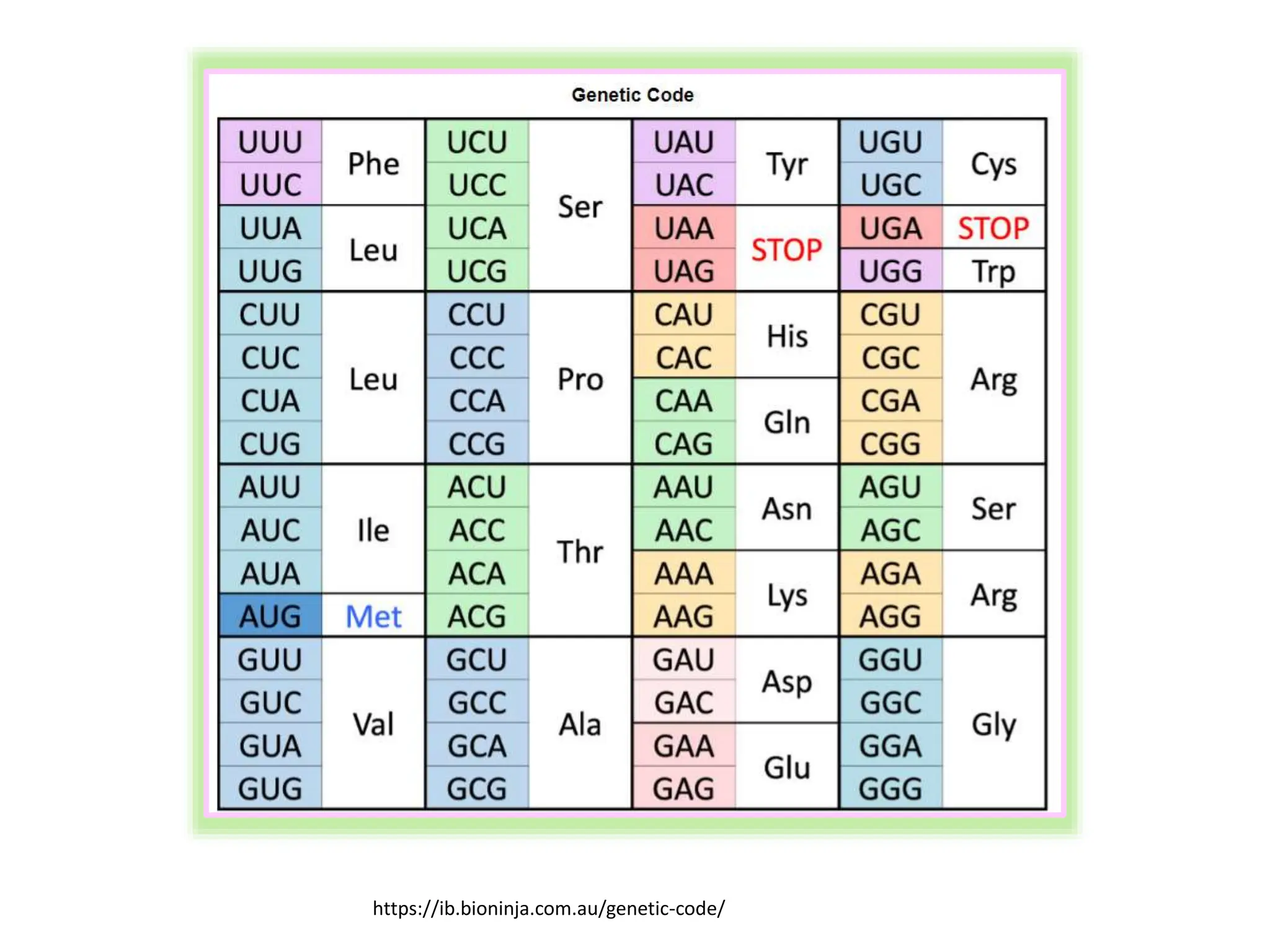
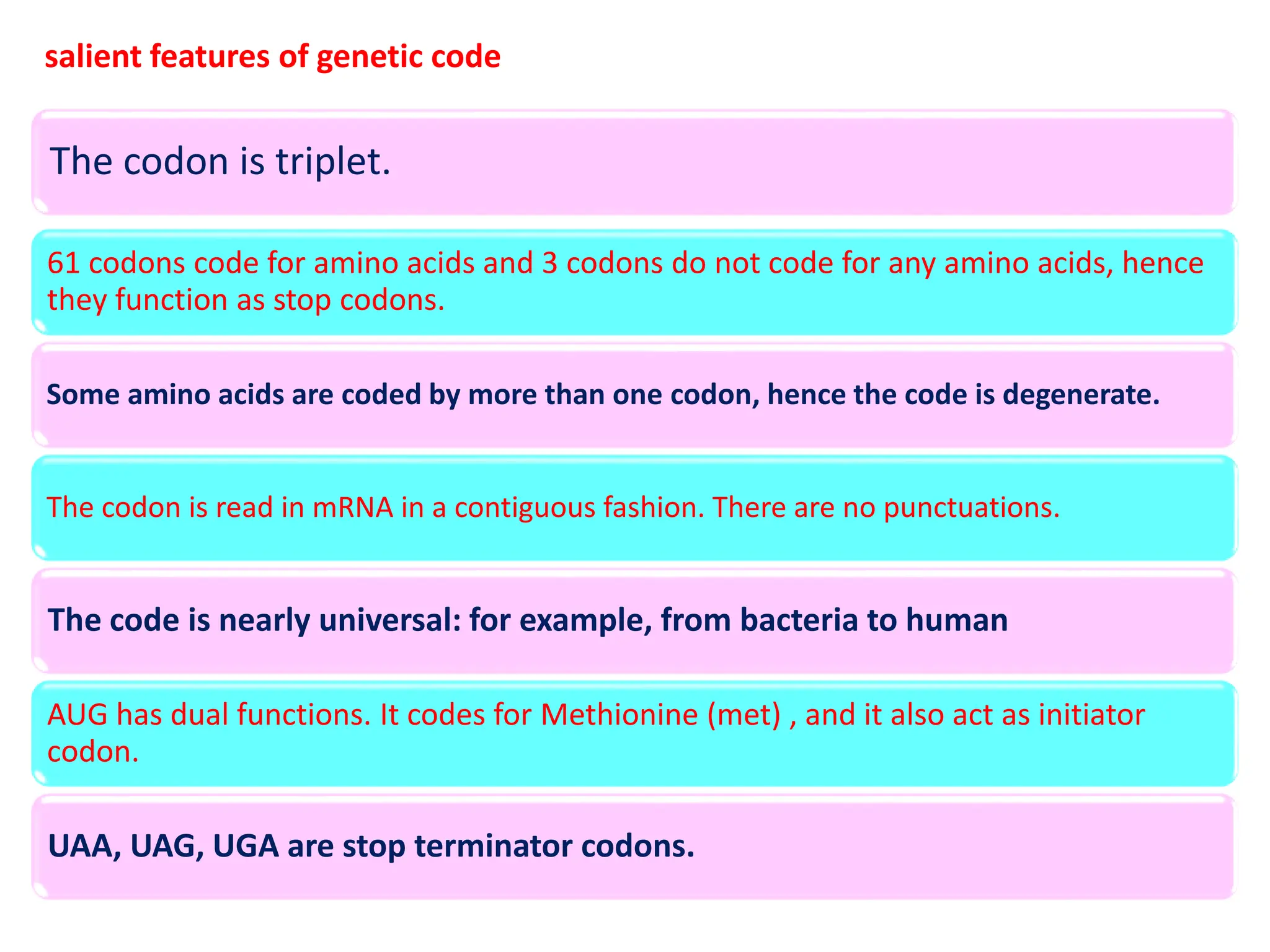
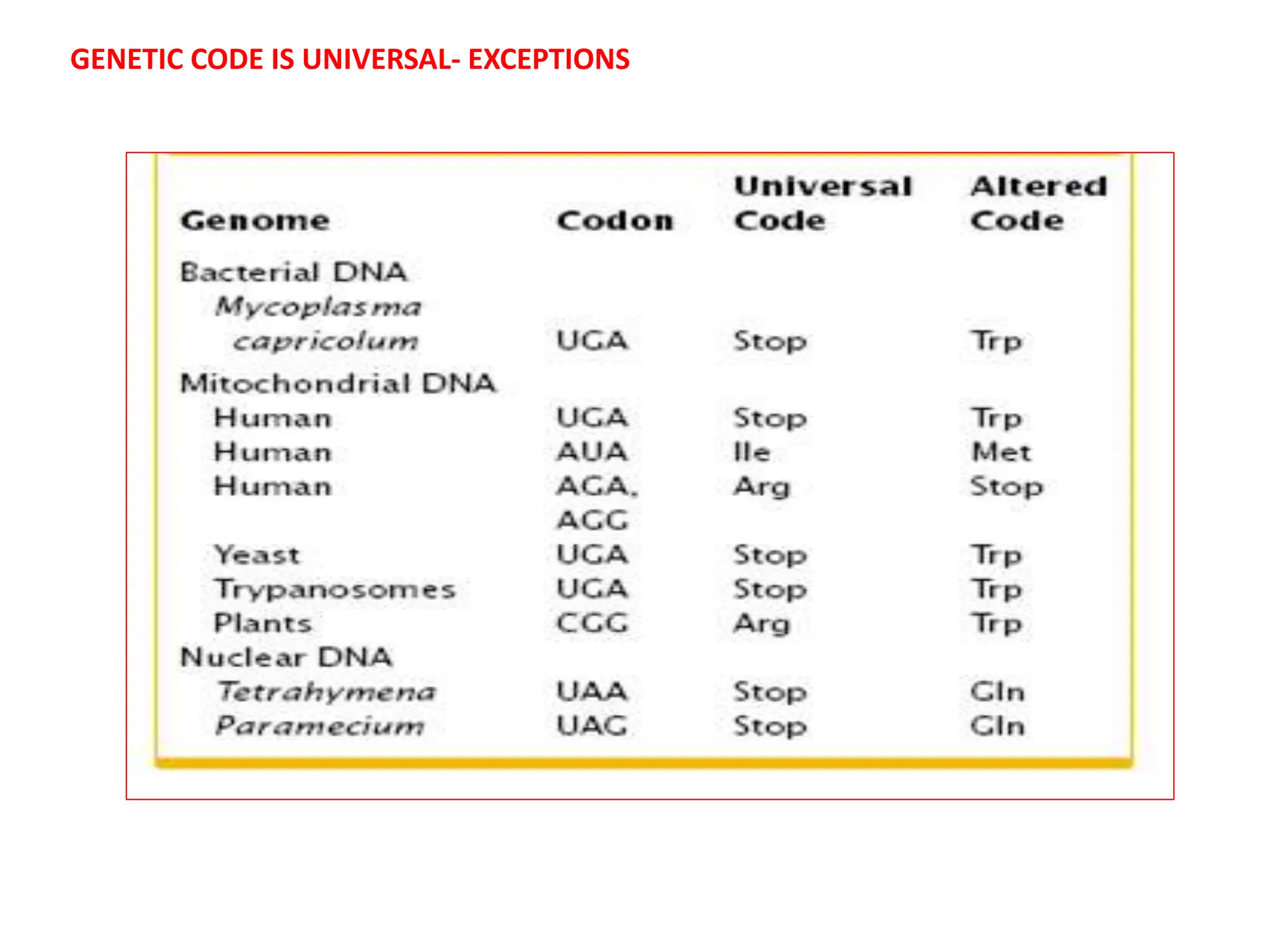
The genetic code consists of rules that translate DNA or RNA sequences into protein sequences via codons, which are triplets of nucleotides. Key contributors like George Gamow, Har Gobind Khorana, Marshall Nirenberg, and Severo Ochoa advanced understanding of codons and their roles in protein synthesis, highlighting features such as the code's universality and degeneracy. The document explains the roles of codons and anticodons in this process, including details about start and stop codons.