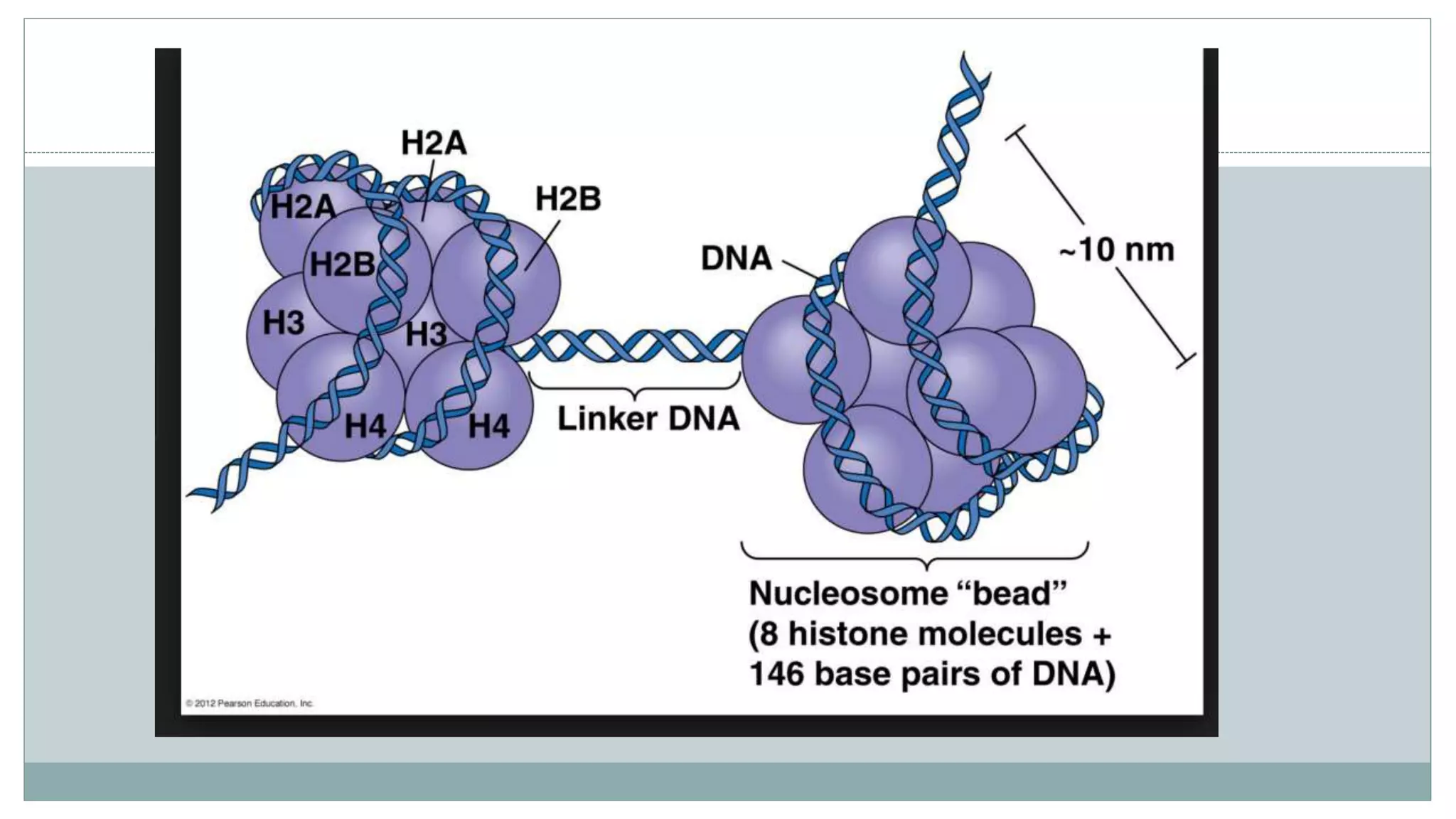
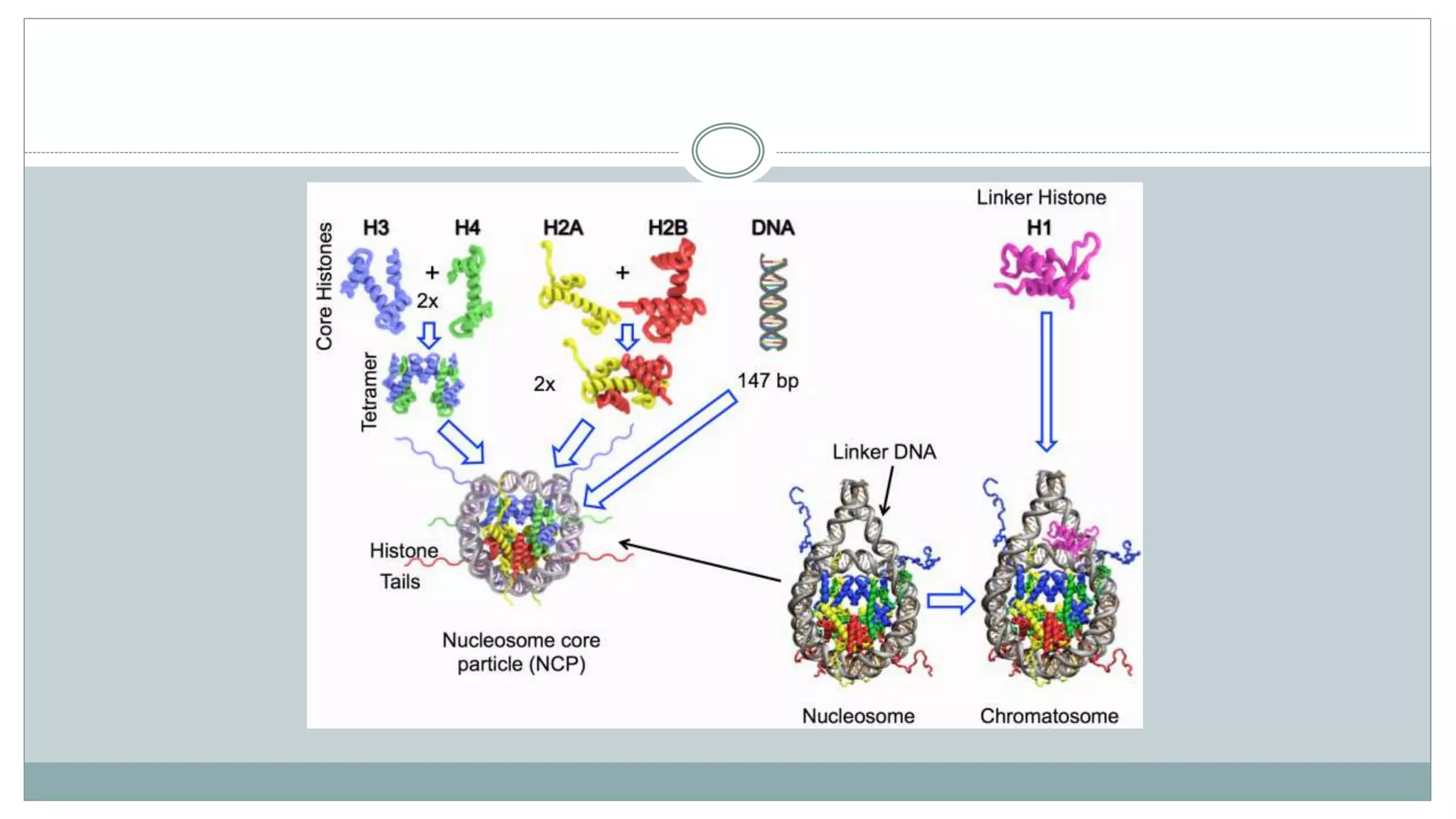
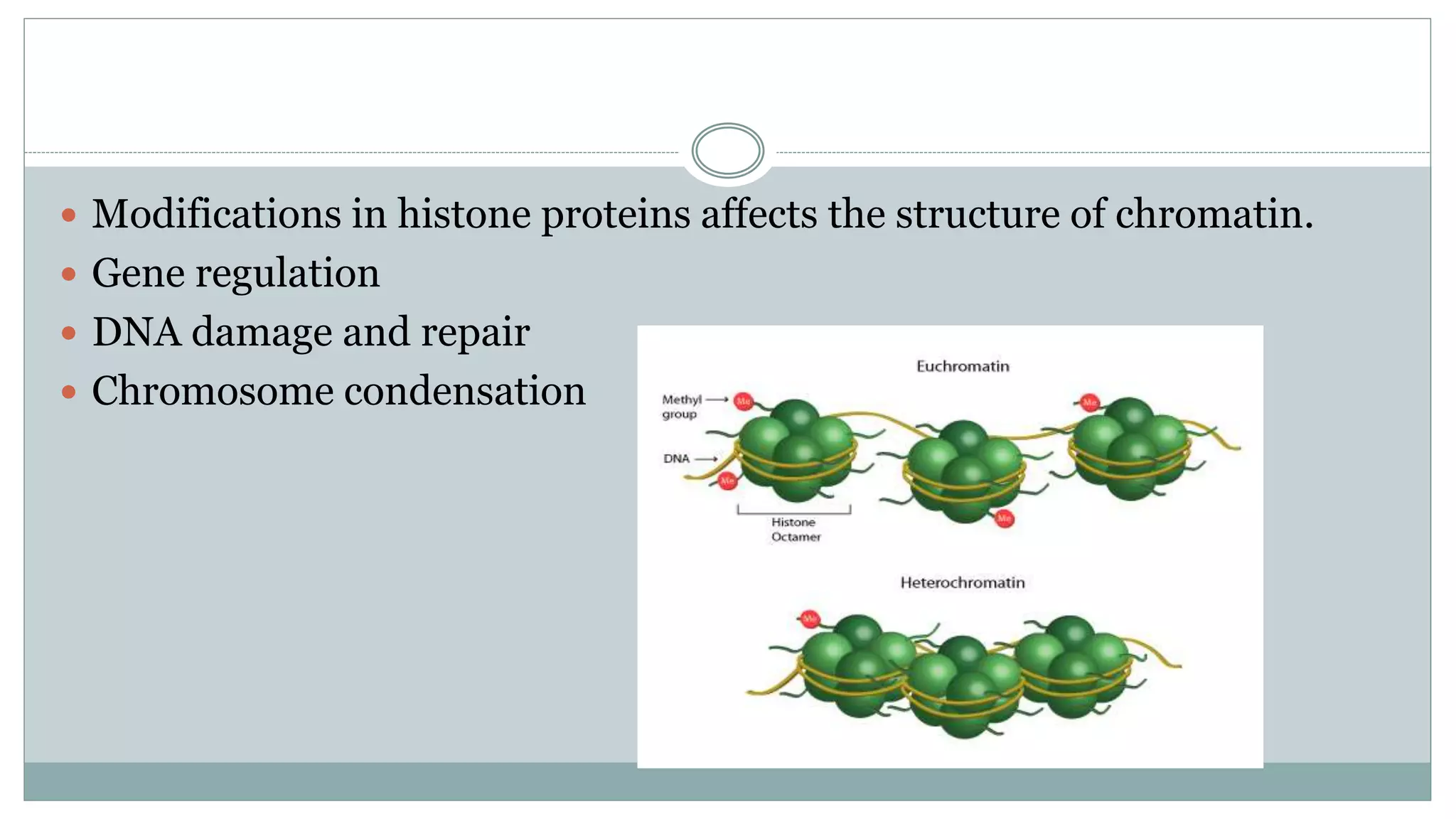
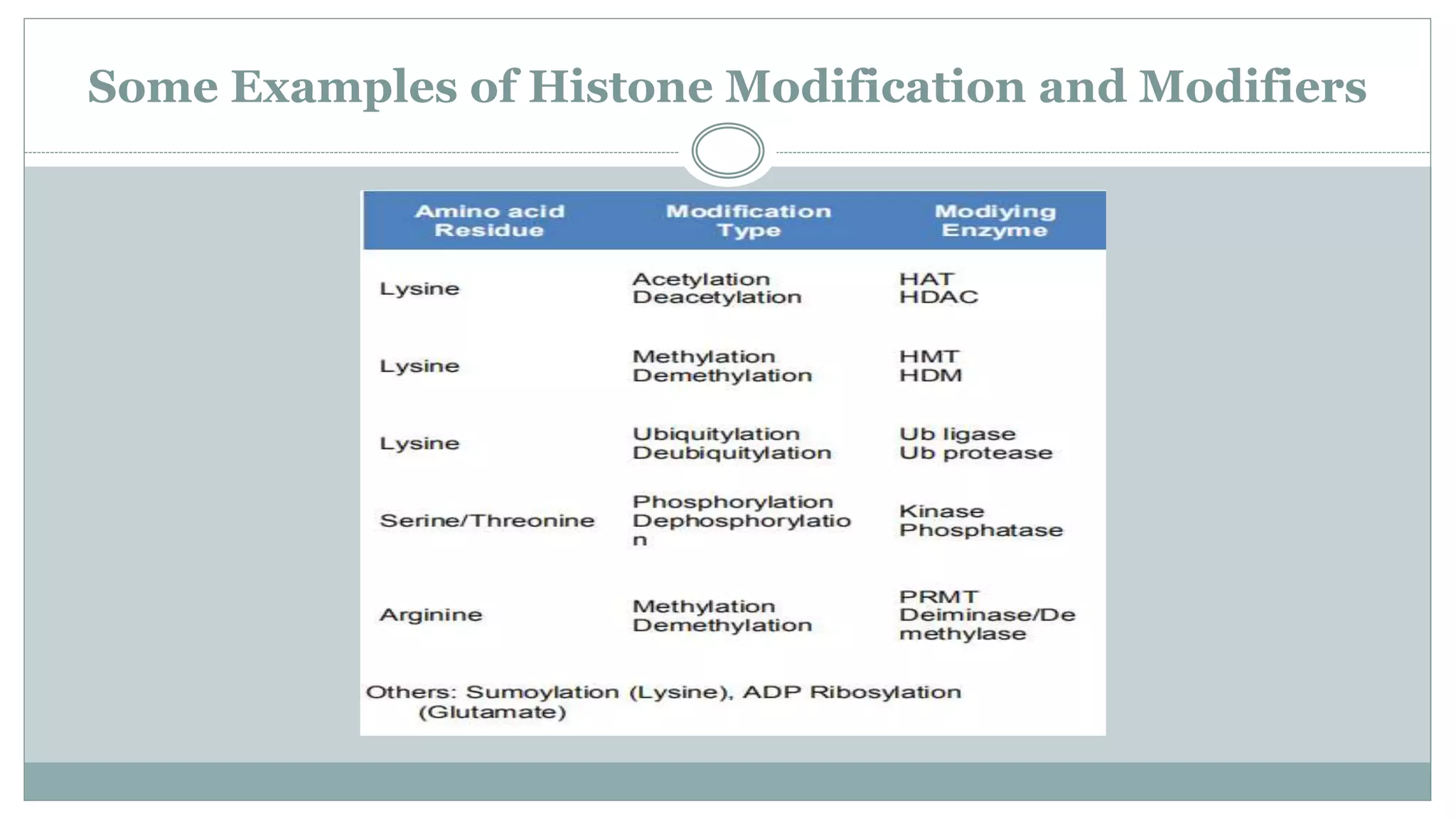
