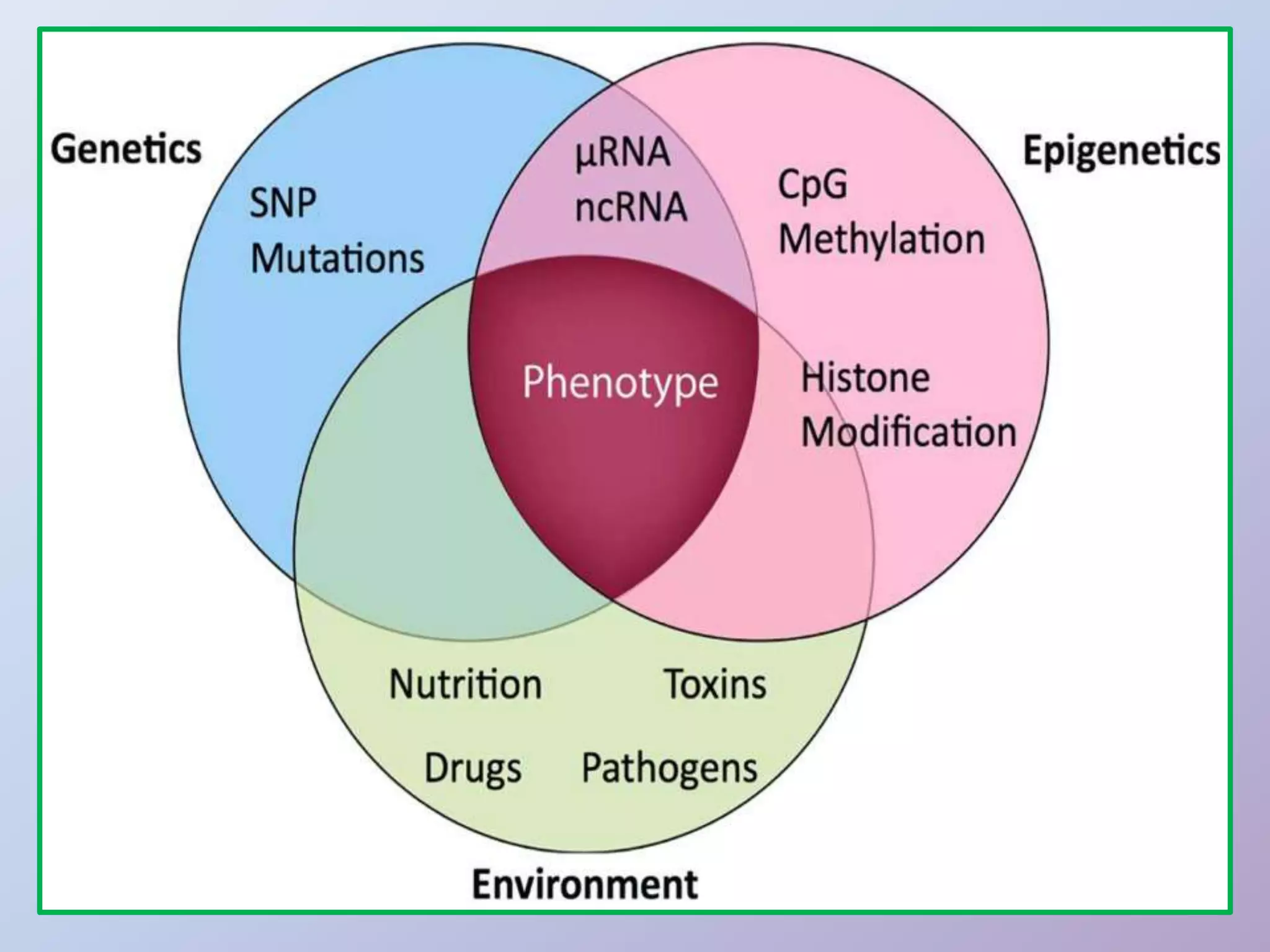
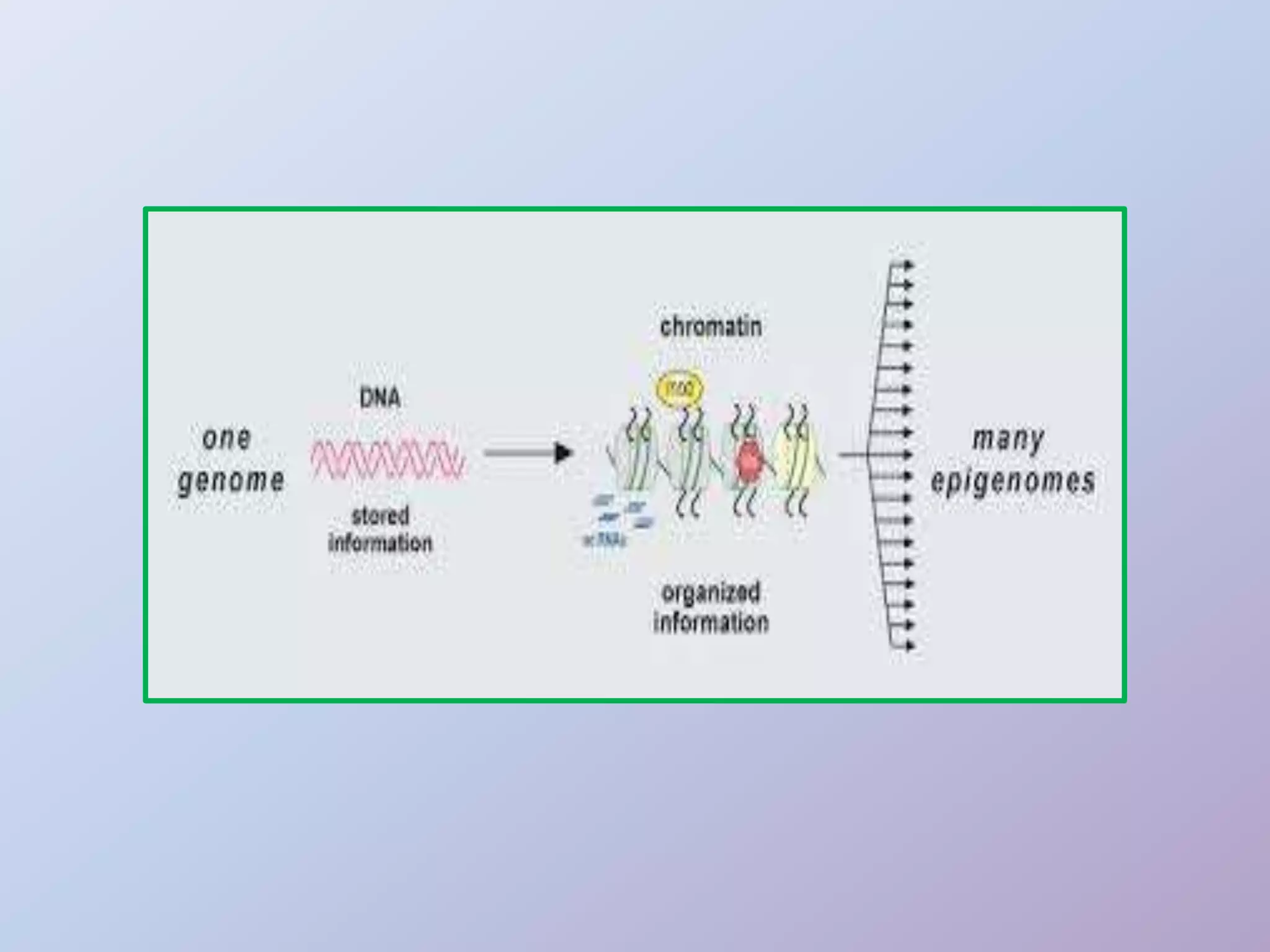
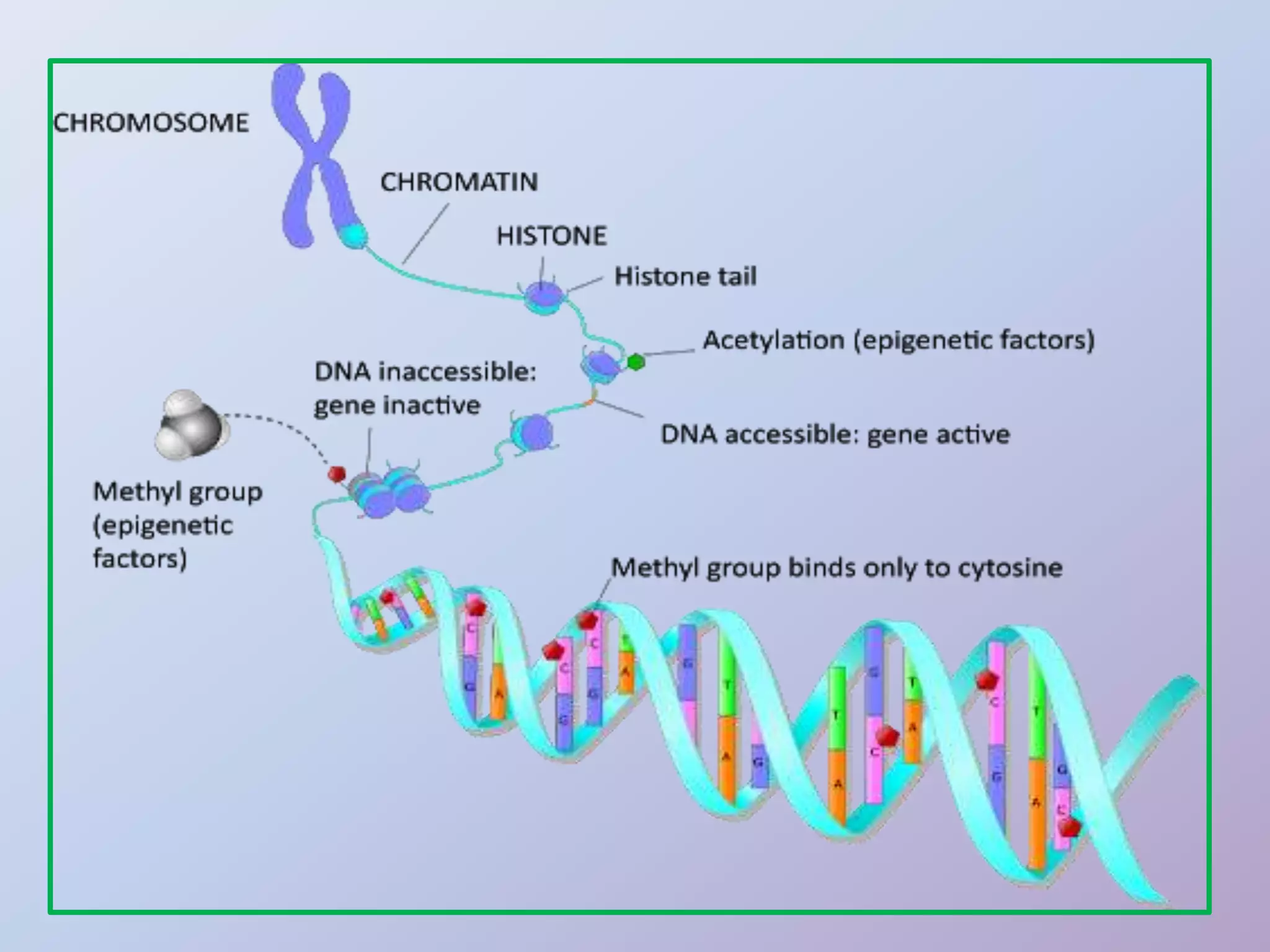
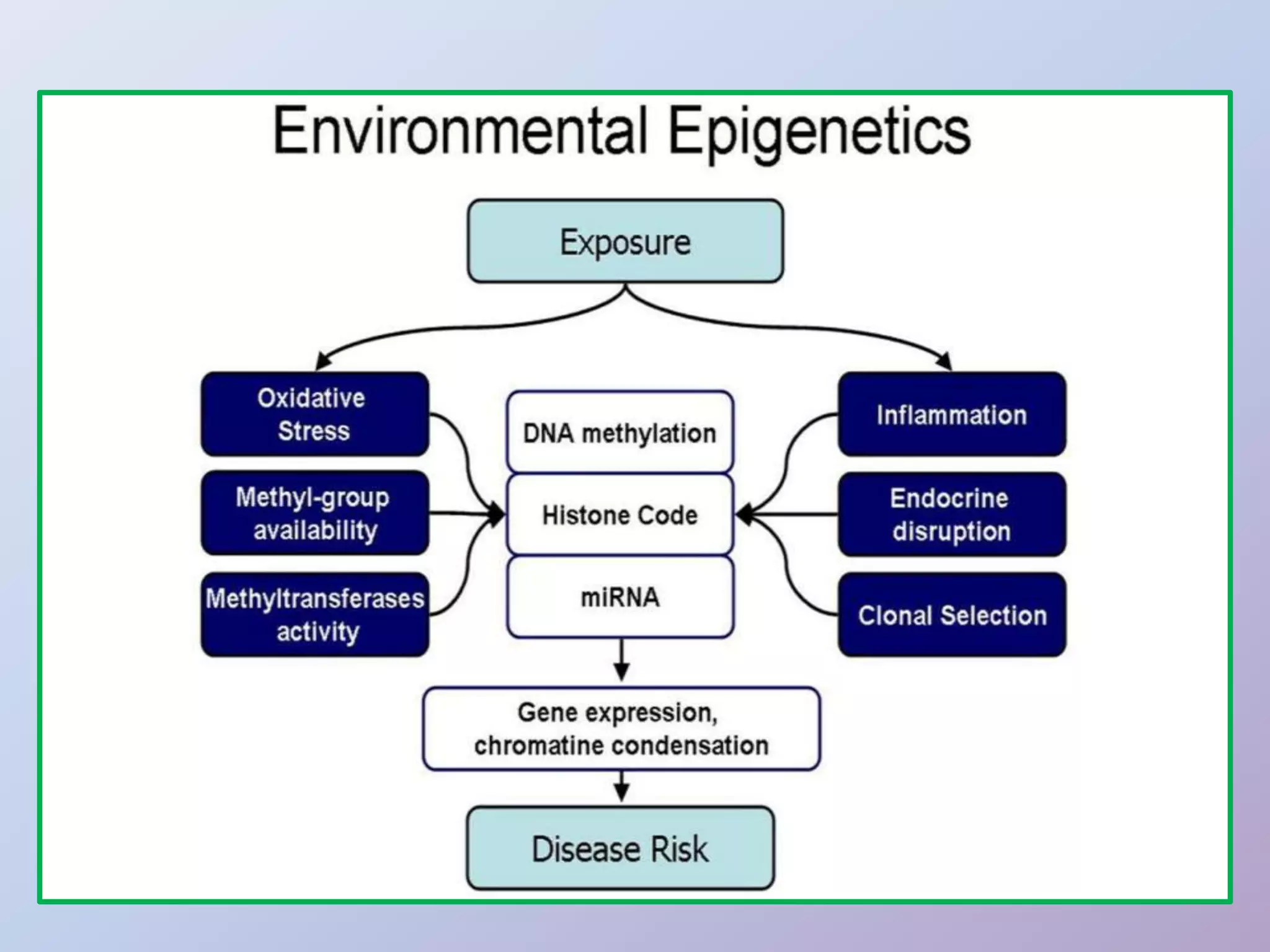
Epigenetics is the study of heritable phenotypic changes that do not involve alterations to the DNA sequence. Epigenetic changes are influenced by factors like age, environment, lifestyle, and disease state, and can occur through DNA methylation, histone modification, and gene silencing. Epigenetic modifications can develop in different cell types and can be transmitted transgenerationally, potentially influencing traits and disease risk in offspring. Environmental exposures during development like a mother's pollution exposure or nutrition intake can impact epigenetic changes in her child with effects on traits and disease susceptibility.