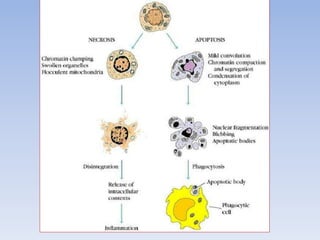
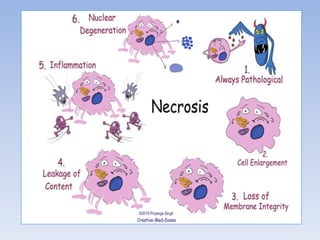
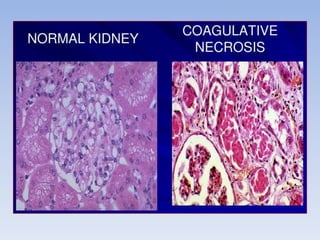
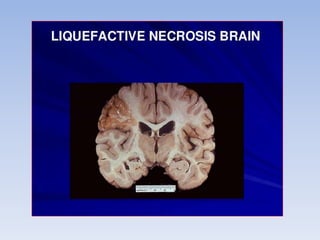
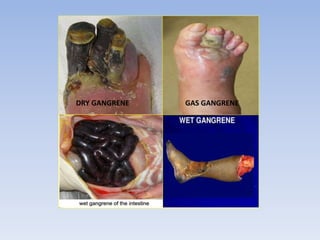
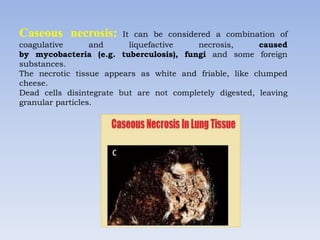
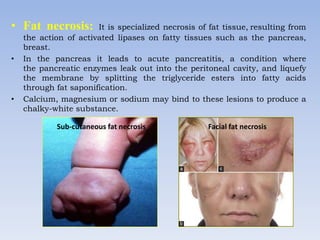
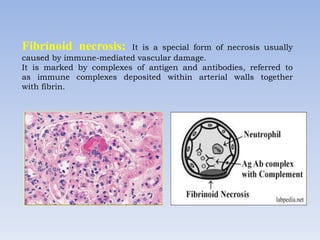
Necrosis is the death of cells and living tissue. It occurs when there is not enough blood flow to tissues. The main types of necrosis are coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, and gangrenous. Coagulative necrosis occurs due to ischemia and results in a gel-like substance in dead tissues. Liquefactive necrosis results from infections and the digestion of dead cells into pus. Caseous necrosis is caused by bacteria and fungi and leaves dead tissue that looks like clumped cheese. Gangrenous necrosis resembles mummified tissue and is characteristic of lower limb and gastrointestinal ischemia. Treatment of necrosis involves restoring blood flow, antibiotics to prevent infection, and debridement to remove dead tissues.