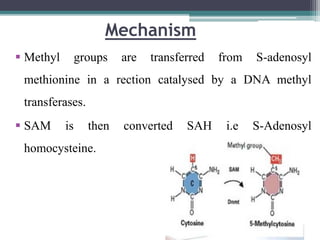
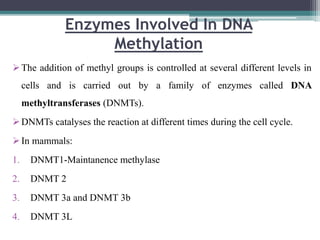
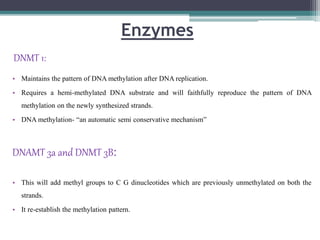
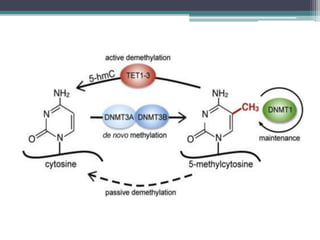
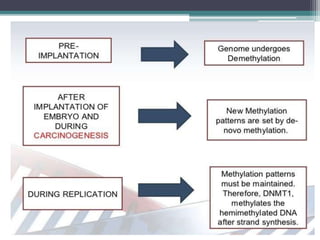
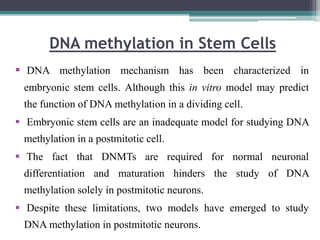
DNA methylation is a biological process where methyl groups are added to DNA, changing gene expression without altering the DNA sequence. It is essential for normal development in mammals and is associated with processes like genomic imprinting and carcinogenesis. DNA methyltransferases are enzymes that catalyze the addition of methyl groups to DNA from S-adenosyl methionine. DNA methylation plays important roles in gene silencing, X-chromosome inactivation, and suppressing viral genomes and repetitive elements incorporated into the host genome. Abnormal DNA methylation is also associated with cancer by transcriptionally silencing tumor suppressor genes.