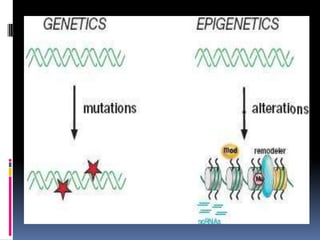
Epigenetics involves heritable changes in gene expression that are not caused by changes in the underlying DNA sequence. These changes are caused by mechanisms such as chromatin remodeling and DNA methylation. While genetics is determined by the DNA sequence, epigenetics influences which genes are expressed through modifications to histone proteins and DNA. These epigenetic modifications play important roles in development and can cause diseases if disrupted, such as imprinting disorders. Significant research is being conducted worldwide at top institutions like Johns Hopkins University to better understand epigenetics and its effects.