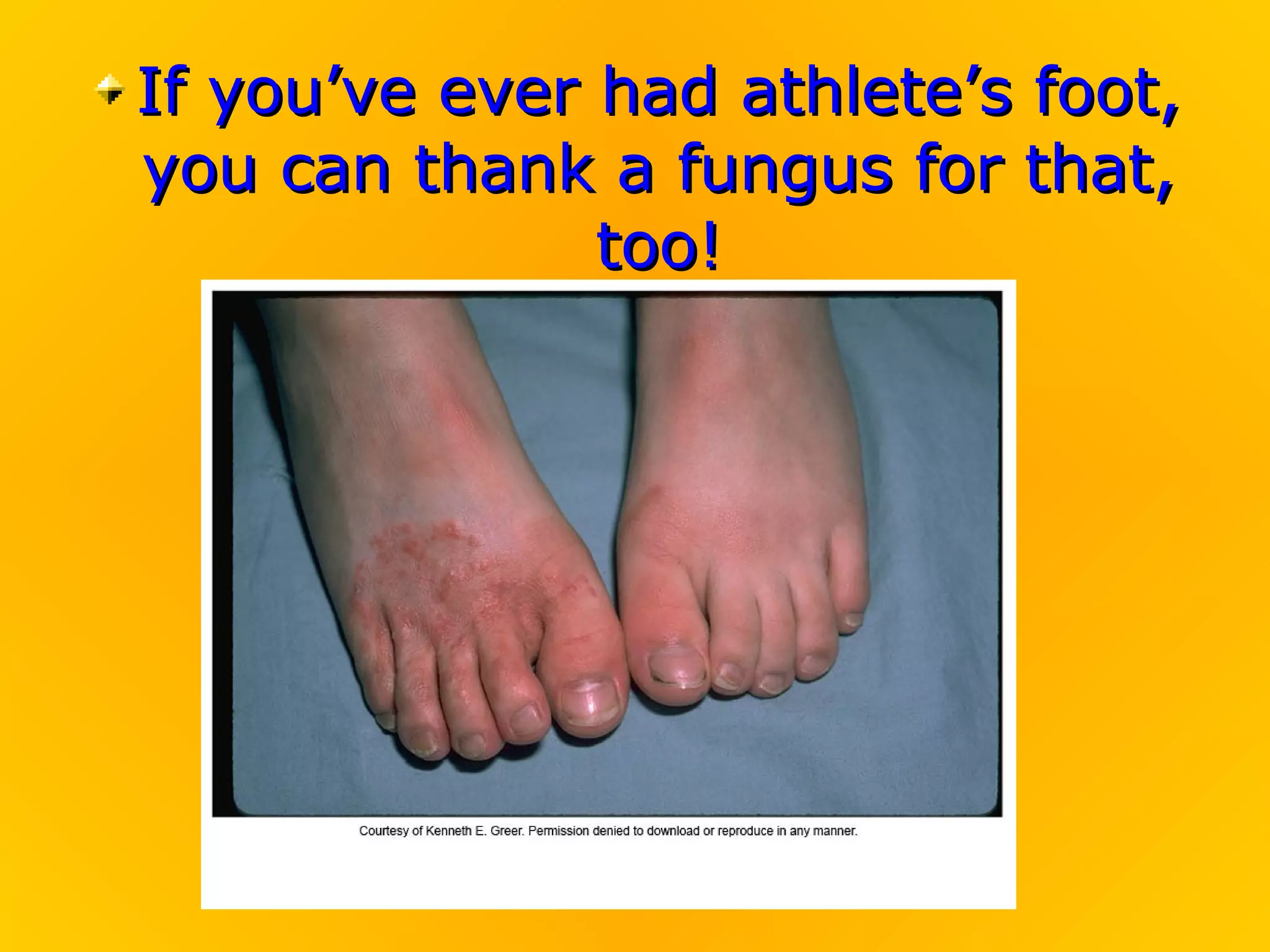
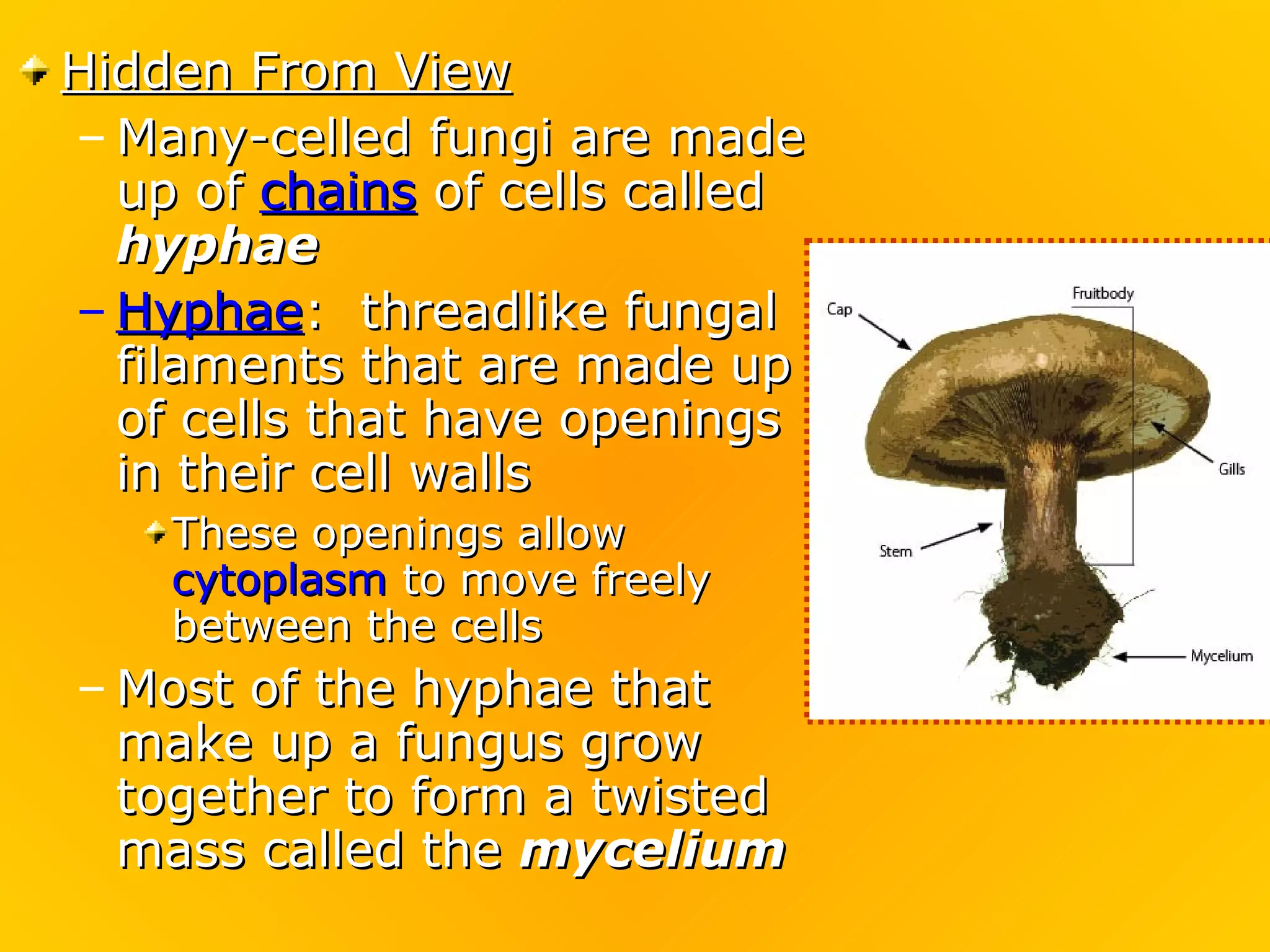
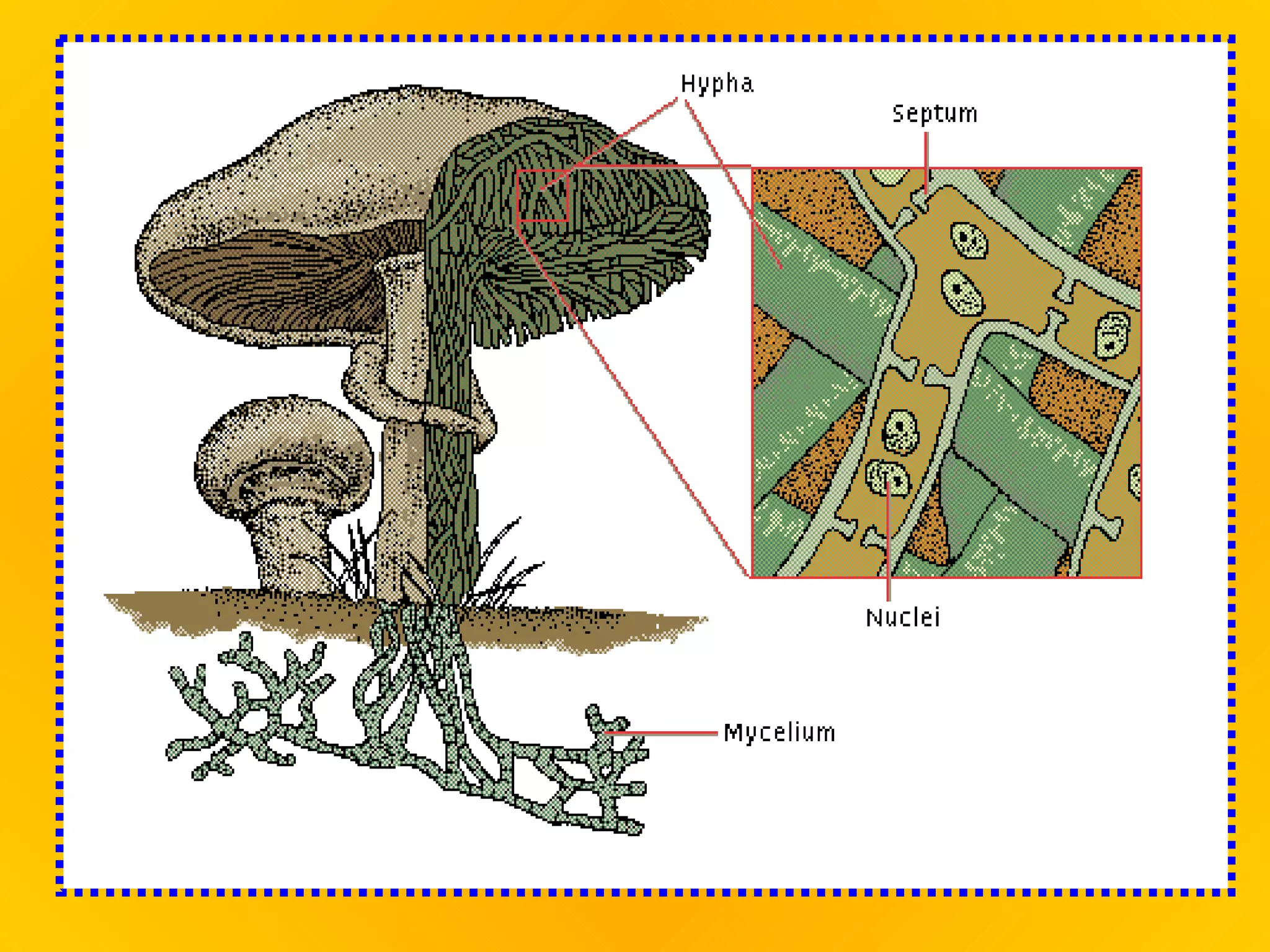
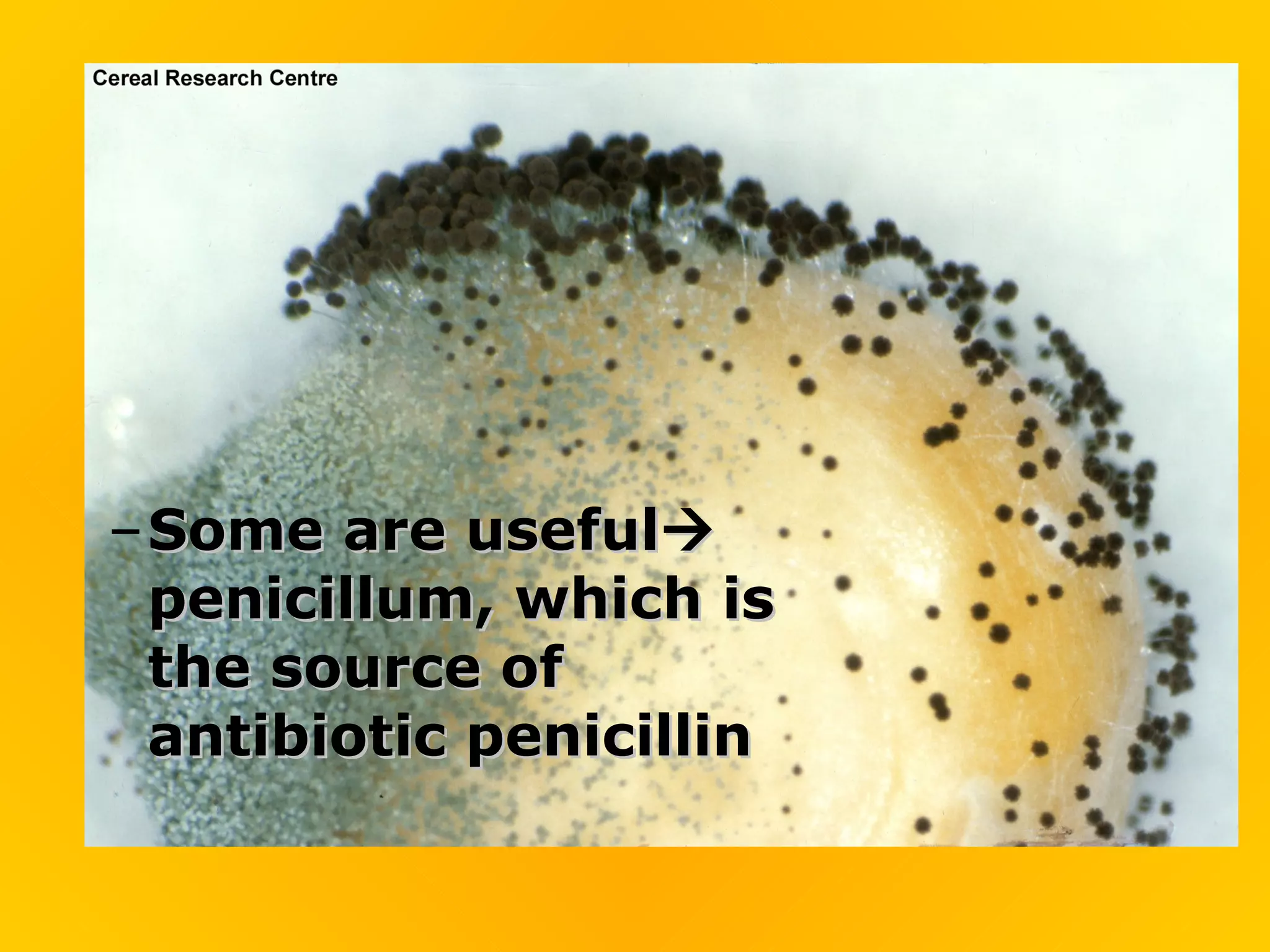
Fungi play an important role in food production. Yeast, a type of fungus, is used to make bread and alcoholic beverages. Other fungi are used to produce cheeses and soy sauce. Fungi have rigid cell walls and feed by absorbing nutrients from dead or living matter. They reproduce both sexually through spores and asexually through hyphae and spores. Major groups of fungi include molds, yeasts, mushrooms, and lichens, which is a symbiotic combination of algae and fungi.