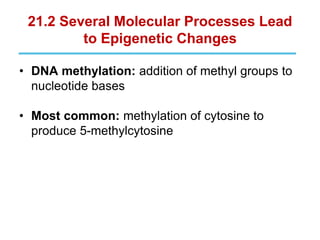
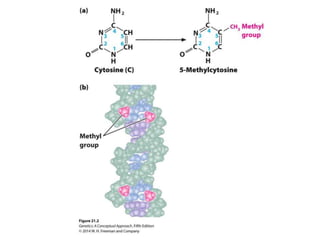
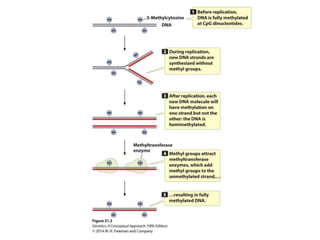
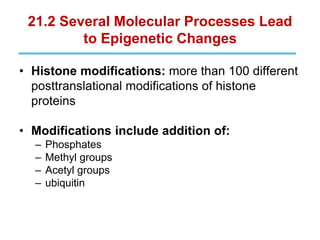
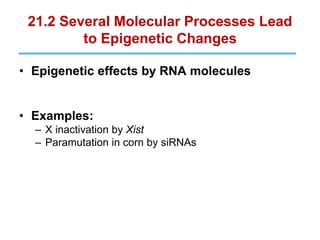
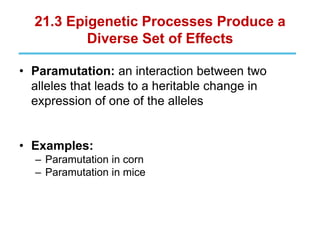
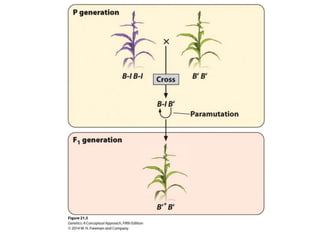
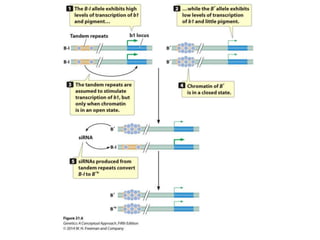
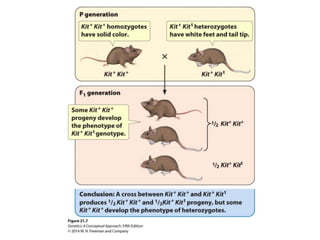
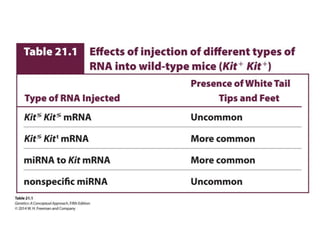
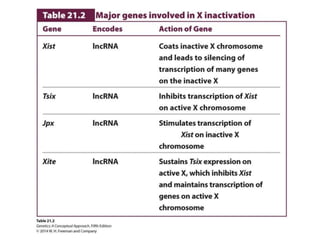
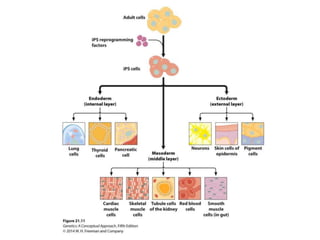
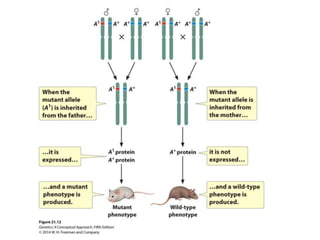
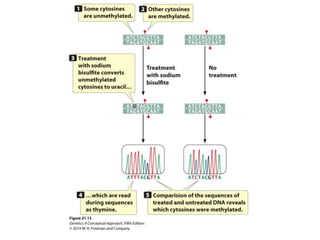
Epigenetics refers to heritable changes in gene expression that occur without changes to DNA sequences. This chapter discusses several molecular processes that lead to epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and RNA molecules. These epigenetic processes produce diverse effects, such as paramutation, behavioral influences, environmental impacts, and cell differentiation. The epigenome represents the overall pattern of chromatin modifications in an organism and can be detected using techniques like bisulfate sequencing and ChIP.