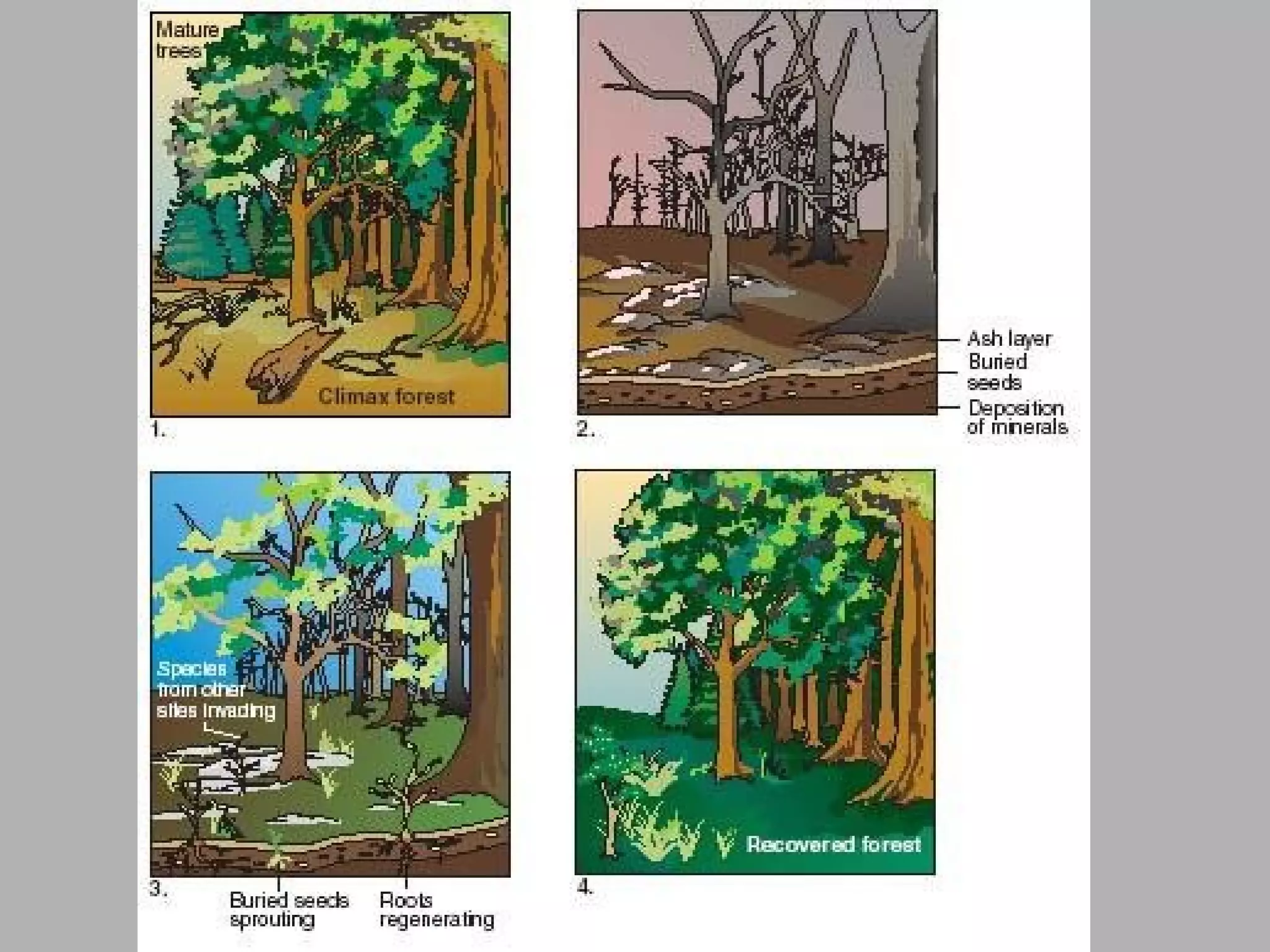
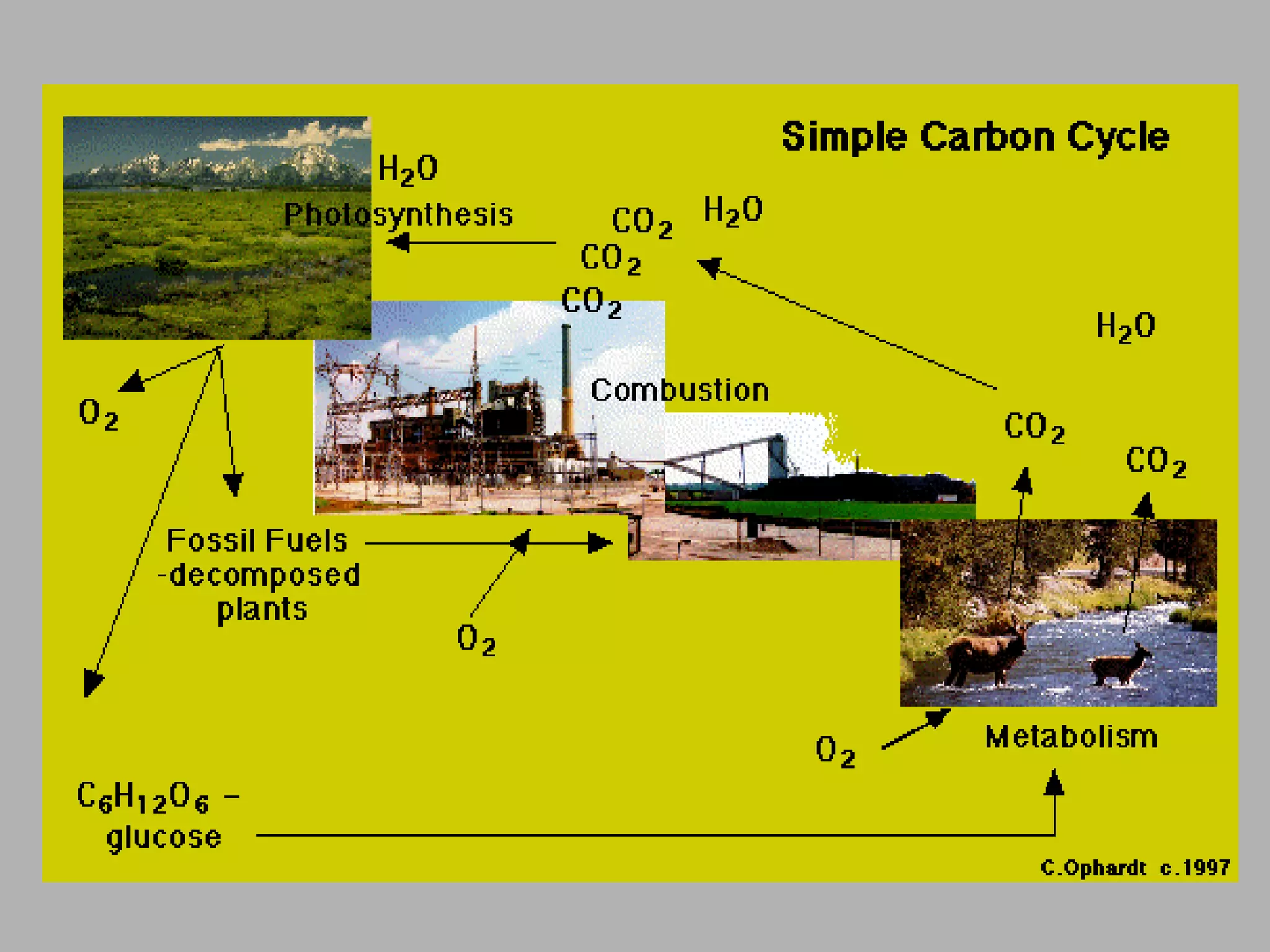
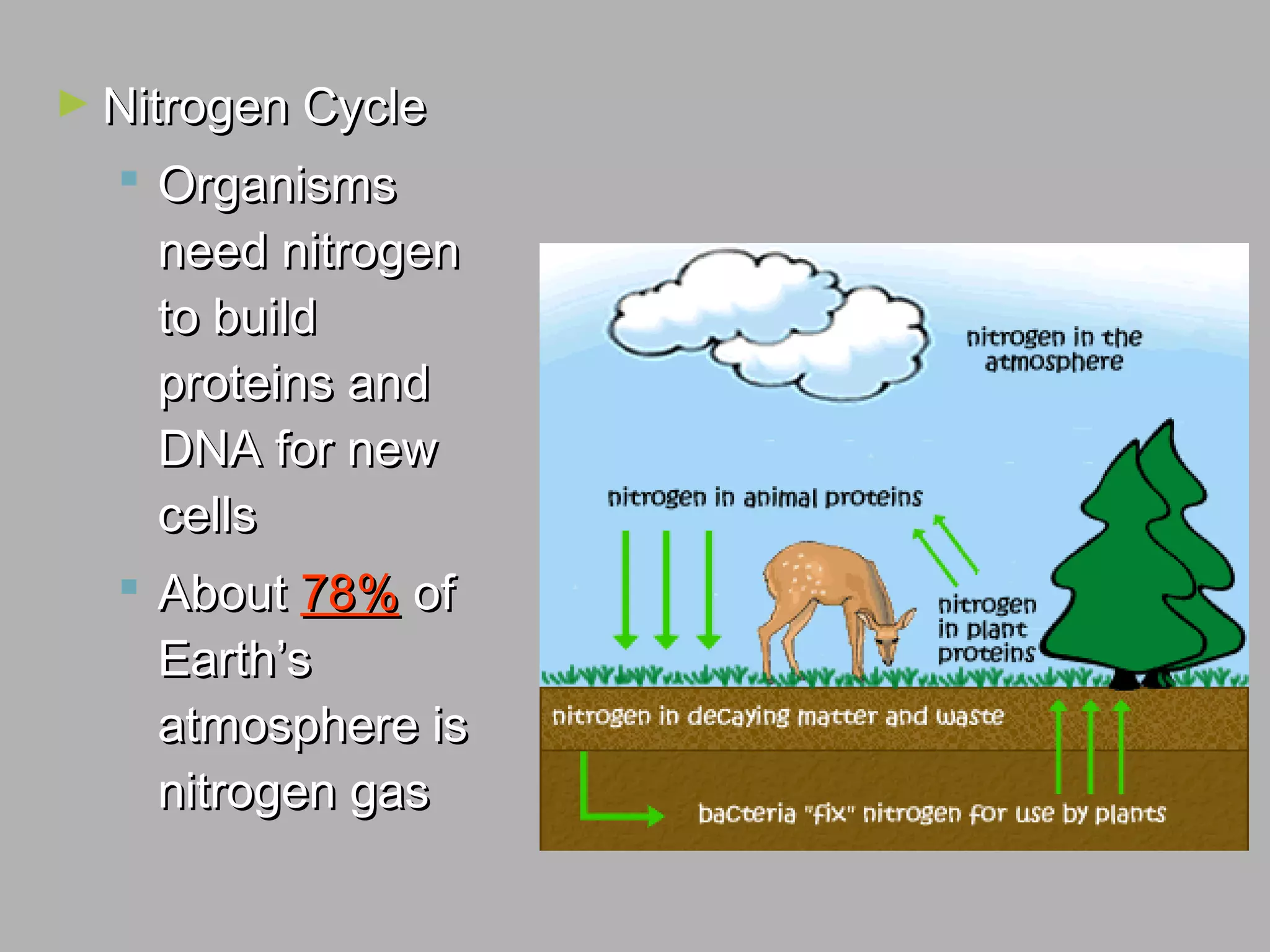
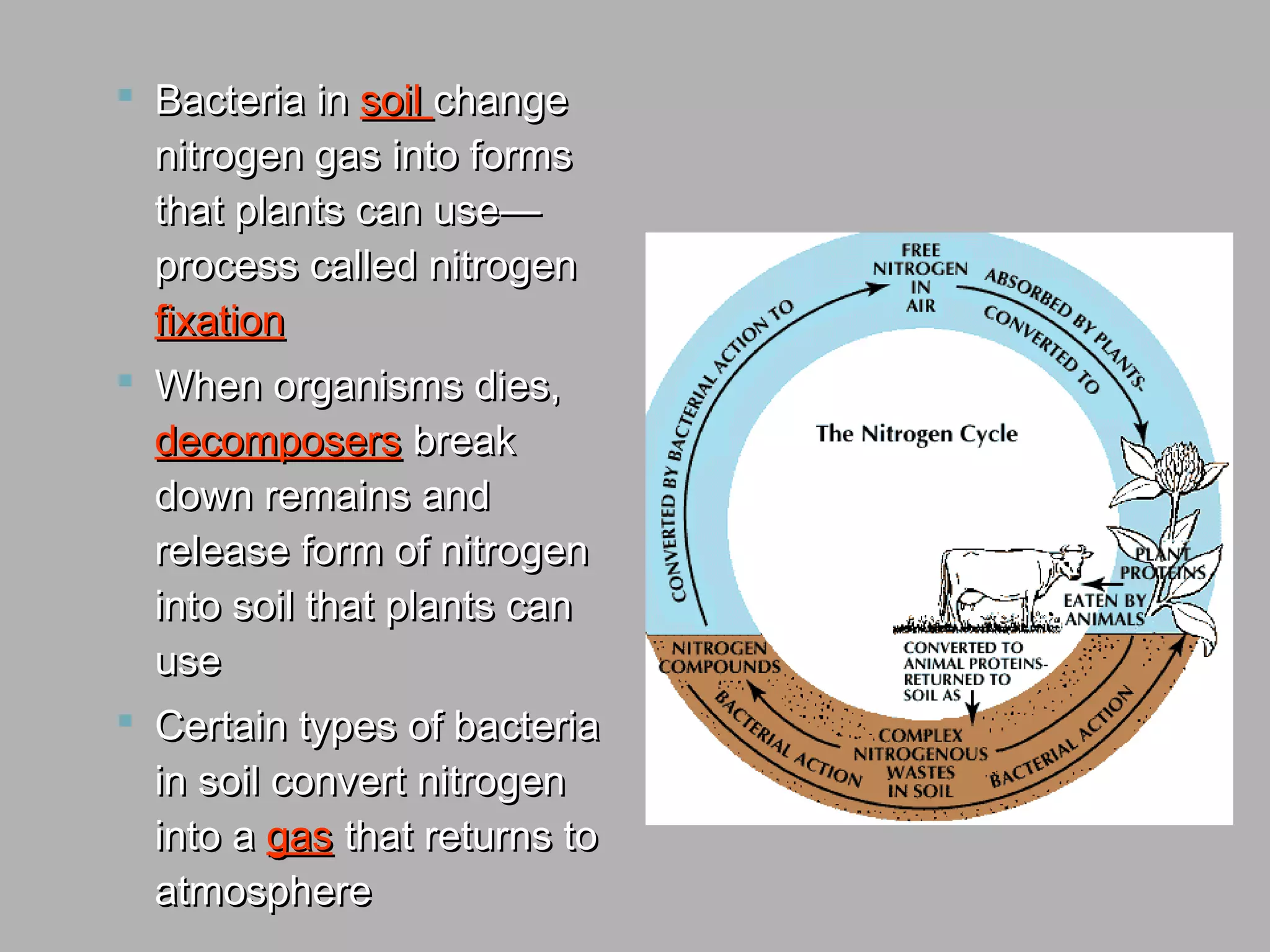
Ecological succession describes how communities change over time through primary and secondary succession. Primary succession occurs in areas without soil, like new bare rock, where pioneer species establish and slowly transform the rock into soil over long periods. Secondary succession follows a disruption, like a forest fire, where the original community regrows through different stages. Mature communities tend to have greater biodiversity and are dominated by climax species well-adapted to the local environment. Cycles of matter, like carbon and nitrogen, are essential to life and involve exchanges between living things and their environment.