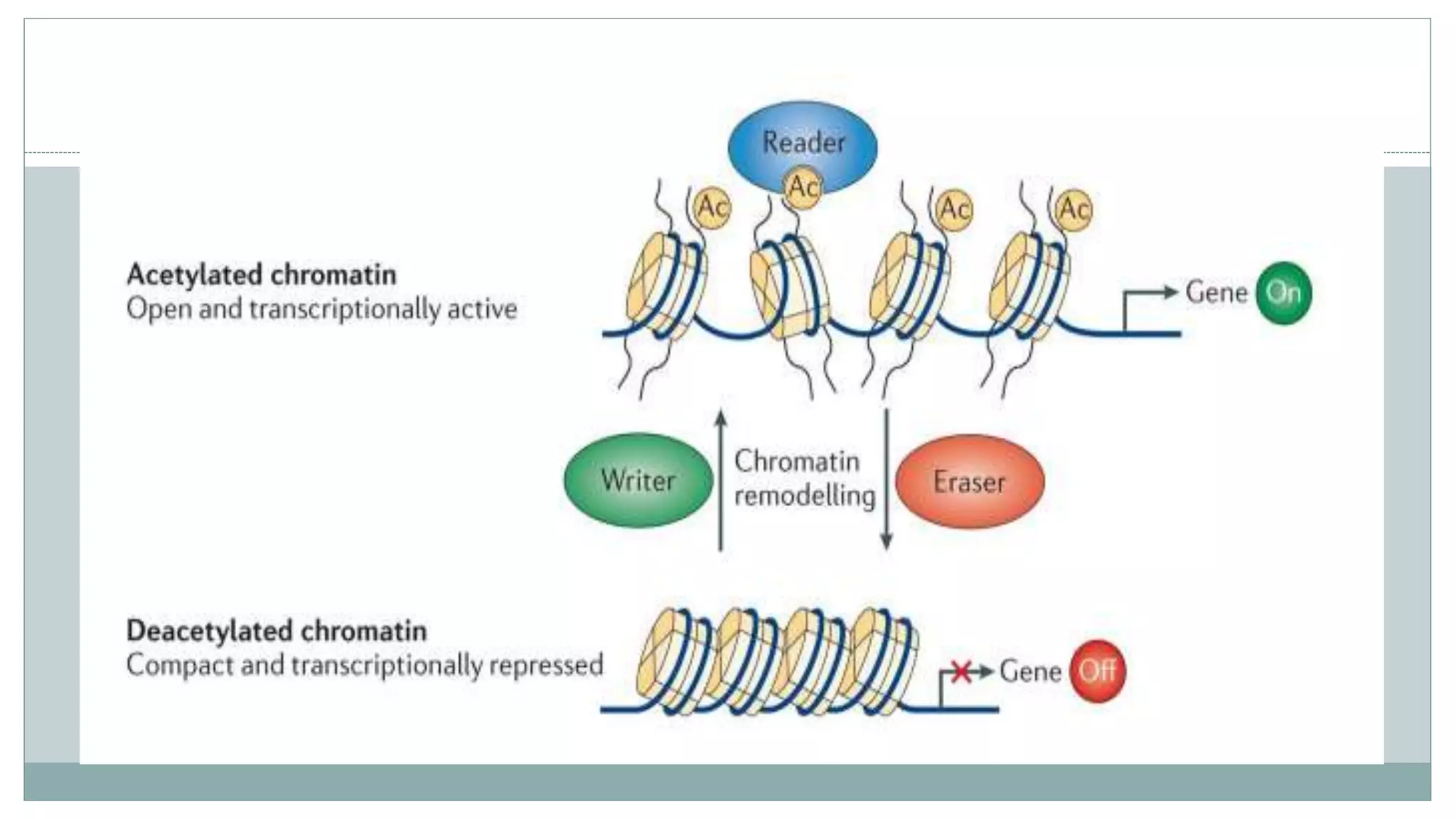
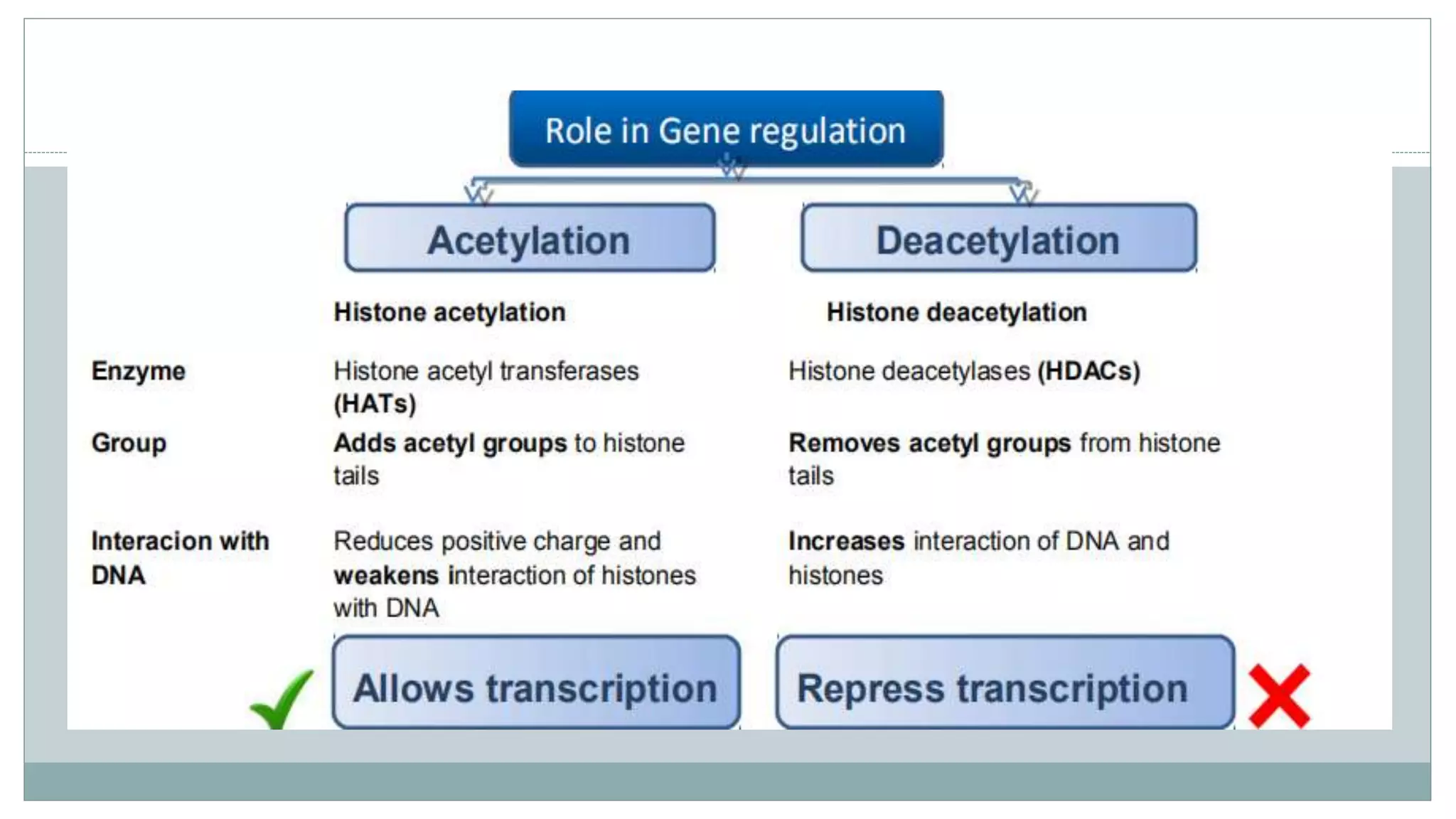
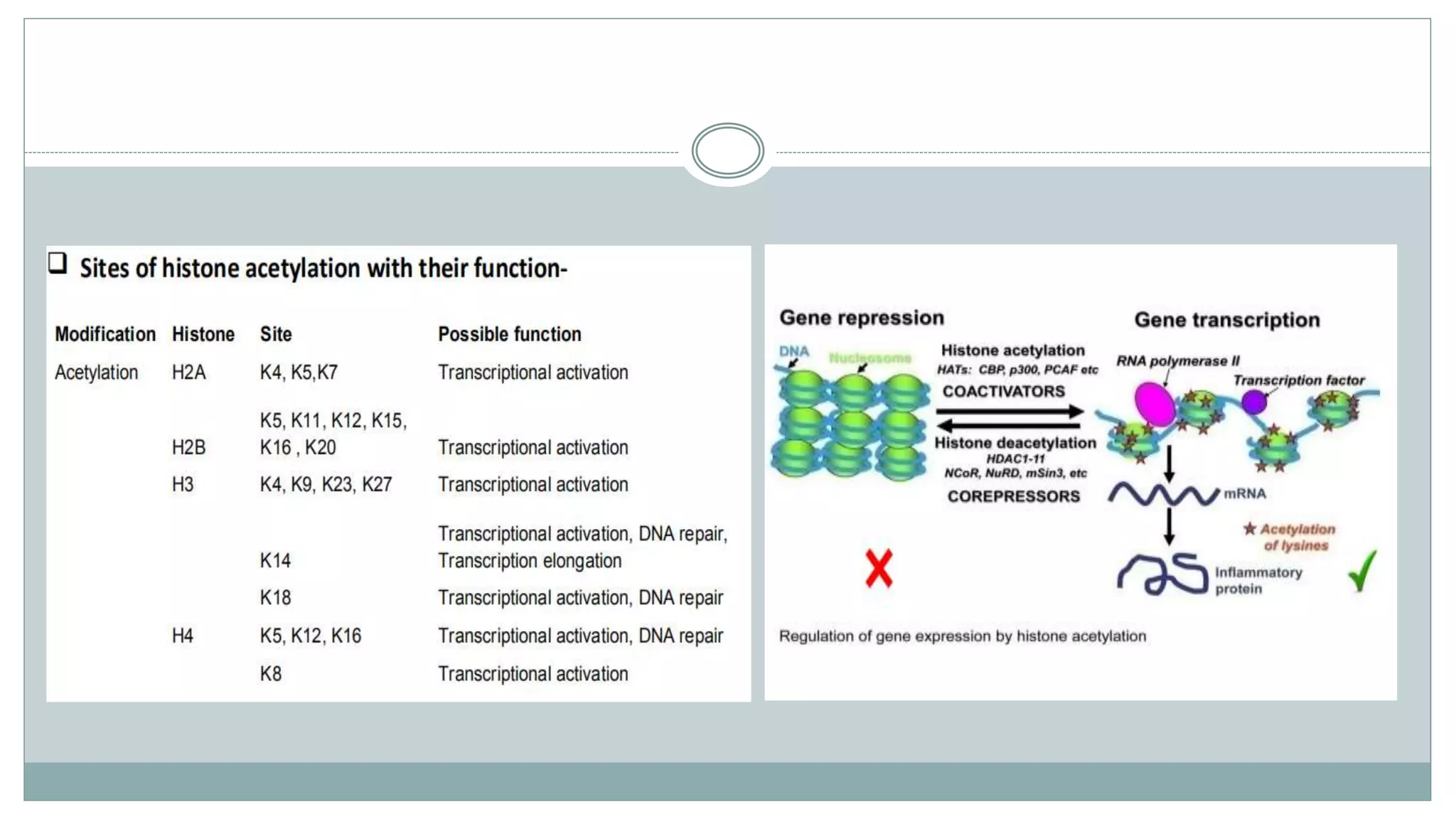
