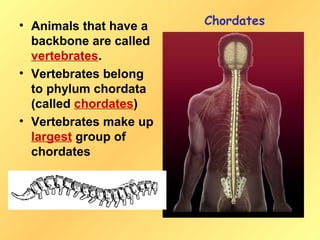
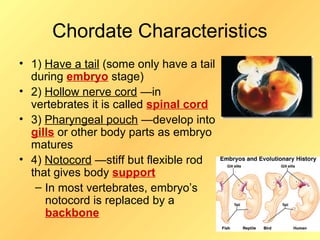
This document discusses chordates and vertebrates. It notes that vertebrates have backbones and belong to the phylum chordata. It also describes two other chordate groups, lancelets and tunicates. Key characteristics of chordates include having a tail, nerve cord, pharyngeal pouches and notochord. The document then focuses on characteristics of vertebrates like their backbone and skull. It classifies vertebrates as either warm-blooded or cold-blooded. Finally, it outlines the three classes of fish and characteristics like breathing with gills and reproduction through external fertilization.