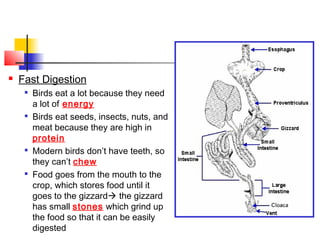
Birds have feathers that help them fly and stay warm. They preen and molt feathers regularly. Birds have fast digestion and eat high protein foods like seeds and insects since they lack teeth. Their light skeletons and powerful muscles allow flight through lift generated by air moving over wings. Birds build nests and care for young through brooding or by having precocial or altricial chicks. There are many kinds of birds including flightless, water, perching, and birds of prey.