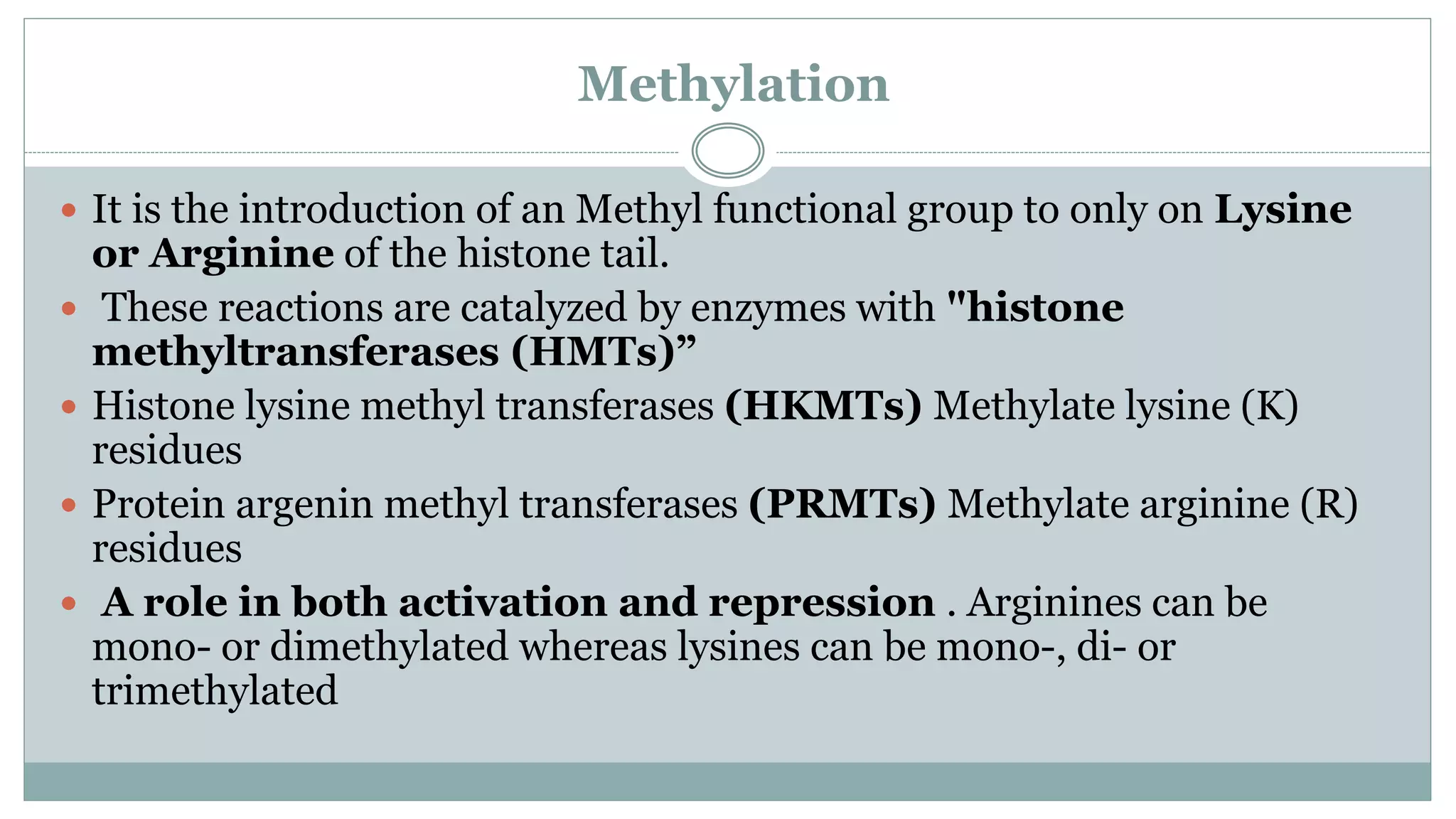
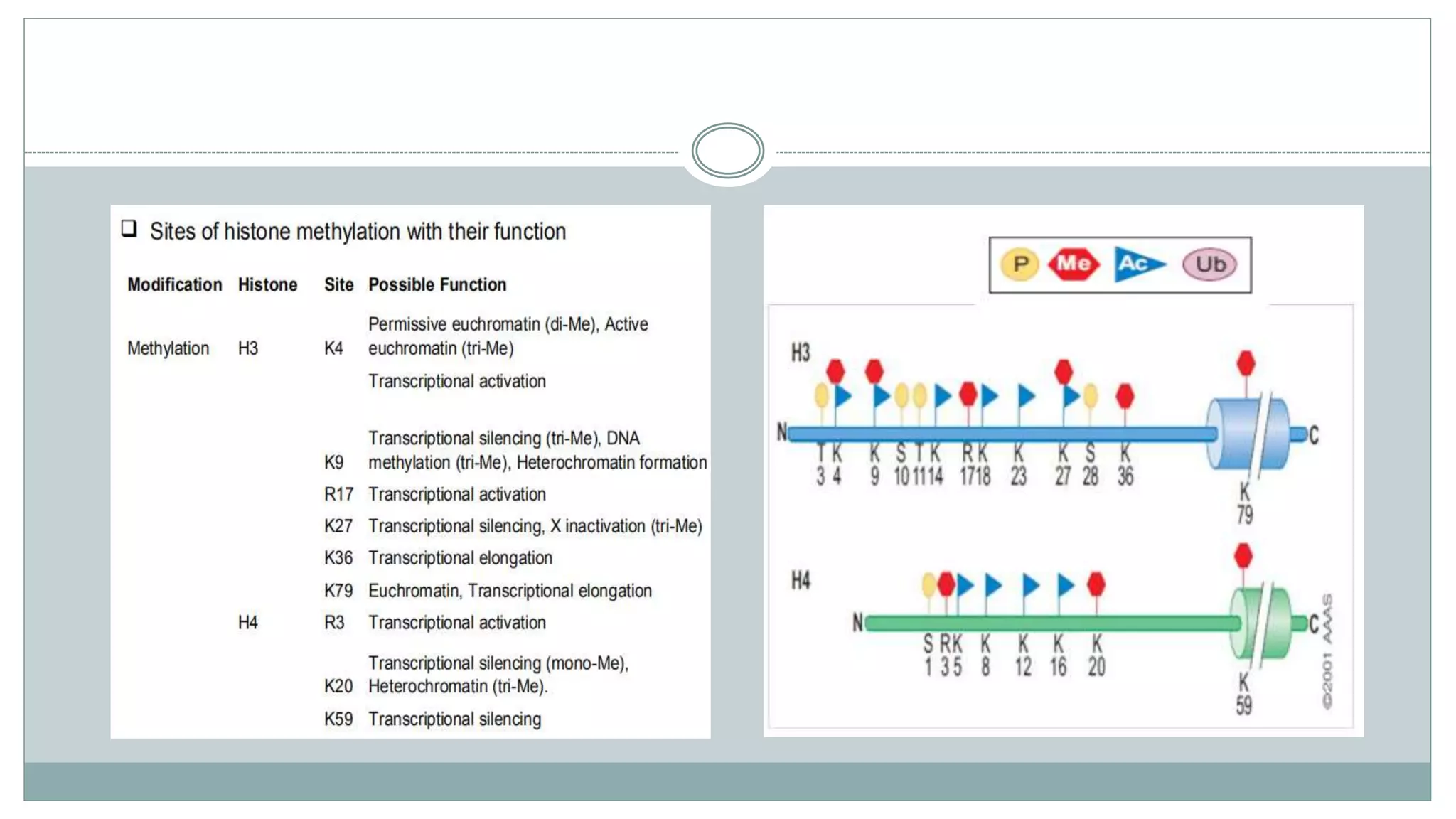
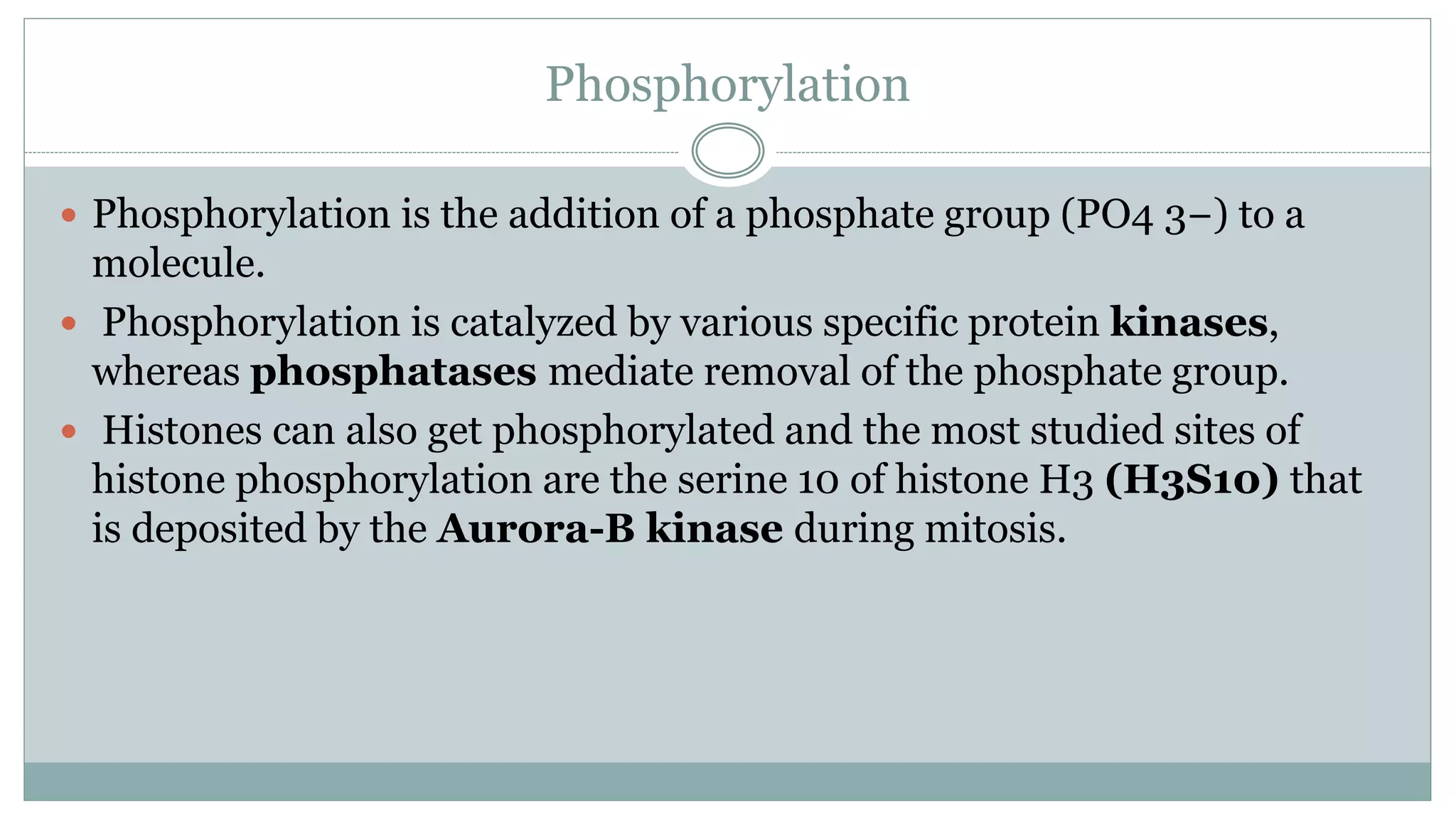
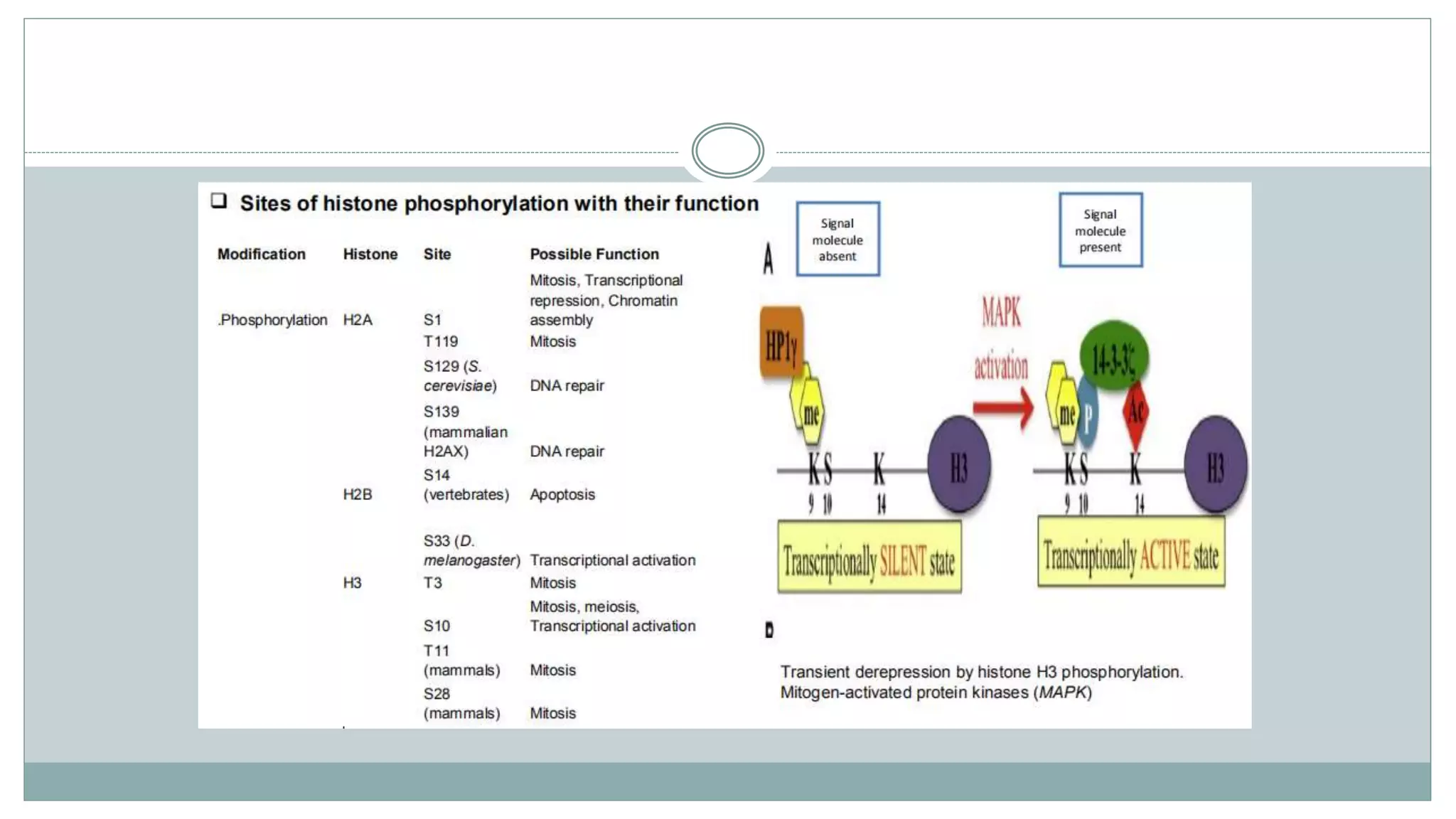
