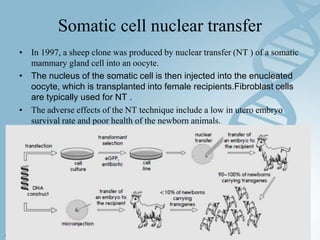
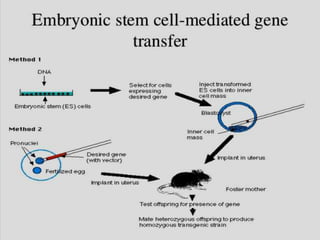
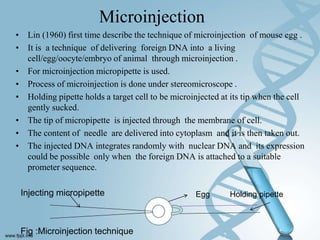
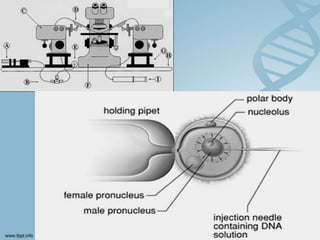
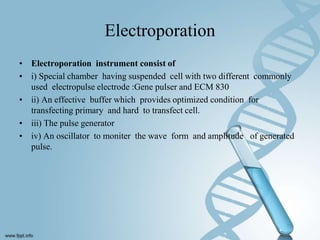
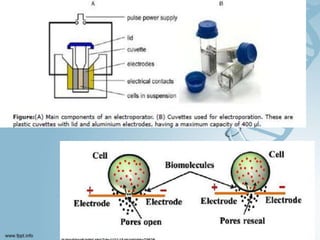
Transfection involves introducing foreign DNA into host cells to produce a new phenotype. There are two main methods of transfection - vector-mediated and non-vector mediated. Vector-mediated transfection uses bacteriophage, retroviral, cosmid, baculovirus, and plasmid vectors to introduce DNA. Non-vector mediated methods include direct techniques like microinjection, electroporation, and particle bombardment, and indirect techniques like calcium phosphate precipitation and DEAE-dextran. Retroviral vectors are modified retroviruses that can introduce foreign DNA into host chromosomal DNA. Microinjection involves injecting DNA directly into cells using a micropipette under a microscope. Electroporation uses electric pulses to create temporary