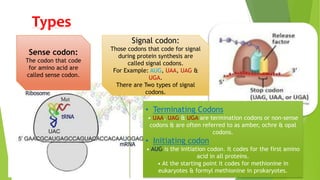
This presentation discusses the genetic code and how it translates DNA and RNA sequences into proteins. The genetic code is universal across all living organisms and consists of 64 codons composed of 3 nucleotides that correspond to 20 amino acids. Codons are classified as sense codons, which code for amino acids, or signal codons like initiation and termination codons. Anticodons on tRNAs pair with mRNA codons to recognize and translate the codons. The genetic code is non-overlapping, degenerate, and Francis Crick's wobble hypothesis explains the pattern of degeneracy by proposing the third position in the anticodon is not as specific.