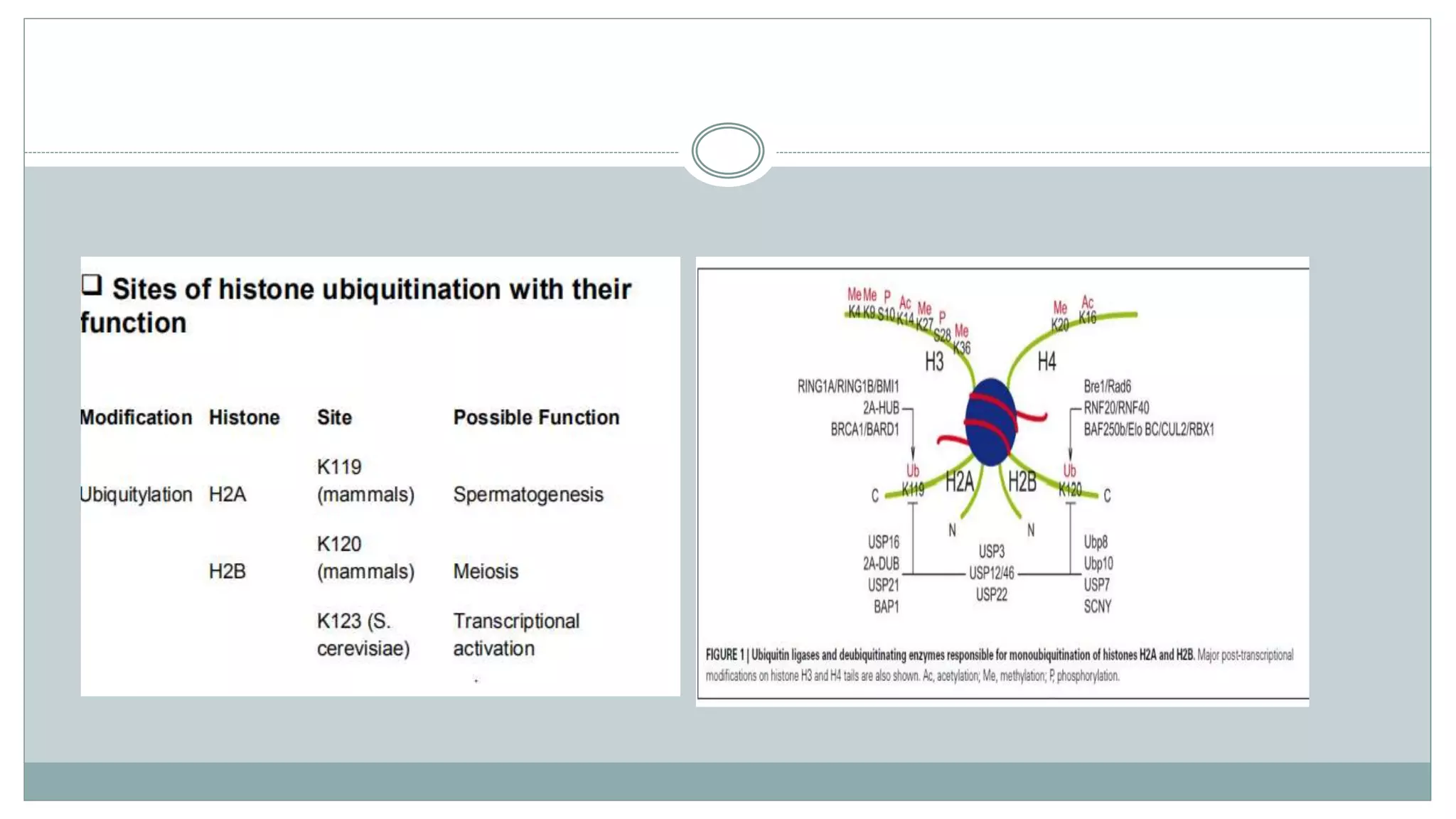
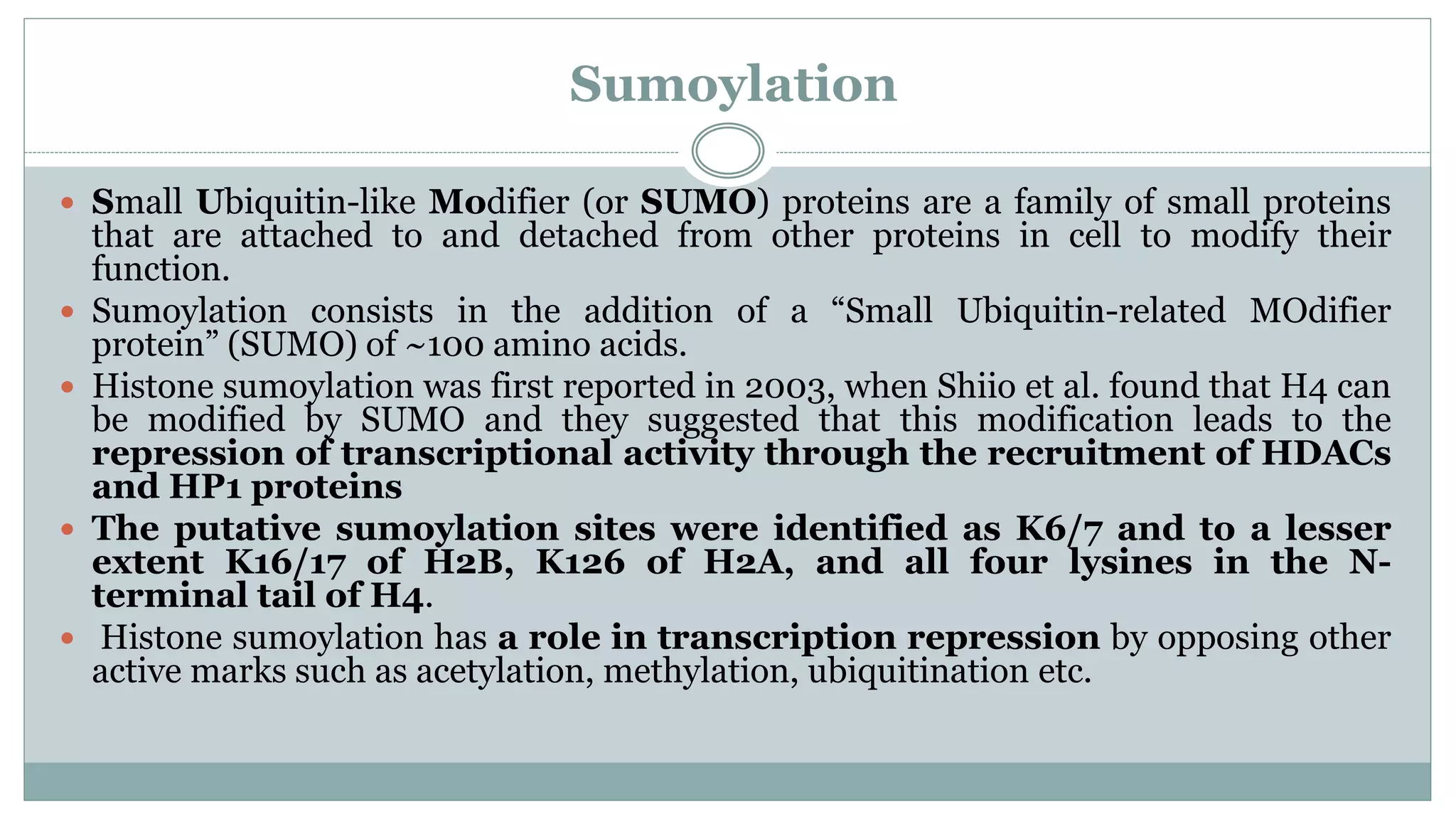
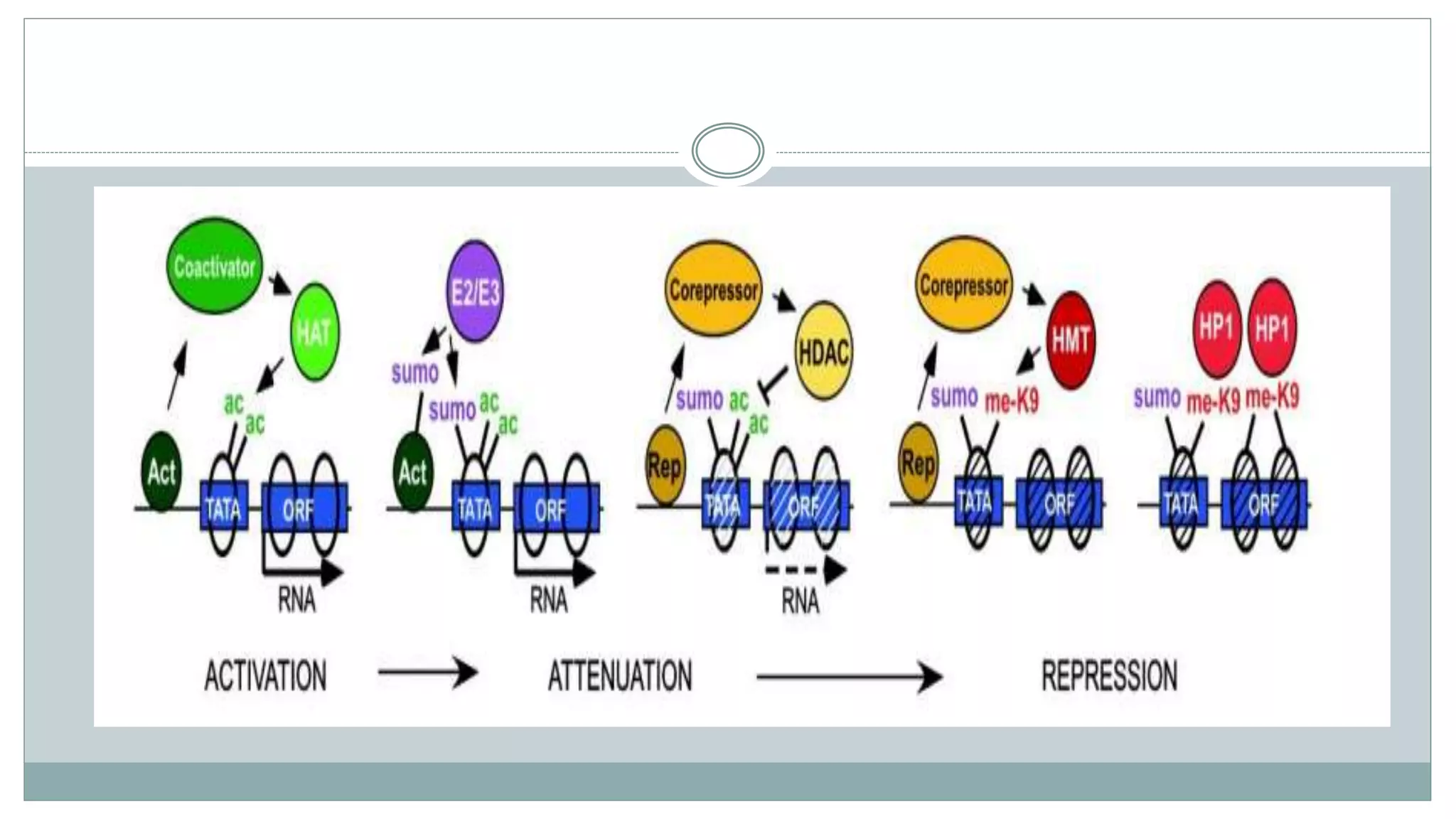
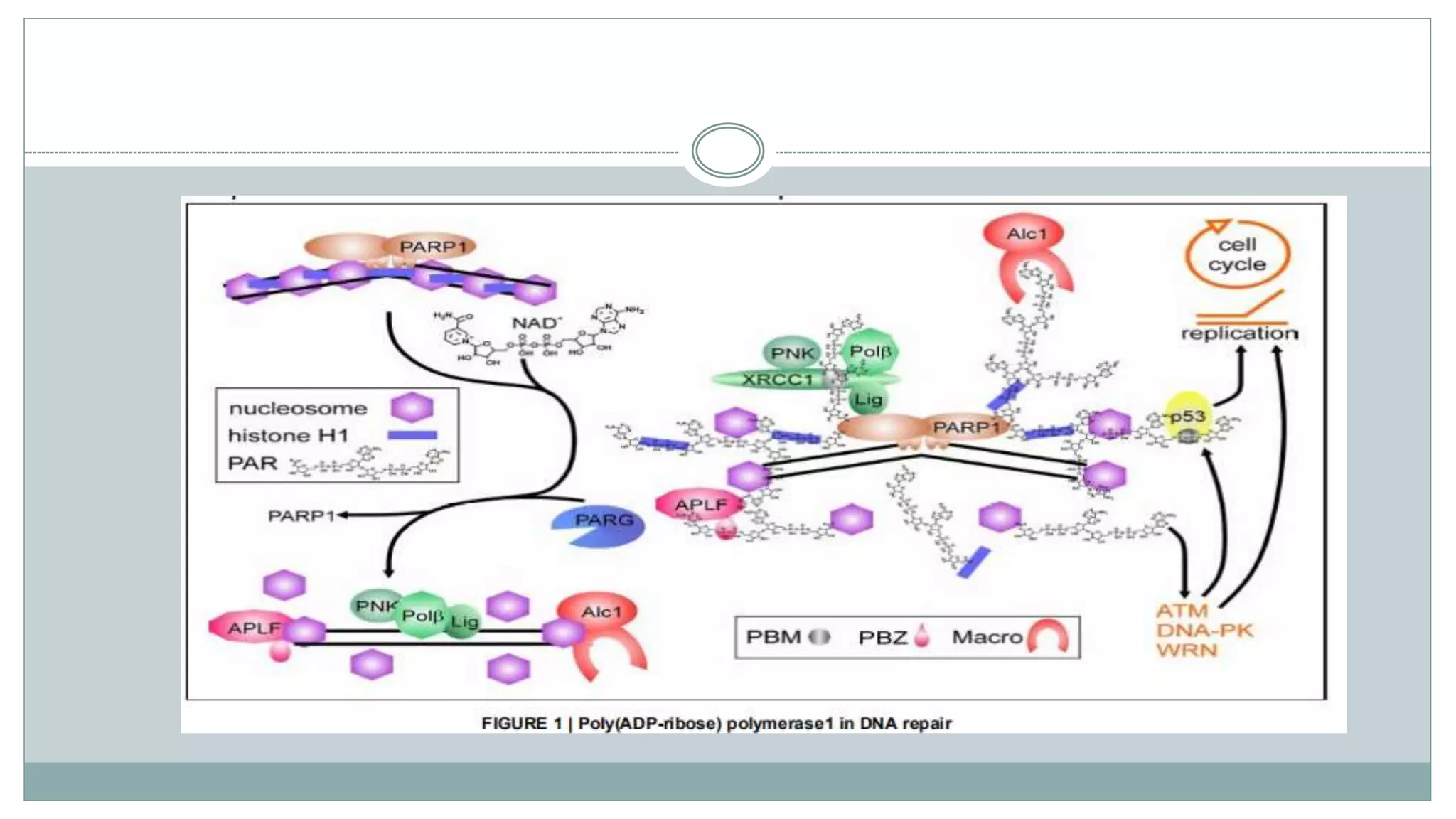
This document summarizes different types of histone modifications. It discusses that histones help condense DNA into chromatin and are subject to post-translational modifications like acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, and ADP-ribosylation. These modifications affect gene expression by changing chromatin structure and recruiting other proteins. For example, acetylation loosens chromatin and methylation can either activate or repress genes depending on the amino acid modified. The document provides examples of different histone modifiers and the effects of various histone modifications.