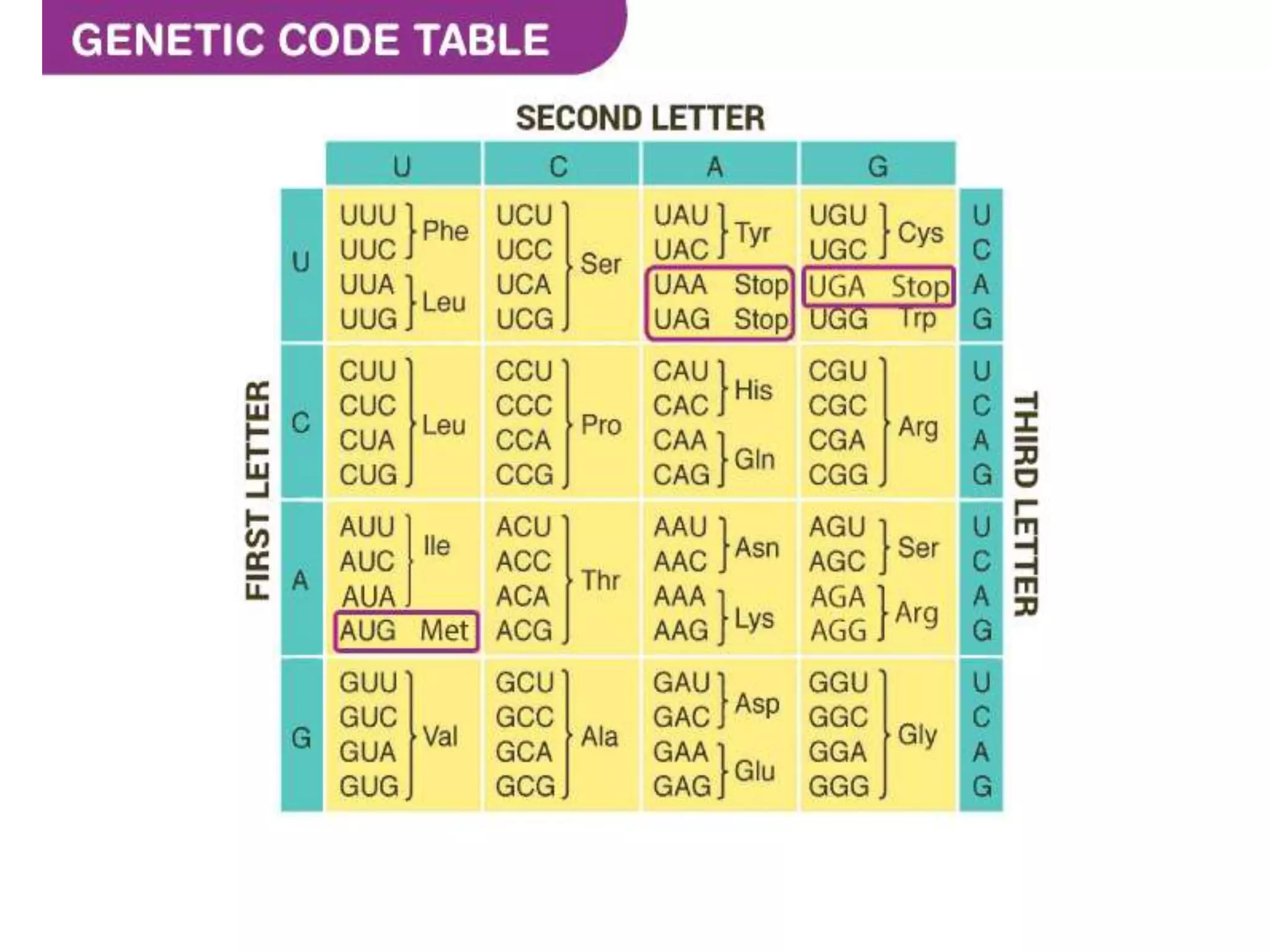
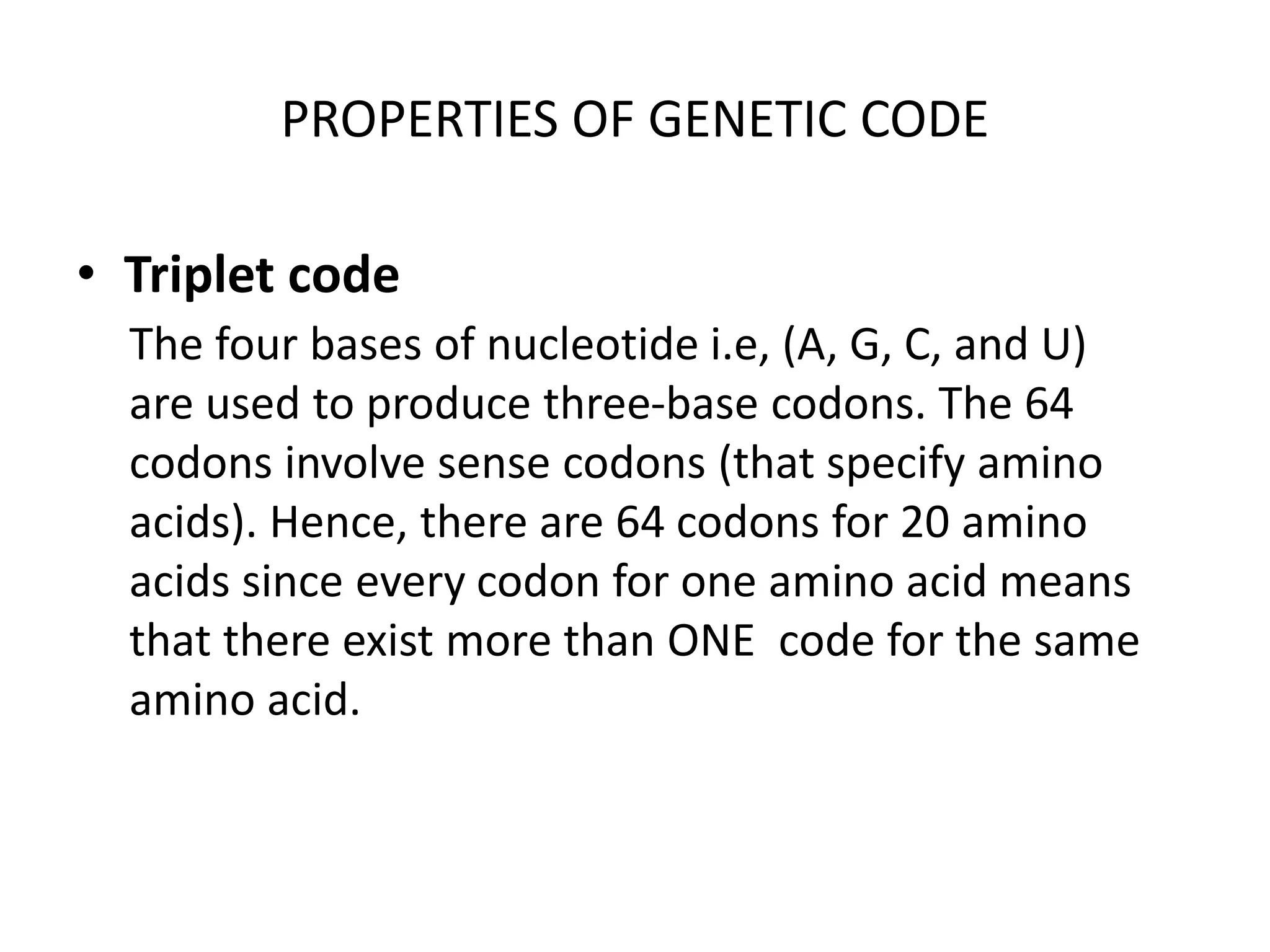
The genetic code is the set of rules by which ribosomes translate nucleic acid sequences into amino acid sequences during biological protein synthesis. It is based on triplets of nucleotides called codons, with 64 possible codons composed of combinations of four nucleotides. Codons are read sequentially in groups of three and each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, with some codons corresponding to termination signals. The genetic code is nearly universal across all living organisms and is non-overlapping, non-ambiguous, and degenerate.